Understand and manage diabetes mellitus with our comprehensive guide on symptoms, causes, and treatments.
This chronic condition affects how our bodies turn food into energy. Keeping blood sugar levels in check is key to managing it. A careful diet and lifestyle changes are needed to stay healthy.
It’s important to understand diabetes mellitus to manage it well. This article will cover symptoms, causes, and treatments. We’ll also talk about the role of diet in managing diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes mellitus is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
- Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in diabetes management.
- A diabetic diet is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
- Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is vital for effective management.
- Lifestyle adjustments are necessary to manage diabetes mellitus.
- Managing blood sugar levels is critical to preventing complications.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a long-term health issue that affects how the body handles blood sugar. It causes high blood sugar levels, which can lead to serious problems if not treated. This condition often comes with insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin.
Because of insulin resistance, the body might make more insulin. This can increase the risk of getting type 2 diabetes. If not managed, type 2 diabetes can cause hyperglycemia, where blood sugar gets too high. This can harm organs and tissues.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Diabetes mellitus is a complex issue that involves many factors like genetics, lifestyle, and environment. Knowing what diabetes is and its basics is key to managing it well.
The Role of Insulin
Insulin is vital for controlling blood sugar levels. It helps cells take in glucose, lowering blood sugar and preventing hyperglycemia. In people with insulin resistance, cells don’t respond well to insulin. This leads to high blood sugar levels and a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Diabetes can greatly affect blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can damage kidneys, nerves, and eyes. It’s crucial to manage blood sugar levels to avoid these complications and prevent long-term harm.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
Diabetes is a complex condition that can show up in many ways. Increased thirst and urination are common signs, as the body tries to get rid of extra glucose. Other symptoms include fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If not treated, diabetes can cause serious diabetes complications, affecting a person’s quality of life.
Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds
It’s crucial to notice these symptoms and get medical help if they don’t go away. Unmanaged diabetes can lead to hypoglycemia, a dangerous drop in blood sugar levels. This can be deadly if not treated quickly.
Early detection and treatment of diabetes can prevent diabetes complications and improve health. Knowing the common signs and symptoms of diabetes is the first step. It helps manage the condition and lowers the risk of hypoglycemia and other serious issues.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders with high blood sugar levels. There are several types, each with its own causes and risk factors. Knowing these types is key for effective management and treatment.
The main types include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and prediabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common, making up about 90% of all diabetes cases. It’s often linked to lifestyle factors like a sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet.
Gestational diabetes happens during pregnancy, usually in the second or third trimester. It’s caused by hormonal changes and insulin resistance. Prediabetes is when blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diabetes. If not treated, prediabetes can turn into type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: an autoimmune disease that destroys insulin-producing cells
- Type 2 diabetes: a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion
- Gestational diabetes: a condition that occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes and insulin resistance
- Prediabetes: a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes
Each type of diabetes mellitus needs a unique approach to management and treatment. By understanding the causes and risk factors of each type, individuals can take steps to prevent or manage the condition. This reduces the risk of complications and improves overall health.
Risk Factors and Causes
It’s important to know the risk factors and causes of diabetes. This knowledge helps in preventing and managing the condition. Diabetes mellitus is a complex condition. It is influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
These factors can lead to insulin resistance. This is when the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin. As a result, blood sugar levels rise.
Some key risk factors for diabetes include:
- Family history: Having a family history of diabetes increases your risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight, especially around the belly, raises your risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Physical inactivity: Not being active can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Diet: Eating too much sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can increase your risk of diabetes.
Environmental factors, like air pollution and certain chemicals, can also play a role. Certain medical conditions, like high blood pressure and high cholesterol, can raise your risk of diabetes.
Knowing the risk factors and causes of diabetes helps you take steps to prevent or manage it. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help control blood sugar levels and prevent insulin resistance.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic factors | Family history of diabetes |
| Lifestyle factors | Obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet |
| Environmental factors | Exposure to air pollution, certain chemicals |
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Diagnosing diabetes mellitus requires several tests to check blood sugar levels. The main tests are the A1C test, fasting plasma glucose test, and oral glucose tolerance test.
These tests measure glucose in the blood. This helps doctors find out if someone has diabetes mellitus. The A1C test, for instance, shows average blood sugar levels over 2-3 months.
Here are the main tests for diabetes mellitus diagnosis:
- A1C test
- Fasting plasma glucose test
- Oral glucose tolerance test
Doctors use these tests to see if someone has diabetes mellitus. They then create a treatment plan to control blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels is key for people with diabetes. It’s important to monitor blood glucose levels often. This helps see how diet and exercise impact them. A diabetic diet is crucial in keeping blood sugar stable, avoiding hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
To manage blood sugar well, knowing target ranges is essential. It’s also important to recognize hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia signs. This knowledge lets people act fast when blood sugar is off, lowering risk of problems. A good diabetic diet helps keep blood sugar steady, preventing hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.

- Regular blood glucose monitoring
- Understanding target ranges for blood sugar levels
- Recognizing the signs of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia
- Following a well-planned diabetic diet
By using these strategies, people with diabetes can manage their blood sugar. This reduces the risk of complications and improves health.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing diabetes mellitus requires a mix of medication, lifestyle changes, and constant monitoring. For those with type 1 or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is key to control blood sugar. This might mean daily injections or using an insulin pump.
A diabetic diet is also vital. It should be balanced, low in sugars, fats, and salt, and rich in fiber, fruits, and veggies. For those with prediabetes, a healthy diet and more exercise can stop type 2 diabetes from developing.
Regular exercise is also crucial. It includes aerobic activities like walking or cycling, and strength training. A healthy diet, exercise, and insulin therapy (if needed) help manage diabetes well. This reduces the risk of serious problems.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly
- Take medication as prescribed
- Eat a balanced diabetic diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
By sticking to these strategies, people with diabetes can live active, healthy lives. It’s important to work with a healthcare team to create a treatment plan that fits your needs and goals.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Keeping blood sugar levels in check is key to avoiding diabetes complications. Uncontrolled blood sugar can cause serious problems like heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. To avoid these issues, it’s vital to live a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating right and staying active.
Here are some ways to stop diabetes complications:
- Check your blood pressure and cholesterol regularly
- Stop smoking and drink less alcohol
- Eat a diet that’s low in sugar and saturated fats
- Do regular exercise like walking or swimming
By following these tips, people with diabetes can lower their risk of complications. It’s also crucial to work with a healthcare team. They can help create a plan to manage blood sugar and prevent complications.
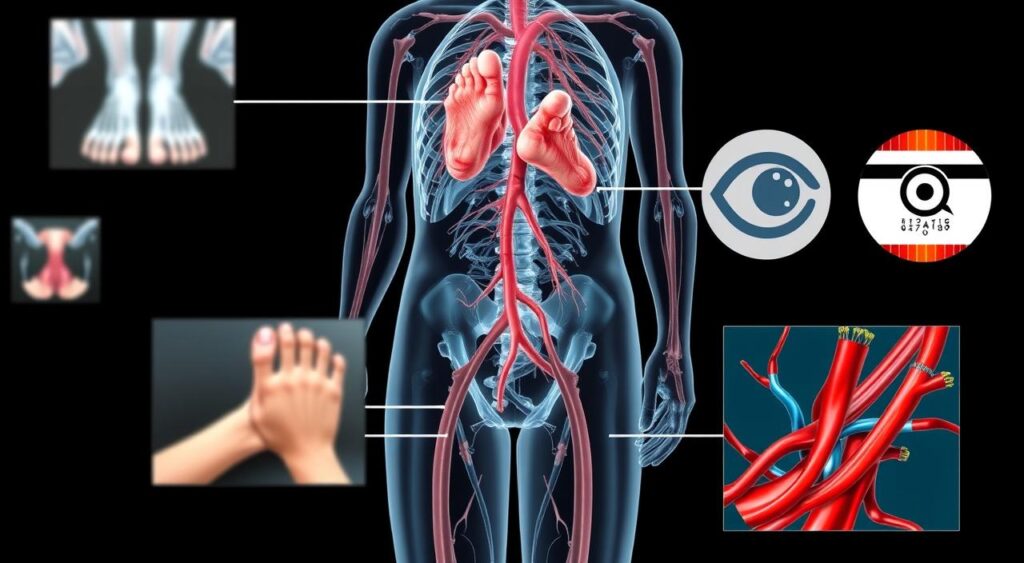
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are also important. They can spot problems early and treat them quickly. By focusing on your health and taking action, people with diabetes can live a long, healthy life. They can avoid the dangers of diabetes complications.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | High blood sugar can harm blood vessels and nerves, raising heart disease risk. |
| Kidney Damage | Diabetes can harm the kidneys’ filters, leading to kidney failure and dialysis or transplant needs. |
| Nerve Damage | High blood sugar can damage nerves, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in hands and feet. |
Conclusion: Living Well with Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a complex condition that needs careful management to stay healthy. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and types of diabetes helps people manage it well.
Medication, insulin therapy, healthy eating, and exercise are key. They help control blood sugar and lower the risk of serious problems. Working closely with doctors is also crucial for managing type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.
With the right approach and self-care, people with diabetes can live well. A balanced lifestyle, staying informed, and managing the condition are important. This way, they can enjoy a good quality of life despite the disease.
FAQ
Q: What is diabetes mellitus?
A: Diabetes mellitus is a long-term health issue. It affects how your body turns food into energy. It happens when your body can’t make or use insulin well, causing high blood sugar.
Q: How does insulin work and impact blood sugar levels?
A: Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. It helps your body use glucose from the blood. Without enough insulin, or if your body can’t use it, blood sugar levels rise.
Q: What are the common signs and symptoms of diabetes?
A: Signs of diabetes include feeling very thirsty and needing to pee a lot. You might also feel tired, see things less clearly, and cuts take longer to heal. If not treated, diabetes can damage nerves and increase the risk of low blood sugar.
Q: What are the different types of diabetes mellitus?
A: There are several types of diabetes. Type 1 is an autoimmune disease. Type 2 is often linked to lifestyle choices. Gestational diabetes happens during pregnancy, and prediabetes is a warning sign for type 2 diabetes.
Q: What are the risk factors and causes of diabetes?
A: Diabetes can be caused by genetics, lifestyle, and environment. These factors can make your body resistant to insulin, affecting blood sugar levels.
Q: How is diabetes mellitus diagnosed and tested?
A: Doctors use tests like the A1C test to diagnose diabetes. These tests check your blood sugar levels. They help find out if you have diabetes or are at risk.
Q: How can I manage my blood sugar levels?
A: Managing blood sugar involves regular checks and knowing your target ranges. It’s also important to recognize high and low blood sugar signs. Eating right and staying active are key to managing blood sugar.
Q: What are the treatment options and management strategies for diabetes?
A: Treatment for diabetes includes medication, insulin, and lifestyle changes. These help manage the condition, prevent complications, and can even stop type 2 diabetes in its tracks.
Q: How can I prevent diabetes complications?
A: To avoid complications, manage your blood sugar, check your blood pressure and cholesterol, and live a healthy lifestyle. This helps prevent heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
