Every year, 1 million new cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis are reported worldwide. This skin parasite infection is a major public health issue. It’s important to know its causes, symptoms, and treatments to manage and prevent it.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is caused by the Leishmania parasite. It spreads through the bite of an infected sandfly.
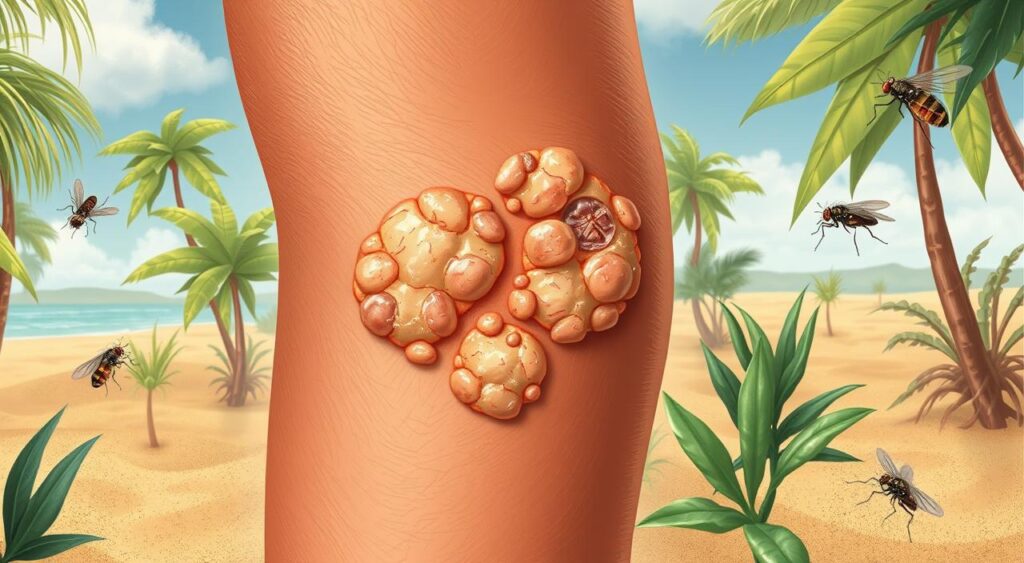
This disease affects millions of people, causing a lot of suffering and death. It’s key to know the signs and symptoms to get medical help fast. This article will cover cutaneous leishmaniasis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Key Takeaways
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a parasitic skin infection caused by the Leishmania parasite.
- The disease is transmitted through the bite of an infected sandfly.
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant morbidity and mortality.
- Recognizing the signs and symptoms of this skin parasite infection is crucial for seeking medical attention promptly.
- Effective treatment options are available for cutaneous leishmaniasis, and understanding these options is vital for managing the disease.
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a significant public health concern, and preventing its spread is essential.
Understanding Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a big health issue around the world, especially in warm and tropical areas. It’s one of three main types of leishmaniasis in people. To get a good grasp of this disease, we need to look at its definition, types, where it’s found, and its history.
The disease is found in many places globally. Leishmaniasis in humans often happens in areas with bad sanitation, poor homes, and near where insects live. Knowing where and when it started helps us fight it better.
Definition and Classification
Cutaneous leishmaniasis causes skin problems that can hurt and change how you look. It spreads through the bite of an infected sandfly. The type of parasite in the person determines the disease’s classification.
Global Distribution
More than 90 countries have cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Most are in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. It’s linked to poverty, war, and moving from place to place, making it a big health worry.
Historical Background
Leishmaniasis has been around for thousands of years. It’s mentioned in old texts and has greatly affected human health. Knowing its history helps us find better ways to stop and control it.
The Parasitic Cause of Leishmaniasis
The Leishmania parasite causes leishmaniasis, a sandfly disease affecting millions globally. It spreads through an infected sandfly bite. This makes leishmaniasis transmission a big worry in certain areas.
Knowing how the parasite lives and spreads is key to stopping the disease. Sandflies play a big part in spreading leishmaniasis. Keeping sandflies away is crucial to controlling the disease.
- The parasite grows inside the sandfly before it’s passed to a human.
- Infected sandflies can give the parasite to many people, posing a big health risk.
- Preventing leishmaniasis transmission is possible with insecticides, bed nets, and other protective steps.
By understanding the parasite behind leishmaniasis and the sandfly’s role, we can fight this sandfly disease effectively.
How Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Spreads
Cutaneous leishmaniasis spreads through the bite of an infected sandfly. Knowing how leishmaniasis transmission works is key to stopping it. The disease is common in some places, so it’s important to know the cutaneous leishmaniasis symptoms and take steps to protect yourself.
People at risk live in or visit areas where the disease is common. Poor living conditions and lack of healthcare also increase the risk. Certain places are more prone to the disease because of the sandfly vector.
Sandfly Transmission
Sandflies are the main carriers of leishmaniasis transmission. They get infected by feeding on an infected host. Then, they can pass the parasite to a new host through their bite.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of getting cutaneous leishmaniasis. These include:
- Living in or visiting areas where the disease is common
- Having poor living conditions
- Lacking access to healthcare
Geographic Hot Spots
Some places are more prone to the disease because of sandflies. Knowing the cutaneous leishmaniasis symptoms and how it spreads helps in preventing it.
| Geographic Location | Prevalence of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
|---|---|
| South America | High |
| Central America | Medium |
| North America | Low |
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the cutaneous leishmaniasis symptoms early. The disease causes skin lesions that can hurt and leave scars. You might also feel fever, swelling, and redness around the sore.
Here are some common cutaneous leishmaniasis symptoms:
- Skin lesions or sores
- Fever
- Swelling and redness around the lesion
- Pain or discomfort
If you notice these symptoms, see a doctor right away. Catching it early can help a lot. It can make treatment better and prevent serious problems.
Knowing the signs of cutaneous leishmaniasis helps you act fast. This can stop serious damage and keep you healthy.
The Life Cycle of Leishmania Parasites
Leishmaniasis in humans is a complex disease caused by the Leishmania parasite. It is spread through the bite of an infected sandfly. Knowing how Leishmania parasites live is key to fighting the disease.
The life cycle of Leishmania parasites has many stages. From the promastigote stage in the sandfly to the amastigote stage in humans. This cycle is vital for the parasite’s survival and growth.
Parasite Development Stages
The parasite goes through several stages:
- Promastigote stage: The parasite’s first stage in the sandfly, where it grows and multiplies.
- Amastigote stage: The parasite’s last stage in humans, where it infects and grows inside cells.
Host-Parasite Interaction
The interaction between the parasite and its host is crucial. The parasite’s ability to infect and grow in human cells depends on many factors. These include the host’s immune response and the parasite’s virulence.
Understanding the life cycle of Leishmania parasites and how they interact with their hosts is vital. By focusing on specific stages of the parasite’s life cycle, researchers can create new treatments. These treatments aim to stop leishmaniasis transmission and help patients.
| Parasite Stage | Host | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Promastigote | Sandfly | Initial stage of parasite development |
| Amastigote | Human | Final stage of parasite development, infects and multiplies within cells |
Diagnosis Methods and Procedures
Getting a correct leishmaniasis diagnosis is key to treating the disease well and avoiding serious issues. To diagnose cutaneous leishmaniasis, doctors use several methods. These include physical checks, lab tests, and sometimes a biopsy.
To confirm leishmaniasis diagnosis, doctors look for the parasite in tissue samples or use molecular tests. The choice of test depends on what resources are available and how bad the symptoms are. Here are some common ways to diagnose:
- Physical examination to spot symptoms like skin lesions
- Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or tissue samples, to find the parasite
- Biopsy to look at a tissue sample under a microscope
- Molecular tests, like PCR, to find the parasite’s DNA
It’s very important to diagnose leishmaniasis early and accurately. This helps in treating it effectively and avoiding long-term problems. Knowing about the different ways to diagnose helps doctors treat patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis quickly and well.
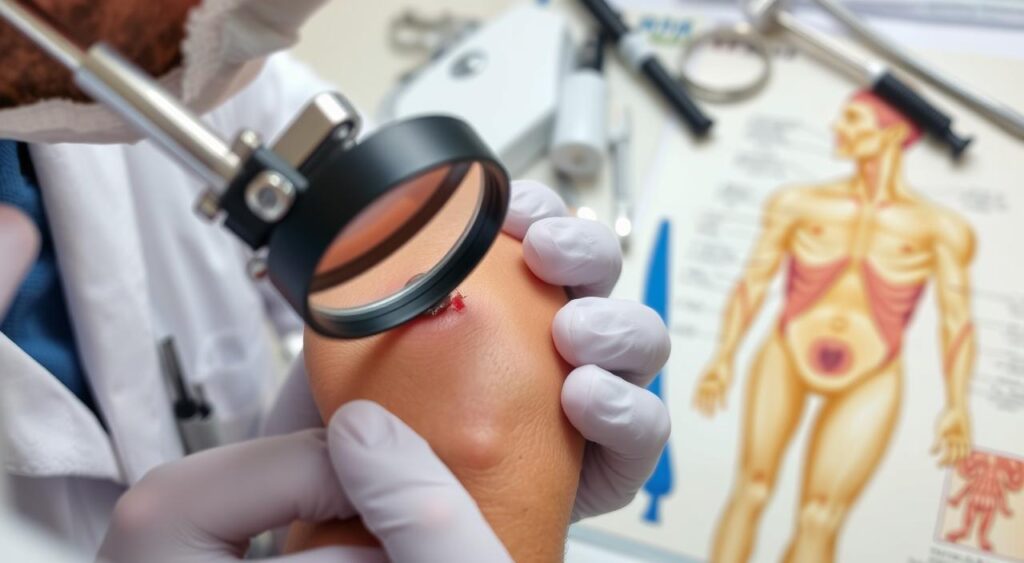
Treatment Options and Approaches
There are many ways to treat leishmaniasis, depending on how bad it is and the patient’s health. The main goal is to get rid of the parasite and help the skin heal.
Doctors use different medicines, like antimonial compounds, to fight cutaneous leishmaniasis. They also use local treatments, like creams or heat therapy, to help the disease.
Pharmaceutical Treatments
Medicines are often the first choice to fight leishmaniasis. Antimonial compounds, like meglumine antimoniate or sodium stibogluconate, work well. But, they can cause side effects like nausea and stomach pain.
Local Therapy Options
For cutaneous leishmaniasis, doctors might use creams or heat therapy. Creams, like paromomycin or miltefosine, are applied directly to the skin. Heat therapy kills the parasite.
Systemic Treatment Methods
For serious cases, doctors might use medicines given through an IV or by mouth. These treatments can have serious side effects, like kidney or liver damage. Always get these treatments from a doctor.
It’s very important to get treatment for leishmaniasis from a doctor. The disease is complex and needs special care. With the right treatment, it’s possible to manage the disease and heal the skin.
Prevention Strategies and Protection Methods
Preventing leishmaniasis is key to stopping its spread. This can be done by combining personal protection and environmental control. By doing so, people can greatly reduce their chance of getting cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Personal protection includes using insect repellents, wearing protective clothes, and staying away from sandfly areas. Wearing long-sleeved shirts and pants helps prevent bites. Also, using insecticide-treated bed nets keeps bites away while sleeping.
Personal Protection Measures
- Using insect repellents
- Wearing protective clothing
- Avoiding areas where sandflies are common
Environmental control means getting rid of sandfly breeding sites and using insecticides. Community efforts, like public health campaigns and vector control, are also vital. Together, we can fight leishmaniasis and promote prevention.
Environmental Control
Getting rid of sandfly breeding sites and using insecticides helps control the disease. This is done through community efforts, like public health campaigns and vector control. By working together, we can lower leishmaniasis cases and support prevention efforts.
Complications and Long-term Effects
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a skin infection caused by a parasite. If not treated, it can cause serious problems. Disfiguring scars are a common issue, affecting both looks and mental health.
Some possible complications and long-term effects include:
- Secondary infections, which can make the condition worse
- Psychological distress, like anxiety and depression
- In rare cases, it can turn into more serious forms, like mucocutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis
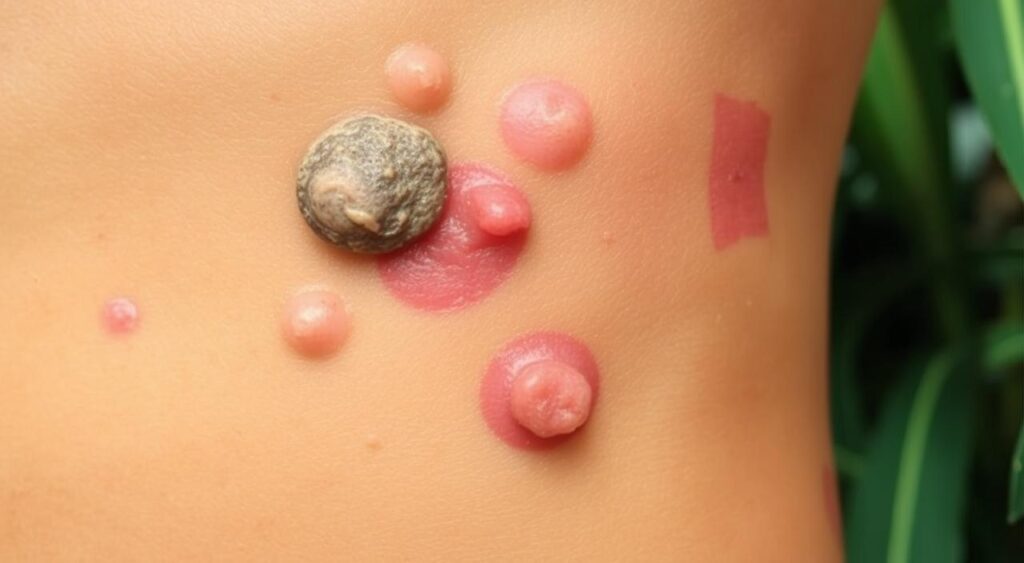
It’s important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Early treatment can prevent long-term issues and reduce risks. By understanding these effects, people can better manage their condition and improve their life quality.
Living with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Dealing with leishmaniasis can be tough, but it’s possible to manage it. By making lifestyle changes and using support resources, patients can live with it. They need to adjust their daily life to avoid making symptoms worse and to prevent spreading the disease.
Healthcare providers, support groups, and educational materials are key in managing the disease. Patients can learn how to care for their skin lesions and avoid scratching them. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is also important. Counseling and emotional support help deal with the disease’s psychological effects.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Avoiding activities that may exacerbate the condition, such as excessive heat or cold
- Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, to prevent sandfly bites
- Using insect repellents and applying them regularly
Support Resources
Support groups and online forums offer a sense of community for those with cutaneous leishmaniasis. They provide advice, emotional support, and a place to share experiences. Healthcare providers also offer guidance on treatment, disease management, and prevention.
By adjusting their lifestyle and using support resources, people with leishmaniasis can manage their condition better. It’s crucial to work with healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan. Staying updated with the latest research and medical advances is also important.
Latest Research and Medical Advances
Researchers are always working to find better treatment for leishmaniasis and ways to prevent it. They are looking into new medicines, better ways to diagnose the disease, and new methods to control the sandflies that spread it.
Some of the latest advances in the field include:
- Development of new medications with improved efficacy and reduced side effects
- Improved diagnostic techniques, such as molecular testing and imaging
- Innovative approaches to vector control, such as genetically modified sandflies
Keeping up with the latest research gives hope to patients and healthcare workers. It opens up new ways to manage and maybe even get rid of the disease.
As research keeps moving forward, it’s key to stay informed about treatment for leishmaniasis and leishmaniasis prevention. This way, we can work towards a future where this disease is no longer a big problem.
| Research Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Treatments | Development of new medications with improved efficacy and reduced side effects |
| Diagnostic Methods | Improved diagnostic techniques, such as molecular testing and imaging |
| Vector Control | Innovative approaches to vector control, such as genetically modified sandflies |
Conclusion
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a big health problem in warm and tropical areas. The skin parasite infection from sandfly disease is common there. Knowing about the disease and how to prevent it is key to controlling it.
By learning and taking steps to prevent it, people can lower their risk of getting cutaneous leishmaniasis. New research and treatments give hope for beating this disease. It’s important for doctors, leaders, and everyone to join forces to fight skin parasite infection and help those with sandfly disease.
FAQ
Q: What is Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: Cutaneous Leishmaniasis is a skin infection caused by a parasite. It spreads through the bite of an infected sandfly.
Q: Where is Cutaneous Leishmaniasis found?
A: It’s found in many parts of the world. This includes tropical and subtropical regions.
Q: How is Cutaneous Leishmaniasis transmitted?
A: It’s spread by the bite of an infected sandfly. This sandfly carries the Leishmania parasite.
Q: What are the symptoms of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: Symptoms include painful skin lesions that can scar. You might also feel fever, swelling, and redness.
Q: How is Cutaneous Leishmaniasis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use physical exams, lab tests, and biopsies to diagnose it. This helps find the parasite.
Q: What are the treatment options for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: Treatments vary based on the disease’s severity. Options include medicines, local treatments, and systemic methods.
Q: How can Cutaneous Leishmaniasis be prevented?
A: Prevention involves personal and environmental steps. Use repellents, wear protective clothes, and control sandfly breeding sites.
Q: What are the potential complications of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: Complications include disfiguring scars and secondary infections. It can also cause psychological distress and lead to more severe forms of the disease.
Q: What support resources are available for people living with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: Support includes healthcare, support groups, and educational materials. These help patients manage symptoms and cope with the disease.
Q: What are the latest research and medical advances in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis?
A: New research aims to improve treatments and prevention. This includes better medicines, diagnostic tools, and ways to control sandflies.
