Did you know Bartholin’s abscess affects up to 2% of women at some point? It’s a painful swelling of the Bartholin’s glands. Knowing about its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key for women’s health.
Key Takeaways
- Bartholin’s abscess is a common gynecological condition affecting the Bartholin’s glands, which play a crucial role in female reproductive health.
- Symptoms include a painful, pus-filled swelling near the vaginal opening, often accompanied by discomfort and disruption to daily activities.
- Prompt medical treatment, which may involve antibiotics, drainage, or surgical intervention, is essential for managing Bartholin’s abscess and preventing complications.
- Home remedies and self-care measures can provide relief and support the healing process, but should be used in conjunction with professional medical care.
- Prevention strategies, such as maintaining good hygiene and addressing underlying health conditions, can help reduce the risk of developing Bartholin’s abscess.
Understanding Bartholin’s Glands and Their Function
Bartholin’s glands are key to female reproductive health. They are small, pea-sized glands at the vagina’s opening. They make a lubricating fluid that keeps the vagina moist and balanced.
Knowing how Bartholin’s glands work is vital. It helps us spot and treat bartholin’s gland infection and other gynecological issues.
Anatomy of Bartholin’s Glands
Bartholin’s glands are on either side of the vaginal opening, just under the skin. They are part of the female external genitalia. Located in the labia minora, they are about 1 to 2 centimeters in diameter.
These glands secrete a clear, mucus-like fluid. This fluid lubricates the vagina and keeps female reproductive health in check.
Normal Secretion Process
When a woman is sexually aroused or experiences other physiological cues, Bartholin’s glands release their fluid. This fluid lubricates the vaginal canal. It makes intercourse more comfortable and protects the vaginal tissues from irritation and infection.
Role in Female Reproductive Health
Bartholin’s glands do more than just lubricate. They help keep the vagina’s acidic pH, which keeps harmful bacteria away. Their secretion also aids in the vagina’s self-cleaning process, removing dead cells and debris.
| Bartholin’s Gland Function | Importance |
|---|---|
| Lubrication | Facilitates comfortable intercourse and protects vaginal tissues |
| pH Maintenance | Creates an acidic environment that discourages bacterial growth |
| Self-Cleaning | Flushes out dead cells and other debris from the vagina |
Understanding Bartholin’s glands is key to female reproductive health and spotting issues like bartholin’s gland infection. Knowing about these glands helps women stay on top of their vaginal health. They can seek medical help quickly if they notice any problems.
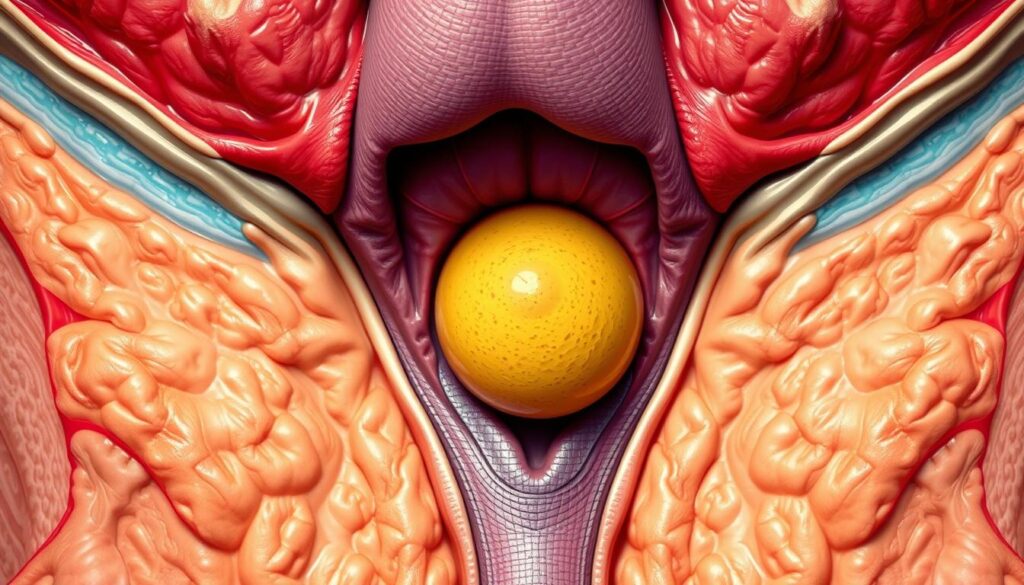
What is Bartholin’s Abscess?
Bartholin’s abscess is a buildup of pus in the Bartholin’s glands. These glands are small and sit on either side of the vaginal opening. They help with lubrication during sex. But, if they get blocked or infected, they can cause a painful abscess.
This abscess is also called bartholinitis or vulvar abscess. It starts with a Bartholin’s cyst, a fluid-filled sac. If this cyst gets infected, it turns into an abscess filled with pus. This can be very painful and may get worse if not treated.
- Bartholin’s abscess is a localized infection of the Bartholin’s glands, small glands located on either side of the vaginal opening.
- It often develops from a Bartholin’s cyst, a fluid-filled sac that forms when the gland’s duct becomes blocked.
- The infection can cause the cyst to become filled with pus, leading to the formation of a painful, swollen abscess.
Knowing the causes and early signs of bartholin’s abscess is key. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage pain and prevent bigger problems.
“Bartholin’s abscess is a common and often overlooked condition that can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life.”
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Bartholin’s abscess is a painful condition that affects the Bartholin’s glands. It can be caused by many factors. Knowing what causes it and who is at risk is key to managing and preventing it.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are a main cause of Bartholin’s abscess. Bacteria like Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus can get into the glands and cause an abscess. Poor hygiene and a weak immune system can make you more likely to get these infections.
Sexually Transmitted Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia and gonorrhea can also cause Bartholin’s abscesses. These infections can spread to the glands, causing inflammation and an abscess. Not using protection and having many partners can increase your risk of getting an STI and developing an abscess.
Other Contributing Factors
- Age: Women between 20 and 30 years old are more likely to get Bartholin’s abscesses.
- Sexual activity: Being more active sexually and using certain birth control devices, like IUDs, can raise your risk.
- Hormonal changes: Changes in hormone levels, like during pregnancy or menopause, can make the glands more prone to infection.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): This condition, often caused by untreated STIs, can lead to Bartholin’s abscesses.
Knowing the common causes and risk factors of Bartholin’s abscess can help you stay safe. Practice good genital hygiene, use protection, and see a doctor if you notice any symptoms.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Bacterial Infections | Bacterial infections, such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, can infiltrate the Bartholin’s glands and lead to the development of an abscess. |
| Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) | Sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia and gonorrhea, can spread to the Bartholin’s glands and cause inflammation and abscess formation. |
| Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) | Pelvic inflammatory disease, often caused by untreated STIs, can contribute to the development of Bartholin’s abscesses. |
Recognizing Early Warning Signs
Spotting the early signs of a bartholin’s abscess is key for quick treatment and avoiding bigger problems. The first symptoms might be small, but knowing them can help women get help early.
A mild ache or tenderness near the bartholin’s glands is often the first sign. This area might look a bit swollen or red, but it’s usually small. Some women might also feel a burning or pressure feeling.
As the bartholin’s abscess gets worse, the swelling gets bigger. This can make a noticeable lump near the vaginal opening. The pain can also get worse, especially when having sex or sitting.
At first, a bartholin’s abscess might seem like just a simple vulvovaginitis infection. But the swelling and pain in one spot are clear signs of an abscess.
By catching these early signs and getting medical help fast, women can get better treatment. This can help stop the bartholin’s abscess from getting worse. Quick action is important for a good outcome and quick recovery.
Key Symptoms of Bartholin’s Abscess
Bartholin’s abscess is a common gynecological issue. It has distinct symptoms that can affect a woman’s health and well-being. Knowing these symptoms is key for quick diagnosis and treatment.
Physical Manifestations
A Bartholin’s abscess often shows as a swelling or lump near the vagina’s opening. This swelling is usually red, warm, and tender. These signs point to an infection or inflammation.
Pain Patterns and Intensity
Bartholin’s abscess can cause a lot of discomfort. The pain can be in one spot or spread to other areas. It can range from mild to very severe, making everyday tasks and sex hard.
Associated Symptoms
- Fever and chills: A Bartholin’s abscess can cause fever and body aches.
- Difficulty urinating: Swelling and pain can make it hard to fully empty the bladder.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse: The vulvar area’s inflammation and tenderness can make sex painful or impossible.
Recognizing and acting on these symptoms is crucial. It helps people get the medical help they need. This can ease their discomfort and aid in healing.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Diagnosing a Bartholin’s gland infection or abscess involves a detailed check-up by a healthcare provider. This helps find the cause and plan the right treatment. Let’s look at the common tests used for bartholin’s gland infection and other gynecological conditions.
The first step is a detailed physical check. Your doctor will look at the affected area and feel the Bartholin’s gland. They check for swelling, tenderness, or a mass. This gives important clues about the condition.
At times, a fluid sample from the Bartholin’s gland is taken. This is called aspiration or drainage. It helps find out if it’s a bacterial or fungal infection. The fluid is then tested in a lab, including culture and sensitivity analysis.
| Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual and palpatory assessment of the affected area |
| Fluid Aspiration/Drainage | Collection and analysis of fluid from the Bartholin’s gland |
| Imaging Tests | Ultrasound or CT scan to visualize the gland and surrounding structures |
Imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans might be used too. They give a clearer view of the gland and nearby areas. These tests help tell a Bartholin’s abscess apart from other gynecological conditions and help plan treatment.
Healthcare providers use a physical exam, fluid analysis, and imaging tests to accurately diagnose. This way, they can create a good treatment plan for Bartholin’s gland infections and related gynecological conditions.

Medical Treatment Options
Bartholin’s abscess is a painful swelling of the Bartholin’s glands. It often needs quick medical help. Doctors might suggest different treatments, from simple methods to surgery, based on the bartholin’s abscess or bartholin’s cyst severity.
Surgical Interventions
For bartholin’s abscess that keeps coming back, surgery might be needed. Doctors might do an incision and drainage or marsupialization. Marsupialization makes a permanent hole to stop future blockages and infections.
Antibiotics and Medications
Antibiotics help treat the bacterial infection behind the bartholin’s abscess. Doctors also suggest pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. These help with the pain and swelling.
Post-Treatment Care
After treatment, taking good care of yourself is key. You might need to follow wound care, use sitz baths, and wait to get back to normal activities. It’s important to see your doctor again to check on healing and prevent future problems.
Handling bartholin’s abscess needs teamwork between you and your healthcare team. Knowing your treatment options and following care advice helps you recover fast. It also lowers the chance of pelvic inflammatory disease or other issues.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Measures
Dealing with a bartholin’s abscess can be tough, but there are ways to help. Home remedies and self-care can ease symptoms and aid in healing. These methods are simple yet effective in supporting your body’s recovery.
The sitz bath is a great option. Sitting in warm, shallow water for 15-20 minutes several times a day can ease pain and swelling. It helps with circulation and drainage, speeding up healing.
Warm compresses are also helpful. They increase blood flow, which aids in healing. Hold a clean, warm (not hot) washcloth against the bartholin’s abscess for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
Managing pain is key during recovery. Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help. Always follow the dosage and talk to a doctor if pain doesn’t get better or gets worse.
Don’t forget about vulvovaginitis and genital hygiene. Use gentle, fragrance-free products and avoid harsh soaps. Wear loose, breathable clothes to reduce friction and promote air circulation.
By using these home remedies and self-care tips, you can manage a bartholin’s abscess effectively. Remember to see a doctor if symptoms don’t improve or get worse. They may need to intervene in some cases.
| Home Remedy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sitz Bath | Reduces pain, swelling, and discomfort |
| Warm Compresses | Increases blood flow and promotes healing |
| Over-the-Counter Pain Medications | Provides relief and reduces inflammation |
| Gentle Genital Hygiene | Minimizes irritation and supports recovery |
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Changes
Keeping your female reproductive health in check and avoiding gynecological conditions like Bartholin’s abscess starts with healthy habits. By adding preventive steps to your daily life, you can lower the chance of getting this issue.
Hygiene Practices
Good personal hygiene is key to keeping your vagina healthy and infection-free. This means:
- Gently clean your genital area with warm water and mild, fragrance-free soap, avoiding harsh scrubbing or douching
- Wear breathable, moisture-wicking undergarments to cut down on moisture and bacterial growth
- Change sanitary pads and tampons often during your period
- Practice safe, protected sex to lower the risk of STIs
Dietary Considerations
Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients is also important for your female reproductive health and immune system. This helps prevent gynecological conditions. Here are some dietary tips:
- Eat more probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented veggies to keep your vaginal microbiome healthy
- Include a variety of fruits and veggies high in antioxidants to boost your immune system
- Try to eat less sugary and processed foods, as they can upset your vaginal flora balance
By focusing on these preventive steps and lifestyle changes, you can protect your female reproductive health. This helps reduce the risk of Bartholin’s abscess and other gynecological conditions.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Care
Bartholin’s abscess and pelvic inflammatory disease can usually be treated well. But, there are times when you need to see a doctor right away. Knowing when to act fast is very important.
Severe, unbearable pain in the affected area is a warning sign. Also, high fever, chills, or flu-like symptoms are serious and shouldn’t be ignored. If the swelling or redness spreads quickly, it’s a sign you need help fast.
- Severe, debilitating pain
- High fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms
- Rapidly spreading swelling or redness
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, go to the emergency room right away. Bartholin’s abscess and pelvic inflammatory disease can quickly become life-threatening if left untreated. Your health and safety are the most important things.
“Early intervention is the key to managing Bartholin’s abscess and preventing complications. Don’t wait to seek medical help if you’re experiencing severe symptoms.”
Conclusion
Understanding Bartholin’s abscess is key to good female reproductive health. This condition can be managed with early detection and treatment. Taking steps to prevent it is also important.
Look out for signs like swelling and pain in the genital area. If you notice these, see a doctor right away. With the right care, most cases can be treated well, making you feel better.
Keep your genital area clean and live a healthy lifestyle. Being aware of any changes in your reproductive system is crucial. Your reproductive health is vital to your overall well-being. Taking care of it is the best way to stay healthy.
FAQ
Q: What is a Bartholin’s abscess?
A: A Bartholin’s abscess is a buildup of pus in a Bartholin’s gland. These glands are found on each side of the vaginal opening. It happens when a gland gets blocked or infected, causing a painful lump in the vulvar area.
Q: What are the common symptoms of a Bartholin’s abscess?
A: The main symptoms include a painful, swollen lump in the vulvar area. You might also see redness, tenderness, and have trouble sitting or walking. Fever, chills, and discomfort during sex are other signs.
Q: How is a Bartholin’s abscess diagnosed?
A: Doctors usually diagnose it by examining the vulvar area. They might also do tests like fluid analysis or imaging studies. This helps confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Q: What are the treatment options for a Bartholin’s abscess?
A: Treatment often includes antibiotics, drainage, and sometimes surgery. Doctors may also suggest sitz baths, warm compresses, and pain meds to help with symptoms during recovery.
Q: Can a Bartholin’s abscess be prevented?
A: Yes, you can prevent it by practicing good hygiene and living a healthy lifestyle. Getting medical help quickly for any vulvar discomfort or swelling is also key. Regular sexual health screenings can help catch and treat infections early.
Q: When should I seek emergency medical care for a Bartholin’s abscess?
A: Seek emergency care if you have severe pain, high fever, rapid swelling, or signs of a spreading infection. These could mean a serious issue that needs quick treatment.
