Did you know that 1 in 5 people will face a blood clotting disorder at some point? Many cases are due to acquired disorders of coagulation. This condition makes it hard for blood to clot, raising the risk of bleeding or forming clots. It’s important to know about these disorders to get the right treatment.
Key Takeaways
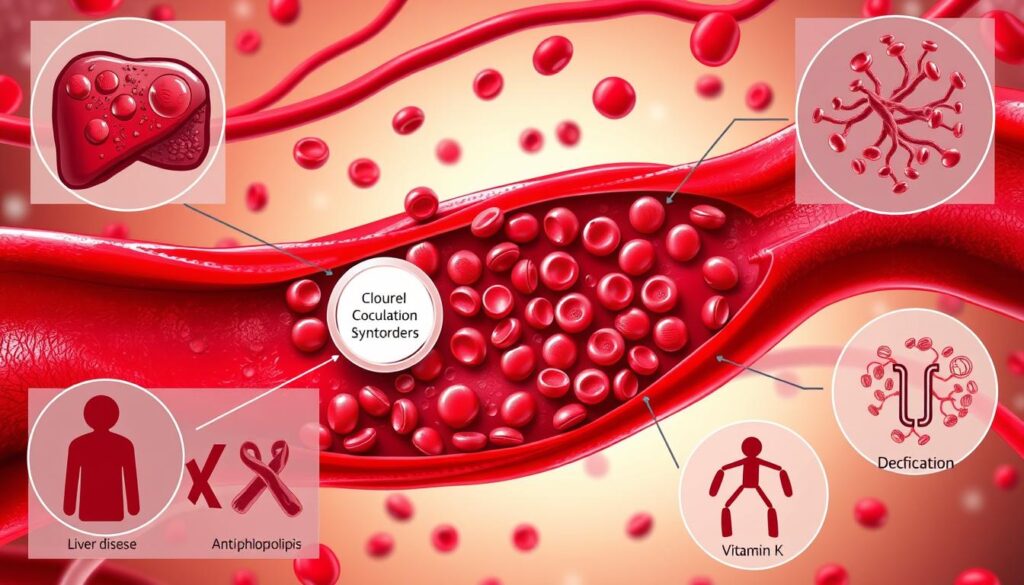
- Acquired coagulation disorders affect the blood’s clotting ability, increasing the risk of bleeding or clotting.
- These disorders can be caused by many things, like medical conditions, medicines, and lifestyle choices.
- It’s key to understand the difference between inherited and acquired disorders to get the right treatment.
- Untreated blood clotting disorders can lead to serious problems, so early detection and treatment are crucial.
- Managing acquired coagulation disorders well involves making lifestyle changes, managing medicines, and regular check-ups.
- Keeping up with the latest research and medical breakthroughs in coagulopathy is important for those affected.
- Recognizing the signs of acquired coagulation disorders can help get medical help quickly, reducing risks.
Understanding Acquired Disorders of Coagulation
Acquired coagulation disorders, like acquired hemophilia, happen in a person’s lifetime. They affect how blood clots. These disorders can come from medical issues, medicines, or lifestyle choices. Disseminated intravascular coagulation is a type where the blood clots in small blood vessels all over the body.
Normal clotting involves many steps. Acquired disorders can mess with these steps. This can lead to too much bleeding or clotting. Secondary coagulopathies happen because of other health problems, like liver disease or cancer.
It’s important to know the difference between inherited and acquired coagulation disorders. Inherited ones, like hemophilia, you have from birth. Acquired ones start later in life. Here are some main differences:
- Inherited disorders come from genetic changes
- Acquired disorders come from outside factors
- Inherited disorders are there from birth
- Acquired disorders can start at any age
Definition and Basic Mechanism
Acquired coagulation disorders mess with blood clotting. This can lead to too much bleeding or clotting. They happen because of many things, like health issues, medicines, or lifestyle.
Common Types of Acquired Coagulopathy
Acquired coagulopathy is when the blood can’t clot right, making it hard to stop bleeding. This happens when the body can’t make enough clotting factors. Coagulation disorders treatment helps manage this and prevent worse problems.
Some common types of acquired coagulopathy include:
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Liver disease-related coagulopathy
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Acquired hemophilia A
These conditions can be treated with coagulation disorders treatment. This might mean replacing clotting factors or managing other health issues. It’s key to get medical help fast if you think you have acquired coagulopathy.
Knowing about the different types of acquired coagulopathy and how to treat them is important. Recognizing symptoms and getting help quickly can help avoid serious issues. Acquired factor deficiencies can be managed with coagulation disorders treatment. With the right care, people can live healthy, active lives.
| Type of Coagulopathy | Cause | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) | Sepsis, trauma, cancer | Replace clotting factors, manage underlying condition |
| Liver disease-related coagulopathy | Liver disease, cirrhosis | Vitamin K supplementation, manage underlying liver disease |
| Vitamin K deficiency | Poor diet, malabsorption | Vitamin K supplementation |
Risk Factors and Underlying Causes
Acquired coagulation disorders, like coagulopathy and blood clotting disorders, come from different sources. Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and managing them. Medical issues, such as liver disease and cancer, can raise the risk of coagulopathy. Also, some medicines, like anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, can cause coagulopathy and acquired platelet dysfunction.
Lifestyle and environmental factors, like smoking and obesity, also play a role. Here are some important factors to remember:
- Medical conditions: liver disease, cancer, and other chronic diseases
- Medications: anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and other medications that affect blood clotting
- Lifestyle and environmental factors: smoking, obesity, and other factors that affect overall health
Knowing these risk factors helps people take steps to lower their chance of getting acquired coagulation disorders. By understanding what causes coagulopathy and blood clotting disorders, people can work with their doctors. Together, they can find ways to manage these conditions and avoid serious problems.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Acquired disorders of coagulation show up in different ways. It’s key to spot the signs and symptoms. Common ones are bruising, bleeding, and thrombosis. These can point to secondary coagulopathies that need quick medical help.
Some common signs of acquired disorders of coagulation include:
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding
- Prolonged bleeding after injury or surgery
- Swelling or pain in the legs, which can be a sign of deep vein thrombosis
If you notice any of these symptoms, get medical help right away. Acquired disorders of coagulation can cause serious problems if not treated. Spotting the signs early helps in getting the right treatment and managing your condition.
Diagnosis and Laboratory Testing
Acquired coagulation disorders need a detailed diagnosis to find the cause and plan treatment. The first step is usually screening tests like complete blood counts and coagulation panels. These tests look for any issues with blood clotting.
More tests might follow, like factor assays and platelet function tests. These give more info about the disorder. They help find if there’s a lack of certain factors in the blood, which is common in these disorders.
At times, imaging like ultrasound and CT scans are needed. They help find any other issues that might be causing the problem. A full diagnosis is key to making a treatment plan that works for each person and keeps complications away.
Initial Screening Tests
- Complete blood counts
- Coagulation panels
- Platelet function tests
Specialized Coagulation Studies
These tests help diagnose and keep track of acquired coagulation disorders. They include those caused by a lack of certain factors. Knowing the cause helps doctors create a treatment plan. This plan helps manage symptoms and avoid serious problems.
Treatment Approaches and Management Strategies
Treating acquired coagulation disorders, like acquired hemophilia, focuses on managing the underlying cause. It also aims to prevent complications. This might include using medications like anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents. These help lower the risk of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Some common treatment methods include:
- Medications to manage bleeding or clotting
- Lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise
- Regular checks on blood clotting factors and platelet count
In severe cases of acquired hemophilia, hospital care might be needed. This is to handle bleeding episodes and avoid complications. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider. This way, a personalized treatment plan can be made and the condition managed well.
Understanding the treatment options and management strategies for acquired coagulation disorders is key. It helps individuals manage their condition better. This reduces the risk of complications, like disseminated intravascular coagulation.
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Medications | Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents to manage bleeding or clotting |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Dietary changes and exercise to reduce the risk of complications |
| Regular Monitoring | Regular monitoring of blood clotting factors and platelet count |
Complications and Emergency Situations
Acquired coagulation disorders can cause serious problems. These include sudden bleeding and blood clots. It’s key to know the signs and get help fast if needed.
Some common issues include:
- Acute bleeding episodes, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly
- Thrombotic events, such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, which can be caused by blood clotting disorders
- Organ dysfunction, which can occur due to inadequate blood flow or bleeding
People with these disorders should know the risks. They should get regular check-ups and follow their treatment plans. This way, they can lower the risk of serious problems and live better, even with coagulopathy or platelet dysfunction.
Seeking medical help right away is vital if symptoms show up. Quick action can greatly improve outcomes. By understanding risks and taking steps, those with acquired coagulation disorders can manage their condition well and avoid emergencies.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Acute bleeding episodes | Severe bleeding that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly |
| Thrombotic events | Blood clots that can cause deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism |
| Organ dysfunction | Inadequate blood flow or bleeding that can cause organ damage |
Living with Acquired Coagulation Disorders
Acquired disorders of coagulation can really change how you live, needing careful care and check-ups to avoid problems. You might need to change your diet and exercise more. Working with your doctor to make a plan for your condition is key.
Some important things to think about when living with these disorders include:
- Following your doctor’s advice on medicine
- Eating well and staying active to lower risks
- Keeping up with new research and treatments
- Having a support group of family, friends, and doctors
Being proactive and informed can help manage these disorders. This can lower the chance of serious problems and improve your health. It’s important to know that with the right care, you can live a full and happy life.

Managing acquired coagulation disorders means looking at all parts of your life. Working with your healthcare team and sticking to your treatment plan can help you face challenges. This way, you can improve your life’s quality.
| Condition | Description | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Acquired Disorders of Coagulation | Conditions that affect the blood’s ability to clot | Medication, lifestyle modifications, regular medical check-ups |
| Secondary Coagulopathies | Coagulation disorders that develop as a result of another medical condition | Treatment of underlying condition, medication, lifestyle modifications |
Prevention and Risk Reduction
To prevent and lower the risk of acquired coagulation disorders, a full plan is needed. This plan includes making lifestyle changes, managing medications, and keeping up with regular check-ups. By doing these things, people can lower their chance of serious problems and stay healthier.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is key to avoiding and lowering the risk of acquired coagulation disorders. Some important changes include:
- Eating more fruits and vegetables
- Doing regular exercise like walking or swimming
- Stopping smoking and drinking less alcohol
These changes can help lower the risk of blood clots and improve health overall.
Medication Management
Managing medications is also vital in preventing and reducing the risk of acquired coagulation disorders. This means taking anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents as your doctor tells you to. These medicines can stop blood clots and lower the risk of serious problems.
Regular Monitoring Guidelines
Regular checks are crucial in preventing and reducing the risk of acquired coagulation disorders. This includes getting blood tests and medical check-ups often. By watching for any issues with blood clotting, people can lower their risk of serious problems and stay healthier.
| Monitoring Test | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Blood tests | Every 3-6 months |
| Medical check-ups | Every 6-12 months |
Latest Research and Medical Advances
Research and medical advances are making big strides in treating acquired coagulation disorders. Acquired hemophilia, a rare but serious condition, has seen new treatment options. Disseminated intravascular coagulation, a complex condition, is also getting a lot of study to find better treatments.
New developments include gene therapy and stem cell transplantation for treating acquired coagulation disorders. These new methods aim to fix blood clotting problems. This can reduce bleeding risks and improve life quality.
Key research areas include:
- Creating new medicines for acquired hemophilia and disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Improving current treatments to lessen side effects and work better
- Looking into what causes acquired coagulation disorders to find ways to prevent them
As research keeps moving forward, we’ll see better treatments and outcomes for those with acquired coagulation disorders. By keeping up with the latest news, patients and healthcare providers can work together. This helps manage these complex conditions and improves health.
| Condition | Treatment Options | Current Research |
|---|---|---|
| Acquired Hemophilia | Replacement therapy, desmopressin | Gene therapy, stem cell transplantation |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation | Supportive care, anticoagulation therapy | Investigation of underlying causes, development of new treatments |
Conclusion: Managing Your Coagulation Health
Managing your coagulation health is key to avoiding and treating acquired coagulation disorders. Knowing the causes, signs, and treatment choices for these blood clotting disorders helps. This way, people can act early to lower risks and boost their health.
It’s important to have regular check-ups and talk with your doctor about acquired platelet dysfunction and other coagulopathies. Following your treatment plan, making healthy lifestyle changes, and keeping up with new research helps. This way, you can manage your coagulation health better.
With the right support and effort, people with acquired coagulation disorders can live well. By focusing on your coagulation health, you can lessen the effects of these conditions. This leads to a better life quality.
FAQ
Q: What are acquired coagulation disorders?
A: Acquired coagulation disorders happen during a person’s life, unlike inherited ones. They affect how blood clots, raising the risk of bleeding or blood clots.
Q: How do normal blood clotting processes work?
A: Normal clotting is a complex process. It involves coagulation factors and platelets working together. Acquired disorders can disrupt this, leading to bleeding or blood clots.
Q: What are the common types of acquired coagulopathy?
A: Common types include acquired factor deficiencies and disorders needing treatment. Treatment focuses on managing the condition and preventing complications.
Q: What are the risk factors and underlying causes of acquired coagulation disorders?
A: Risk factors include medical conditions like liver disease and cancer. Certain medications and lifestyle factors like smoking also play a role.
Q: How are acquired coagulation disorders diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves initial tests, specialized studies, and imaging. These help find clotting issues and underlying conditions.
Q: How are acquired coagulation disorders treated?
A: Treatment includes managing the underlying condition and using medications. Lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are also important.
Q: What are the complications and emergency situations associated with acquired coagulation disorders?
A: Complications include severe bleeding and blood clots. These need immediate medical help. Recognizing symptoms and seeking care quickly is key.
Q: How can individuals with acquired coagulation disorders manage their condition?
A: Management involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular check-ups. This helps prevent complications and keeps coagulation health in check.
Q: What are the latest research and medical advances in the field of acquired coagulation disorders?
A: New research and advances, like gene therapy and stem cell transplantation, are improving treatment. They help better understand and manage acquired coagulation disorders.
