Did you know that 1.62 billion people worldwide suffer from anaemia? Most of them are women and children, as reported by the World Health Organization. This condition happens when there are fewer red blood cells or less hemoglobin in the blood. It’s very important to diagnose anaemia correctly to treat it properly.
For pregnant women, anaemia is especially serious. It can harm both the mother and the baby. That’s why it’s so crucial to catch it early.

Key Takeaways
- Anaemia affects approximately 1.62 billion people worldwide, mostly women and children.
- Understanding anaemia is essential for recognizing its signs and seeking proper anaemia diagnosis and treatment.
- Anaemia in pregnancy can have severe consequences for both the mother and the baby, making early detection critical.
- Recognizing the symptoms of anaemia is vital for prompt medical attention and effective treatment.
- Anaemia can be managed and prevented through a combination of dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle modifications.
- Regular health check-ups can help identify anaemia early on, reducing the risk of complications.
- Education and awareness about anaemia can help individuals take control of their health and seek proper medical care when needed.
Understanding Anaemia: A Comprehensive Overview
Common symptoms of anaemia include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. These happen because red blood cells, which carry oxygen, aren’t working right. Red blood cells are key to keeping the body healthy, and problems with them can cause serious issues.
What Is Anaemia?
Anaemia is when you have fewer or less working red blood cells. It can be caused by not enough iron, vitamins, or chronic diseases. Knowing what causes anaemia helps us spot symptoms and get the right treatment.
How Anaemia Affects Your Body
Anaemia can make you feel tired, weak, and short of breath. These signs happen because your red blood cells aren’t moving oxygen well. This means less oxygen gets to your body’s parts.
The Role of Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells are vital for our health. They carry oxygen to all parts of the body. If they don’t work right, it can lead to big health problems. Knowing how red blood cells work helps us understand anaemia symptoms and find the right treatment.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Anaemia
It’s important to know the signs of anaemia early. Symptoms include feeling tired, weak, and having pale skin. You might also feel short of breath or dizzy. In serious cases, anaemia can cause heart problems and affect pregnancy outcomes.
To diagnose anaemia, doctors look at your physical exam, medical history, and lab tests like a complete blood count (CBC). Treatment for anaemia varies based on the cause and how severe it is. If your symptoms don’t get better or get worse, you should see a doctor.
When dealing with anaemia, consider these important points:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC)
- Underlying cause and severity of the condition
- Symptoms of anaemia, such as fatigue and weakness
Knowing the common signs of anaemia is the first step to getting help. Anaemia diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve your life. They can also lower the risk of serious problems.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Feeling weak and tired |
| Weakness | Lack of energy and strength |
| Pale skin | Unusual paleness of the skin |
The Main Types of Anaemia
Anaemia is when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells are key for carrying oxygen to your body’s tissues. There are many types of anaemia, each with its own cause and symptoms. Knowing about these types is important for preventing and managing anaemia, especially during pregnancy.
Here are some of the main types of anaemia:
- Iron deficiency anaemia, the most common type, often results from not enough iron or poor absorption.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia, caused by a lack of vitamin B12 in the diet or poor absorption.
- Sickle cell anaemia, a genetic disorder that affects hemoglobin production.
- Aplastic anaemia, a rare condition where the bone marrow fails to produce blood cells.
It’s crucial to know the different types of anaemia and their causes. This knowledge helps in preventing and treating anaemia. It’s especially important for those at high risk, like pregnant women.
Early detection and treatment can greatly improve your quality of life. It also reduces the risk of complications from anaemia.
Risk Factors for Developing Anaemia
Several factors can lead to anaemia. These include a poor diet, chronic diseases, and pregnancy. A diet without enough iron, vitamin B12, and folate can cause anaemia. Also, diseases like kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer can raise the risk.
Pregnant women face a higher risk of anaemia because of their increased need for iron and other nutrients. It’s vital to prevent anaemia during pregnancy. Some main risk factors for anaemia are:
- Poor diet
- Chronic diseases
- Pregnancy
- Lack of essential nutrients
Knowing these risk factors is key for anaemia diagnosis and prevention. By understanding these, people can lower their risk of anaemia and stay healthy.
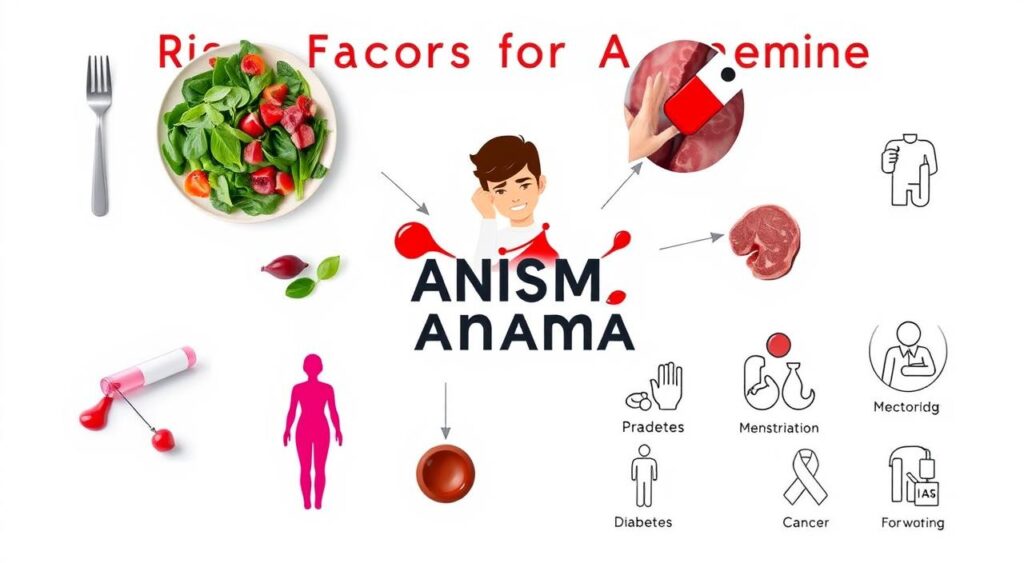
Anaemia can be managed and prevented with a healthy diet and lifestyle. Regular health checks and anaemia diagnosis are crucial. They help catch the condition early, allowing for timely treatment and anaemia prevention.
Understanding Iron Deficiency: The Leading Cause of Anaemia
Iron deficiency is a big health issue, causing about 50% of anaemia cases. It happens when the body lacks enough iron to make haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Diagnosing iron deficiency is key for treating anaemia. Doctors will check you physically, ask about your health history, and do blood tests. These tests check haemoglobin, iron, and other nutrients. If not treated, iron deficiency can cause fatigue, weakness, and poor thinking skills.
To manage iron deficiency, knowing how iron is absorbed is important. Factors that affect iron absorption include:
- Vitamin C: enhances iron absorption
- Calcium: inhibits iron absorption
- Phytates: found in whole grains and legumes, can reduce iron absorption
Eating a balanced diet with iron-rich foods helps. These include red meat, poultry, fish, and fortified cereals. If needed, doctors can prescribe iron supplements to help restore iron levels.
| Dietary Iron Sources | Iron Content per Serving |
|---|---|
| Red meat (3 oz serving) | 3-4 mg |
| Poultry (3 oz serving) | 2-3 mg |
| Fish (3 oz serving) | 2-3 mg |
| Fortified cereals (1 cup serving) | 10-18 mg |
Diagnosing Anaemia: Tests and Procedures
To diagnose anaemia, doctors do a physical check, ask about your health history, and run lab tests. A common test is the complete blood count (CBC). It counts red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This test is key for anaemia diagnosis and finding the cause.
More tests might be needed, like iron studies, vitamin B12 levels, and hemoglobin electrophoresis. These help figure out why you have anaemia. For example, if it’s due to iron deficiency, you might get iron supplements.
It’s very important to catch and treat anaemia early, especially in pregnant women. It affects both the mother and the baby. Here are some tests used to find anaemia:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Iron studies
- Vitamin B12 levels
- Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Knowing about these tests helps you manage your anaemia better. It ensures you get the best care possible.
| Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Measures the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood |
| Iron studies | Measures the level of iron in the blood |
| Vitamin B12 levels | Measures the level of vitamin B12 in the blood |
| Hemoglobin electrophoresis | Measures the different types of hemoglobin in the blood |
Treatment Options for Different Types of Anaemia
Treating anaemia depends on the cause and how severe it is. Effective treatment for anaemia can ease symptoms and stop complications. For example, iron supplements treat iron deficiency anaemia. Vitamin B12 injections are needed for vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia.
Changing your diet can also help prevent anaemia. Eating more iron and vitamin B12 can manage the condition. Include foods like red meat, spinach, and beans in your meals. Also, taking folic acid and vitamin C supplements can boost iron absorption and prevent anaemia, especially in pregnant women.
Medication Options
- Iron supplements
- Vitamin B12 injections
- Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
Dietary Changes
Eating right is key to managing anaemia. Boosting iron and vitamin B12 in your diet can help. A balanced diet with iron and vitamin B12-rich foods can prevent anaemia.
Supplements and Vitamins
Supplements like folic acid and vitamin C can enhance iron absorption and prevent anaemia. Always talk to a healthcare professional before starting any supplements to make sure they’re right for you.
Managing Anaemia During Pregnancy
Anaemia in pregnancy is a big worry. It can cause problems like preterm labor and low birth weight. It’s key to manage anaemia to keep mom and baby healthy.
Getting a proper anaemia diagnosis is very important. This means regular blood tests to check iron and hemoglobin levels.
Prenatal Care Requirements
Prenatal care for anaemia includes:
- Regular blood tests to monitor iron levels and hemoglobin
- Dietary changes to increase iron intake
- Supplementation with iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12
Safe Treatment Options
Safe treatments for anaemia in pregnancy are iron supplements, folic acid, and vitamin B12 injections. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that fits you.

Treating anaemia during pregnancy needs careful management. By following prenatal care and safe treatments, women can manage anaemia well. This helps avoid complications.
Preventing Anaemia Through Diet and Lifestyle
To prevent anaemia, you need a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Eating foods rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid is key. Red meat, spinach, and fortified cereals are great sources of these nutrients.
Regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep also help. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a prevention plan. This plan might include regular tests to check your iron levels and other nutrients.
Here are some lifestyle changes to prevent anaemia:
- Eat a balanced diet with iron-rich foods
- Take iron supplements if needed
- Exercise regularly for better health
- Manage stress with meditation or yoga
- Get enough sleep for your body’s health
By adopting these changes and consulting with a healthcare provider, you can lower your risk of anaemia. Regular tests can catch any issues early, allowing for quick treatment and prevention.
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Importance in Preventing Anaemia |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | Red meat, spinach, fortified cereals | Essential for producing healthy red blood cells |
| Vitamin B12 | Red meat, poultry, fish | Plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells |
| Folic acid | Leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals | Helps produce healthy red blood cells and prevent anaemia |
Living with Chronic Anaemia
Living with chronic anaemia means you need a solid plan to manage it well. You should know about the different types of anaemia and how to handle them. Also, preventing anaemia is key to stopping it from getting worse.
Managing chronic anaemia daily involves a few important steps. These include taking medicine, changing your diet, and making lifestyle changes. Some key strategies include:
- Taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- FOLLOWING a balanced diet rich in iron and other essential nutrients
- Engaging in regular exercise to improve overall health
For long-term health, it’s important to keep an eye on iron levels, hemoglobin, and kidney function. Working with a healthcare provider to create a personalized plan is crucial. This plan should consider your specific needs and health status. By knowing about the different types of anaemia and taking steps to prevent it, you can manage your condition better and live a better life.

By being proactive in managing chronic anaemia, you can lower the risk of complications. It’s important to be aware of the different types of anaemia and the need for prevention. Working closely with a healthcare provider to create a personalized plan is key to improving your health outcomes.
| Management Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Medication | Taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider |
| Dietary Changes | FOLLOWING a balanced diet rich in iron and other essential nutrients |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Engaging in regular exercise to improve overall health |
When to Seek Medical Attention
If symptoms of anaemia don’t get better or get worse, you should see a doctor. This is key for a correct anaemia diagnosis and finding the right treatment for anaemia.
Signs like severe fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath are emergencies. It’s also important to keep up with regular blood tests to check iron and hemoglobin levels.
A healthcare provider can create a plan just for you. This might include:
- Regular blood tests to monitor iron levels and hemoglobin
- Dietary changes to increase iron intake
- Supplements or medication to treat underlying causes of anaemia
By working with your doctor and following these guidelines, you can manage your anaemia well. It’s important to get help if your symptoms don’t improve or get worse. Quick action can greatly improve your life quality.
| Monitoring Guidelines | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Regular blood tests | Every 3-6 months |
| Dietary changes | Ongoing |
| Supplements or medication | As prescribed by a healthcare provider |
Special Considerations for Different Age Groups
When it comes to anaemia, different age groups face unique challenges. Pregnant women, for instance, are more likely to get anaemia in pregnancy. This is because they need more iron and nutrients.
Children and older adults also face a higher risk of anaemia. It’s vital to work with a healthcare provider. They can help create a plan for prevention and treatment, including anaemia diagnosis and treatment.
Here are some important things to consider for each age group:
- Regular health check-ups to monitor for signs of anaemia
- A balanced diet that includes iron-rich foods
- Supplements or vitamins as recommended by a healthcare provider
By following these steps, people can lower their risk of getting anaemia. It’s also important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse.

| Age Group | Risk Factors | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Pregnant Women | Increased demand for iron and other nutrients | Regular health check-ups, balanced diet, supplements or vitamins |
| Children | Poor diet, increased demand for iron and other nutrients | Regular health check-ups, balanced diet, supplements or vitamins |
| Older Adults | Chronic diseases, poor diet, decreased absorption of nutrients | Regular health check-ups, balanced diet, supplements or vitamins |
Natural Remedies and Complementary Treatments
Managing anaemia can be helped by natural remedies and treatments. These can ease symptoms and boost health. A healthy diet and lifestyle are key to preventing anaemia and making it less severe.
Herbal supplements, like iron and vitamin B12 herbs, can boost iron and hemoglobin levels. Stress management, regular exercise, and enough sleep also help. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that includes these natural options.
- Dietary changes to increase iron and vitamin B12 intake
- Herbal supplements such as iron-rich herbs and vitamin B12-rich herbs
- Stress management techniques such as meditation and yoga
- Regular exercise to improve overall health and reduce symptoms of anaemia
Using these natural remedies and treatments in a treatment plan can help manage anaemia. It also reduces the risk of complications. This is vital for preventing and treating anaemia effectively.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Anaemia Management
Managing anaemia well is key to keeping red blood cells healthy and avoiding problems. Working with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan is important. This way, you can handle your anaemia diagnosis and prevention better.
Eating a balanced diet with iron-rich foods like spinach and beans helps. Regular exercise is also crucial. These steps can help prevent anaemia.
It’s vital to check your iron levels and hemoglobin often. Blood tests can spot issues early. By being proactive, you can boost your health and reduce risks.
By focusing on anaemia management, you can lower the risk of complications. Knowing the signs and symptoms of anaemia is important. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are also key.
With the right knowledge and support, you can manage your anaemia effectively. This improves your overall well-being.
FAQ
Q: What is anaemia and how is it diagnosed?
A: Anaemia is when you have fewer red blood cells or less hemoglobin. Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and blood tests to diagnose it. Tests like a complete blood count (CBC) and iron studies are common.
Q: What are the common symptoms of anaemia?
A: Symptoms include feeling tired, weak, and pale. You might also get short of breath or dizzy. In severe cases, it can cause heart problems and affect pregnancy outcomes.
Q: What are the different types of anaemia?
A: There are several types, like iron deficiency and vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia. Sickle cell anaemia and aplastic anaemia are others. Each type has its own cause and symptoms, and treatment varies.
Q: How can anaemia be prevented?
A: Eating a balanced diet with iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid helps. Regular exercise, managing stress, and enough sleep also prevent it. Prenatal care and health check-ups are key for pregnant women and others at risk.
Q: What are the treatment options for anaemia?
A: Treatment depends on the cause and severity. Options include iron supplements, vitamin B12 injections, and special medications. Changing your diet and sometimes blood transfusions are also used.
Q: How does anaemia affect pregnant women?
A: It can lead to preterm labor and low birth weight. Pregnant women need more iron and nutrients. Regular prenatal care and monitoring are crucial.
Q: Can anaemia be managed through natural remedies and lifestyle modifications?
A: Yes, natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help. Herbal supplements and stress management are beneficial. But, always consult a healthcare provider for a personalized plan.
Q: What are the risk factors for developing anaemia?
A: Poor diet, chronic diseases, and pregnancy increase the risk. A diet lacking essential nutrients can cause it. Diseases like kidney disease and cancer also raise the risk.
Q: How can anaemia be managed in different age groups?
A: Different age groups have unique needs to prevent and manage anaemia. Pregnant women, children, and older adults are at higher risk. Working with a healthcare provider is essential for a tailored plan.
