Manage chickenpox effectively with our expert advice. Discover causes, symptoms, and effective home remedies for a speedy recovery.
In the United States, 90% of kids get chickenpox, also known as varicella, by adulthood. This disease, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, hits people of all ages. But it’s most common in kids. Knowing how to care for chickenpox is key to managing it well.
Key Takeaways
- Chickenpox is a highly infectious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus.
- It is most prevalent in children, but people of all ages can be affected.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for chickenpox is crucial for effective care and management.
- Chickenpox, or varicella, can have serious complications if not properly managed.
- Vaccination is available to prevent chickenpox and reduce the risk of complications.
- Effective care and management of chickenpox involve a combination of medical treatment and home care.
Understanding Chickenpox and Its Causes
Chickenpox is a contagious illness caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This virus leads to chickenpox symptoms, which can vary from mild to severe. The virus spreads through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. It also spreads through direct contact with the rash or touching contaminated surfaces.
To prevent chickenpox, it’s important to know how it spreads. Prevention methods include avoiding close contact with those who have chickenpox. Washing hands often and not touching your face are also key. Recognizing early signs of chickenpox can help stop its spread.
The varicella-zoster virus is very contagious. People who haven’t had chickenpox or haven’t been vaccinated are at risk. Factors that increase the risk of infection include:
- Close contact with someone who has chickenpox
- Weak immune system
- Not being vaccinated against chickenpox
Knowing the causes of chickenpox and how it spreads helps prevent it. By taking preventive steps and understanding the varicella-zoster virus, you can lower your risk of getting chickenpox and its symptoms.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Chickenpox
Chickenpox symptoms can range from mild to severe. It’s key to spot them early for better management. The first signs might look like those of other illnesses, such as fever, headache, and fatigue. But, a rash is a clear sign of chickenpox.
The rash starts as small, itchy blisters. These blisters then crust over and heal. Knowing these symptoms is crucial to avoid complications and stop the spread of chickenpox. Some common signs include:
- Fever and headache
- Fatigue and loss of appetite
- A rash that progresses from small blisters to crusted lesions
Spotting these symptoms early helps get medical help quickly. This can prevent serious problems. Being aware of chickenpox signs helps manage the condition and stop it from spreading.
Chickenpox is contagious, and those with weak immune systems face bigger risks. Recognizing early signs and acting fast can stop the illness from spreading. This ensures effective management of chickenpox symptoms.
Common Chickenpox Symptoms and Stages
Chickenpox symptoms can vary, but they usually follow a pattern. You might first feel fever, headache, and tiredness. Then, a rash will show up. Knowing the stages of chickenpox symptoms is key for chickenpox treatment and care.
The stages of chickenpox symptoms include:
- Initial symptoms: fever, headache, and fatigue
- Development of rash: a red, itchy rash that appears on the skin
- Progression of blisters: the rash develops into blisters that eventually crust over and heal
- Recovery phase: the blisters heal and the skin returns to normal
During these stages, chickenpox symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter meds. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with fever and headache. It’s important to watch how symptoms change and get medical help if needed.
Knowing about chickenpox symptoms and stages helps manage the condition. Effective chickenpox treatment and care can ease symptoms and aid in recovery.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fever | A high temperature, usually above 100.4°F (38°C) |
| Headache | A headache that can range from mild to severe |
| Fatigue | Feeling tired or weak, which can interfere with daily activities |
Managing Chickenpox at Home
Managing chickenpox treatment at home is key for a quick recovery. It’s important to make the patient’s environment comfortable. They should rest a lot and drink plenty of water.
It’s also crucial to stop the virus from spreading. This is especially true for pregnant women and those with weak immune systems.
Relieving symptoms is a big part of chickenpox treatment at home. You can use over-the-counter meds to lower fever and ease itching. Cool compresses can also help with itching and discomfort.
It’s important to keep the patient away from others until the rash crusts over. This helps prevent the virus from spreading.
Some good home care tips for chickenpox treatment include:
- Encouraging the patient to drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated
- Using calamine lotion or oatmeal baths to soothe itchy skin
- Keeping the patient’s nails clean and short to prevent scratching and infection
By following these tips, patients can recover faster and avoid complications. Always talk to a healthcare professional for specific advice on treating chickenpox at home.

Treatment Options and Relief Measures
Managing chickenpox involves several treatment options and relief measures. There’s no cure for the virus, but these steps can ease symptoms and lower the risk of complications. The chickenpox vaccine helps prevent the disease. For those who have it, treatment aims to relieve symptoms.
Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with fever and headache. Natural remedies, such as oatmeal baths or cool compresses, can also ease itching and discomfort. Sometimes, medical help is needed, especially for those at high risk or with severe symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Medications
- Acetaminophen to relieve fever and headache
- Ibuprofen to reduce inflammation and relieve pain
Natural Remedies
- Oatmeal baths to soothe itchy skin
- Cool compresses to reduce fever and relieve discomfort
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek medical help if you’re at high risk for complications or symptoms are severe. This includes people with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, and those with certain medical conditions. The chickenpox vaccine can prevent the disease. But for those who have it, quick treatment is key to avoid complications.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Over-the-Counter Medications | Relieve symptoms like fever and headache |
| Natural Remedies | Soothe itchy skin and reduce fever |
| Medical Help | Necessary for high-risk individuals or severe symptoms |
Special Considerations for Adults with Chickenpox
Chickenpox can be more serious in adults than in kids. Adults with weak immune systems, like those with HIV/AIDS or on chemotherapy, face a higher risk. It’s crucial to prevent spreading the virus and get medical help if symptoms worsen.
Some important points for adults with chickenpox include:
- Increased risk of pneumonia and other respiratory complications
- Higher risk of bacterial infections, such as group A strep
- Increased risk of encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain
Adults should also know about long-term effects like postherpetic neuralgia. This is a condition with ongoing pain after the rash goes away. To avoid complications, stay hydrated, rest well, and see a doctor for severe symptoms.
It’s key to stop chickenpox from spreading, especially for adults at risk. This can be done by:
Practicing good hygiene, like washing hands often and avoiding close contact, can help prevent the spread of chickenpox.
By taking these steps and getting medical help when needed, adults can lower their risk of serious problems and recover faster.
Prevention Through Vaccination
Preventing chickenpox is key, especially for kids. It helps avoid serious problems and stops the virus from spreading. The chickenpox vaccine is a top choice for prevention. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says kids get two doses.
The first dose is given between 12-15 months. The second dose comes 4-6 years later. This vaccine works well, with an 85-90% success rate. It’s a must in places like schools and hospitals. Adults who haven’t had chickenpox or been vaccinated should also get it, especially in high-risk jobs.
Vaccine Schedule
The chickenpox vaccine schedule is clear:
- First dose: 12-15 months
- Second dose: 4-6 years
Effectiveness Rates
The vaccine’s success rate is 85-90%. This means 85-90% of those vaccinated won’t get chickenpox.
Who Should Get Vaccinated
All kids and adults who haven’t had chickenpox should get vaccinated. It’s crucial for those in high-risk jobs like healthcare or teaching. Vaccination helps stop the disease from spreading. It keeps everyone safe, especially in places where people are close together.
| Age Group | Vaccine Dose | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| 12-15 months | First dose | 85-90% |
| 4-6 years | Second dose | 85-90% |
Potential Complications and Risk Groups
Chickenpox can cause serious problems, especially for those at high risk. These issues include bacterial infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis. It’s important to know who’s at risk and how to avoid these problems.
People with weak immune systems face a higher risk. Long-term effects of chickenpox can be severe, like scarring, blindness, and brain damage. If symptoms get worse, it’s crucial to see a doctor.
High-Risk Individuals
- People with weakened immune systems
- Newborns and infants
- Adults over 60 years old
Serious Complications
Some serious problems from chickenpox are:
- Bacterial infections
- Pneumonia
- Encephalitis
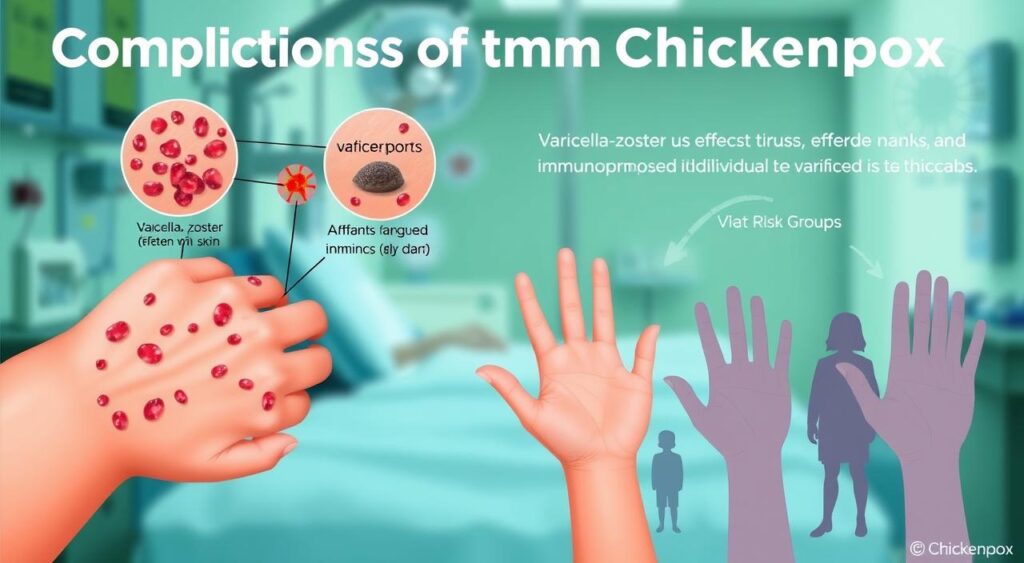
Long-term Effects
Chickenpox can sometimes cause lasting damage. This includes scarring, blindness, and brain problems. If symptoms don’t get better, it’s important to get medical help.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Bacterial infections | Can lead to serious health issues, such as sepsis |
| Pneumonia | Can cause respiratory failure and death |
| Encephalitis | Can lead to brain damage and neurological disorders |
School and Work Guidelines During Infection
When dealing with chickenpox in children, it’s key to follow the right steps to stop it from spreading. Kids with chickenpox should stay home until their rash crusts over. This usually takes 5-7 days after the rash starts.
Adults with chickenpox should also stay away from work until they’re no longer contagious. This is usually 10-14 days after the rash starts. It’s important to keep the workplace healthy by not spreading the virus.
Some important steps to take during an infection include:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water
- Avoiding close contact with others, especially those with weakened immune systems
- Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Avoiding sharing of personal items, such as towels and utensils
By following these steps, we can stop chickenpox from spreading. It’s also good to know that getting vaccinated can help prevent chickenpox, especially in chickenpox in children.
Conclusion: Managing Chickenpox Effectively
Dealing with chickenpox means knowing the varicella-zoster virus and how it spreads. Spotting early signs and managing symptoms well helps. It also helps to prevent the virus from spreading.
By staying informed and following health advice, you can manage chickenpox well. This guide offers tips to help you through it. It shows how to overcome the illness and come out stronger.
FAQ
Q: What is the varicella-zoster virus?
A: The varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox, a contagious disease. It can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
Q: How does chickenpox spread?
A: Chickenpox spreads easily. It can spread through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. It also spreads through touching the rash or contaminated surfaces.
Q: What are the early signs of chickenpox?
A: Early signs include fever, headache, and feeling tired. Then, a rash appears. The rash starts as small, itchy blisters that crust over and heal.
Q: What are the common symptoms and stages of chickenpox?
A: Symptoms of chickenpox vary but follow a pattern. First, you might feel feverish, have a headache, and feel tired. Then, a rash appears. The rash turns into blisters that crust over and heal.
Q: How can chickenpox be managed at home?
A: To manage chickenpox at home, rest, drink plenty of water, and use over-the-counter medicines. Use cool compresses to ease itching. Keep the patient isolated to stop the spread.
Q: What are the treatment options and relief measures for chickenpox?
A: Treatments include over-the-counter medicines for fever and headache. Natural remedies like oatmeal baths or cool compresses help with itching. Sometimes, medical help is needed, especially for severe cases or those at high risk.
Q: How do adults differ in their experience with chickenpox?
A: Adults with chickenpox face higher risks. Their symptoms can be more severe, and they are more likely to spread it. Those with weakened immune systems, like HIV/AIDS patients or those on chemotherapy, are at greater risk.
Q: How can chickenpox be prevented through vaccination?
A: Vaccination is the best way to prevent chickenpox. The vaccine is given in two doses, at 12-15 months and 4-6 years. It’s very effective and recommended for all children.
Q: What are the potential complications and risk groups for chickenpox?
A: Chickenpox can lead to serious complications, especially in those with weakened immune systems. Complications include bacterial infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis. Long-term effects can include scarring, blindness, and neurological damage.
Q: What are the guidelines for school and work during a chickenpox infection?
A: It’s important to follow guidelines for school and work during an infection. Kids should stay home until their rash crusts over. Adults should avoid work until they’re no longer contagious. Good hygiene is key to prevent spread.
