Did you know achalasia cardia is a rare condition that affects only about 1 in 100,000 people? It’s a complex disorder that makes swallowing and digesting food hard. This can lead to serious symptoms. It’s important to know the causes, signs, and treatments to improve life quality.
Key Takeaways
- Achalasia cardia is a rare esophageal disorder that affects the muscle function of the lower esophageal sphincter.
- Symptoms include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, regurgitation, and weight loss.
- While the exact cause is not fully understood, genetic and autoimmune factors may play a role.
- Diagnosis often involves a combination of tests, including manometry and endoscopy.
- Treatment options range from medication and botulinum toxin therapy to surgical interventions.
Understanding Achalasia Cardia: An Overview
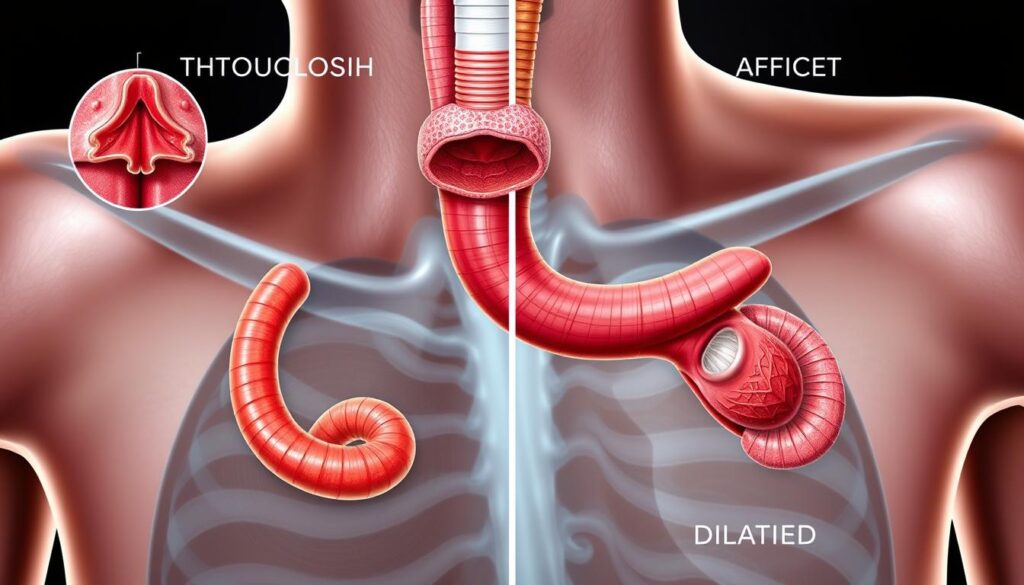
Achalasia Cardia is a rare condition that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This muscle connects the esophagus to the stomach. It makes it hard for the LES to relax, disrupting swallowing and causing digestive problems.
Definition and Basic Anatomy
Achalasia Cardia means “failure to relax.” The LES becomes stiff, making it hard for food and liquids to move into the stomach. This is because the esophagus doesn’t contract well, making swallowing even harder.
Impact on Daily Life
People with lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction and esophageal motility disorder face big challenges. They struggle with swallowing, food comes back up, and they might feel chest pain. This makes eating and drinking hard, leading to weight loss and poor nutrition.
Common Misconceptions
- Achalasia Cardia is not a form of cancer or a precancerous condition.
- The condition is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
- Achalasia does not cause other serious health issues, such as heart disease or stroke, if properly managed.
“Understanding the true nature of Achalasia Cardia is crucial in addressing the condition effectively and dispelling common myths that may cause unnecessary fear or anxiety among patients.”
Learning about Achalasia Cardia helps people deal with its challenges. They can find the right medical care to manage symptoms and improve their life quality.
The Role of Lower Esophageal Sphincter in Achalasia
Achalasia Cardia is a rare disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This muscle controls food passage from the esophagus to the stomach. In lower esophageal sphincter dysfunction, it fails to relax during swallowing. This leads to swallowing difficulty and other symptoms.
The LES is key to swallowing. Normally, it relaxes to let food through. But in achalasia, it stays tight, blocking food and causing pressure in the esophagus.
This problem with the LES causes achalasia symptoms. The esophagus can’t push food through the tight LES. Patients may have trouble swallowing, regurgitate food, and feel chest pain or discomfort.
- Difficulty swallowing solid and liquid foods
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Chest pain or discomfort during or after meals
- Frequent belching or burping
- Unintentional weight loss due to reduced food intake
Understanding the LES’s role in achalasia is key to managing it. Healthcare providers can develop strategies to help. This can ease swallowing difficulty and improve life quality for those with achalasia Cardia.
| Condition | Mechanism of Swallowing Difficulty | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Achalasia Cardia | Failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax during swallowing, causing a blockage in the passage of food from the esophagus to the stomach. | Esophageal dilatation, aspiration, malnutrition, and increased risk of esophageal cancer. |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) | Weakened or dysfunctional lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach contents to flow back into the esophagus. | Esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus, and an increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. |
Understanding the LES’s role in achalasia helps healthcare providers. They can create better treatments. This improves patient outcomes.
Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Achalasia cardia is a rare condition that affects the esophagus. Researchers have been studying it for years. They have found several important factors that might cause it.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics seem to play a big role in achalasia cardia. Research has found genetic changes that make some people more likely to get it. If your family has achalasia cardia, you might be at higher risk too. This shows how important genetics are in understanding this condition.
Autoimmune Connections
Some think achalasia cardia might be caused by the body’s immune system. Studies have found autoantibodies that might harm the nerves in the esophagus. This could be why the lower esophageal sphincter gets worse, causing symptoms of achalasia cardia.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors might also contribute to achalasia cardia. Some research suggests that infections, like viruses or bacteria, could trigger it in some people. Finding out what environmental factors are involved could help in preventing and managing achalasia cardia.
Researchers are working hard to understand achalasia cardia better. They are looking at genetics, the immune system, and environmental factors. This research is key to finding better ways to diagnose and treat achalasia cardia and other esophageal disorders.
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
It’s important to spot the early signs of achalasia cardia to get timely treatment. People often feel symptoms that get worse over time. Knowing these signs helps get medical help early and boosts treatment success.
Achalasia symptoms include swallowing difficulty, or dysphagia. You might find it hard to swallow solid foods or liquids. It feels like food is stuck in your throat or chest, especially with big bites or certain textures.
Regurgitation is another early sign. This is when you spit up food or saliva from your esophagus. It can happen right after eating or at night, causing coughing, choking, or a sour taste. You might also feel chest pain or discomfort, which can be mistaken for heartburn.
As achalasia gets worse, you might lose weight, feel malnourished, or have breathing problems. You could also feel full or bloated, even after eating a little. The symptoms can vary from person to person.
“Early recognition of achalasia symptoms is critical for timely intervention and improved long-term outcomes.”
If you notice these signs, see a doctor right away. Quick medical help can lead to better treatment and a better life for those with achalasia cardia.
| Early Warning Signs of Achalasia Cardia | Description |
|---|---|
| Swallowing Difficulty (Dysphagia) | Difficulty swallowing solid foods or liquids, often with a sensation of food “getting stuck” |
| Regurgitation | Expulsion of partially digested food or saliva from the esophagus, potentially leading to coughing, choking, or a sour taste |
| Chest Pain or Discomfort | Chest pain or discomfort that may be mistaken for heartburn or other gastrointestinal issues |
| Feeling Full or Bloated | Feeling full or bloated after consuming small portions of food |
| Weight Loss and Malnutrition | Unintentional weight loss and potential malnutrition due to difficulties in swallowing and food intake |
| Respiratory Issues | Respiratory complications, such as coughing or choking, due to the progression of achalasia |
Common Symptoms and Progression
Achalasia cardia is an esophageal motility disorder. It causes physical and psychological symptoms that affect daily life. Knowing the symptoms and how the condition progresses is key for early diagnosis and treatment.
Physical Symptoms
Common physical symptoms include trouble swallowing (dysphagia) and feeling like food is stuck in the chest (esophageal blockage). Patients may also experience regurgitation of undigested food and chest pain. Weight loss, coughing, and hoarseness can occur due to impaired esophageal function.
Psychological Impact
Achalasia also affects the mind. The swallowing issues and discomfort can cause anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. Feeling embarrassed or self-conscious about the condition can worsen the psychological distress.
Disease Progression Stages
Achalasia goes through three main stages:
- Early-stage: Symptoms like occasional difficulty swallowing and mild chest pain may occur.
- Intermediate-stage: Symptoms worsen, with swallowing becoming harder and food feeling trapped in the esophagus.
- Late-stage: The esophageal muscles become very rigid. This makes swallowing impossible and reduces the esophagus size, known as “end-stage” achalasia.
Knowing the stages of achalasia is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Diagnostic Methods and Testing
Getting a correct diagnosis for achalasia cardia is key for good treatment. Doctors use different tests to confirm the condition and check for other issues. The barium swallow test and esophageal motility disorder tests are very important in this process.
The barium swallow test involves swallowing a special liquid called barium. This liquid shows up on X-rays, helping doctors see the esophagus’s shape and how it moves. People with achalasia cardia show a “bird’s beak” shape at the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
- Esophageal manometry is another key test. It checks the pressure and how well the muscles in the esophagus work. This helps doctors understand the LES better.
- Endoscopic exams, like upper endoscopy, let doctors see the esophagus. They can check for other reasons for symptoms.
- CT scans and MRI might also be used. They help doctors see more about the esophagus and any problems.
By using these tests together, doctors can find out if someone has achalasia cardia and why. This helps them choose the best treatment.
“Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective achalasia treatment. The barium swallow test and esophageal motility evaluations provide invaluable insights into the condition, empowering healthcare providers to develop tailored management strategies.”
With a detailed diagnostic process, doctors can really understand what’s going on. This lets them make a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Medical Treatment Options
Achalasia cardia is a condition where the esophagus can’t move food into the stomach well. There are many medical treatments to help manage this. These treatments aim to ease symptoms and improve life quality.
Medication Approaches
Some medicines can relax the muscle at the bottom of the esophagus. This muscle, called the LES, is key in achalasia cardia. Doctors often prescribe nitrates, calcium channel blockers, and phosphodiesterase inhibitors. These drugs help food move into the stomach by lowering LES pressure.
Botulinum Toxin Therapy
Botulinum toxin injection is a non-surgical treatment for achalasia cardia. It involves injecting botulinum toxin into the LES. This makes the muscle relax, helping food move better. It’s seen as a safe and effective option compared to surgery.
Treatment Success Rates
Success rates for treating achalasia cardia vary. Medicines work for 60-80% of people. Botulinum toxin injection works for 70-90% at first. But, the effects of botulinum toxin may fade over time, needing more injections.
| Treatment Approach | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| Medication Therapy | 60-80% |
| Botulinum Toxin Injection | 70-90% (initial) |
Choosing a treatment for achalasia cardia should be done with a doctor’s help. They consider the patient’s needs, preferences, and health.
Surgical Interventions for Achalasia
For those with achalasia cardia who don’t get better with medicine or other treatments, surgery might be needed. The two main surgeries are heller myotomy and pneumatic dilation.
Heller Myotomy
Heller myotomy cuts the muscle of the lower esophageal sphincter. This makes it easier for food to go down. It’s done when other treatments fail. It can help symptoms last for a long time, with success rates of 80% to 90%.
Pneumatic Dilation
Pneumatic dilation uses a balloon to stretch the muscle. This helps the muscle relax and food to pass better. It’s a safe and effective treatment, with success rates of 60% to 90%.
| Surgical Intervention | Success Rate | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Heller Myotomy | 80% – 90% | Leakage, bleeding, infection, reflux |
| Pneumatic Dilation | 60% – 90% | Perforation, bleeding, reflux |
Both surgeries have their own good and bad sides. The choice depends on the person’s condition, what they prefer, and the doctor’s advice. It’s important to follow up and make lifestyle changes to manage the condition well.
“The goal of surgical intervention is to improve the patient’s quality of life by addressing the underlying causes of achalasia and providing long-term relief from the debilitating symptoms.”
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
Recovering from achalasia cardia treatment takes time and effort. Knowing the recovery timeline, lifestyle changes, and follow-up care is crucial. This helps patients manage their journey well.
Recovery Timeline
Most patients see symptom improvement after several weeks to months of treatment. The exact time depends on the treatment and condition severity. It’s important to be patient as the esophagus and sphincter need time to adjust.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help ease digestion and prevent discomfort.
- Avoiding large, heavy meals and lying down immediately after eating is recommended.
- Incorporating soft, easy-to-swallow foods into the diet can make mealtime more comfortable.
- Staying hydrated by sipping water throughout the day can facilitate swallowing and prevent dehydration.
Follow-up Care Protocol
Regular check-ups with the healthcare team are vital. They help monitor progress and address concerns. Patients may have imaging tests to check treatment success and watch for complications.
| Timeline | Care Requirement |
|---|---|
| 1-2 weeks post-treatment | Initial follow-up visit to assess recovery and address any immediate concerns |
| 3-6 months post-treatment | Repeat diagnostic tests to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment |
| 6 months to 1 year post-treatment | Ongoing monitoring and management of any persistent or recurring symptoms |
By following their healthcare team’s advice and making lifestyle changes, patients can manage achalasia cardia well. This leads to long-term control of the condition.
Living with Achalasia: Lifestyle Adaptations
Living with achalasia cardia can be tough, but there are ways to manage it. People can make lifestyle changes to live well despite swallowing difficulty. Here are some helpful tips for those with achalasia.
Dietary Modifications
Managing diet is key for achalasia cardia patients. They should eat soft, easy foods. This includes:
- Pureed or well-cooked vegetables
- Soups and broths
- Soft, moist proteins like scrambled eggs or steamed fish
- Smoothies and protein shakes
Eating slowly and taking small bites helps. Avoiding carbonated drinks also helps with swallowing.
Stress Management
Achalasia cardia can cause stress and anxiety. Stress management is crucial. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or therapy can help.
| Lifestyle Adaptation | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Dietary Modifications | Improved swallowing, reduced discomfort, and better nutritional intake |
| Stress Management | Reduced anxiety, improved emotional well-being, and better overall physical health |
| Posture Awareness | Enhanced swallowing function, reduced reflux, and improved digestive comfort |
By making these lifestyle changes, people with achalasia cardia can manage their condition better. This improves their quality of life.

“The key to living well with achalasia cardia is to be proactive, adaptable, and patient with the process of finding the right management strategies.”
Conclusion
Achalasia cardia is a complex condition that affects the esophagus. It can greatly impact a person’s life. We’ve looked at what causes it, its symptoms, and how to treat it.
Getting diagnosed early and starting treatment quickly is key. It helps slow down the condition’s progress. Knowing the signs early lets people get help sooner.
Living with achalasia cardia means focusing on your health. Talk openly with your doctors and try lifestyle changes. This way, you can manage your symptoms and live well.
FAQ
Q: What is Achalasia Cardia?
A: Achalasia Cardia is a rare digestive disorder. It affects the esophagus, the tube that carries food from the throat to the stomach. The main issue is the lower esophageal sphincter can’t relax properly. This makes swallowing hard.
Q: What are the common symptoms of Achalasia Cardia?
A: The main symptoms include trouble swallowing and food coming back up. People may also feel chest pain and lose weight. Other symptoms are heartburn, coughing, and feeling like food is stuck in the chest.
Q: How is Achalasia Cardia diagnosed?
A: Doctors use several tests to diagnose Achalasia Cardia. These include a barium swallow study, esophageal manometry, and endoscopy. These tests check the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter’s function and structure.
Q: What are the treatment options for Achalasia Cardia?
A: There are several treatments for Achalasia Cardia. These include medication, botulinum toxin injection, pneumatic dilation, and surgery like Heller myotomy. The best treatment depends on the case and how severe it is.
Q: How does Achalasia Cardia affect daily life?
A: Achalasia Cardia can make everyday activities hard. It’s tough to eat and drink normally. This can cause discomfort, pain, and make meals inconvenient. It can also lead to weight loss, malnutrition, and social challenges. Managing the condition and making lifestyle changes can help improve life quality.
Q: What is the long-term outlook for patients with Achalasia Cardia?
A: With the right treatment and care, patients with Achalasia Cardia can have a good long-term outlook. But, it’s a chronic condition. It may need ongoing monitoring and treatments to keep the esophagus working well and prevent complications.
