Empyema is a serious medical condition that affects over more people. It leads to major respiratory problems and can be life-threatening in severe cases. This article will delve into the causes, importance, and latest treatments for empyema. It aims to give readers a better grasp of this critical health issue.
Empyema is a serious lung infection. It happens when pus builds up between the lungs and the chest wall. This buildup can be dangerous and puts a lot of strain on the lungs. Knowing what causes it and its stages is key to managing and preventing it.
Key Takeaways
- Empyema is a serious lung infection that leads to the accumulation of pus between the lungs and chest wall
- It affects more people all over world , with significant respiratory consequences
- Identifying the root causes and risk factors is essential for effective treatment and prevention
- A comprehensive understanding of the condition’s stages and available treatment options is crucial for healthcare providers
- Advancements in diagnostic procedures and surgical interventions have improved outcomes for patients with empyema
What is Empyema and Its Clinical Significance
Empyema is a serious condition where the space between the lungs and chest wall gets infected. It’s filled with pus. This can greatly affect breathing and overall health.
Definition and Basic Pathophysiology
Empyema means pus in the pleural space, which should be clean. It can come from bacteria, fungi, or parasites. The body’s fight against infection leads to pus buildup, making the pleural surfaces thick and inflamed.
Impact on Respiratory Health
Empyema can severely affect breathing. The pus and thickened surfaces make it hard for lungs to expand. This causes breathing problems, chest pain, and less lung capacity. Without treatment, it can lead to lung collapse or respiratory failure.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
People with empyema may have fever, cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. They might also feel tired or lose appetite. Seeing a doctor quickly is key to treating empyema and avoiding serious issues.
The Connection Between Pleural Effusion and Empyema
Pleural effusion and empyema are closely related and can harm your breathing. Pleural effusion is when fluid builds up in the pleural space. This can lead to empyema, a serious condition with pus in the pleural cavity.
Parapneumonic effusions are a big worry because they can turn into empyema if not treated. These start as fluid buildup but can get infected, turning into pus and empyema.
| Condition | Description | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Pleural Effusion | Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space | Can lead to empyema if left untreated |
| Empyema | Presence of pus in the pleural cavity | Respiratory distress, lung damage, and potentially life-threatening if not properly managed |
It’s key to understand the link between pleural effusion and empyema. Early treatment can stop empyema from getting worse. This is important because empyema can be very serious if not treated right.
By spotting the signs of pleural effusion early and getting medical help, you can stop empyema from happening. This helps keep your lungs healthy and working well.
Risk Factors and Common Causes of Empyema
Empyema is a serious lung infection where pus builds up in the pleural space. It can happen for many reasons. Knowing what causes it helps us prevent and treat it better.
Primary Medical Conditions Leading to Empyema
Some health issues can make you more likely to get empyema. These include:
- Pneumonia, especially from Streptococcus pneumoniae or Staphylococcus aureus
- Lung abscesses or other lung infections
- Thoracic trauma or surgery, like from a car accident or a lung biopsy
- Malignancies, including lung cancer and metastatic cancers
- Chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and liver or kidney disease
Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors
Other factors can also raise your risk of getting empyema:
- Smoking, which weakens the lungs and makes them more prone to infections
- Excessive alcohol consumption, which can weaken the immune system
- Poor hygiene or living in unsanitary conditions, which can lead to bacterial infections
- Exposure to hazardous materials or pollutants, which can harm the lungs and respiratory system
Population Groups at Higher Risk
Some groups are more likely to get empyema, including:
- Older adults, especially those with health issues
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, like those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing cancer treatment
- People with chronic respiratory diseases like COPD or asthma
- Individuals with a history of previous lung infections or pleural effusions
Knowing the risk factors and causes of empyema helps doctors spot high-risk people. They can then take steps to prevent this serious lung infection.
Diagnostic Procedures for Empyema
Diagnosing empyema, a serious condition, needs a detailed approach. Thoracentesis, a simple procedure, is key in finding the cause and planning treatment.
A healthcare provider uses a thin needle to take a sample of fluid from between the lungs and chest wall. This fluid is then checked in a lab for signs of bacteria, blood cells, and other markers. These signs help confirm if empyema is present.
- Imaging like X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds help see the pleural space. They show where and how big the fluid buildup is.
- Laboratory tests, including cell counts and chemistry analyses, give insights into the fluid. They help tell if it’s related to empyema.
- At times, a thoracoscopy is done. This involves a small camera in the chest to look at the space and take tissue samples.
Using these tools, doctors can accurately find empyema. They then create a treatment plan to tackle the cause and manage any complications.
| Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Thoracentesis | Fluid extraction and analysis to identify the presence of empyema |
| Imaging (X-ray, CT, Ultrasound) | Visualization of the pleural space and location of the pleural effusion |
| Laboratory Tests | Analysis of pleural fluid characteristics to determine the nature of the effusion |
| Thoracoscopy | Direct examination and biopsy of the pleural space for further evaluation |
These detailed diagnostic methods help doctors find and treat empyema. This serious condition needs quick and right treatment to avoid more problems and keep breathing healthy.
Understanding the Stages of Empyema Development
Empyema is when pus builds up in the pleural space. It goes through three main stages. Knowing these stages helps doctors treat it better.
Exudative Phase
The first stage is the exudative phase. Here, the pleural space fills with an inflammatory fluid. This fluid can hurt lung function and cause breathing problems.
Fibrinopurulent Phase
The next stage is the fibrinopurulent phase. The fluid gets thicker and stickier, full of fibrin and pus. This makes it harder to drain and treat.
Organizing Phase
The last stage is the organizing phase. Here, the space fills with fibrous tissue. This can lead to a thick, stiff pleural peel. It can make breathing even harder and might need more serious treatments.
Doctors need to know about these stages to choose the right treatment. They might choose to manage it conservatively or go for surgery.
Conservative Treatment Approaches
Managing empyema often involves using antibiotic therapy and fibrinolytic agents. Antibiotics target the bacteria causing the infection. This is the first step in treating empyema.
Fibrinolytic therapy works by breaking down fibrin in the pleural space. This helps drain the infected fluid. This method is effective in the early stages of empyema.
The choice of treatment depends on the empyema stage, patient health, and condition severity. Conservative treatments are often chosen for patients not fit for surgery.
Advantages of Conservative Treatment
- Avoids risks of surgery
- Works well in early empyema stages
- May lead to faster recovery and shorter hospital stay
Limitations and Considerations
- Not suitable for advanced empyema cases
- May fail and require surgery
- Requires close monitoring and follow-up
Choosing conservative treatment should be done with a healthcare provider’s guidance. They assess the patient’s situation to decide the best treatment.
| Treatment Approach | Mechanism of Action | Potential Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Therapy | Targets the underlying bacterial infection | Can help resolve the infection and prevent further progression of empyema | May not be sufficient on its own for advanced cases |
| Fibrinolytic Therapy | Breaks down fibrin deposits in the pleural space | Facilitates drainage of infected fluid and can be effective in early stages | May not be suitable for all patients, and repeated administrations may be required |
Surgical Interventions and Thoracic Procedures
When treatments for empyema don’t work, surgery might be needed. Two main surgeries are used: video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and open thoracotomy.
Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
VATS is a less invasive surgery. It uses small cuts and a camera to guide the surgery. This method is chosen for its less harm, shorter stay in the hospital, and faster recovery.
VATS is good for certain types of empyema. It’s also used when the lung needs to be freed from adhesions.
Open Thoracotomy Procedures
For more serious empyema, an open thoracotomy might be needed. This surgery uses a bigger cut in the chest. It lets the surgeon directly see and work on the affected lung.
Open thoracotomy is used for severe empyema or when VATS can’t be done.
Post-Surgical Care and Recovery
After surgery, care is key for a good outcome. Patients might need chest tubes, antibiotics, and breathing therapy. These help manage pain, prevent problems, and help the lung expand.
The time to get back to normal varies. It can take weeks to months. This depends on the surgery and the patient’s health.
| Surgical Procedure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) | Minimally invasive Shorter hospital stay Quicker recovery time | Limited to less complex cases Requires specialized equipment and expertise |
| Open Thoracotomy | Allows for direct access to the pleural space Suitable for advanced-stage empyema | More invasive procedure Longer hospital stay and recovery time |
“Surgical intervention is often necessary for empyema when conservative treatments fail to resolve the condition. The choice between VATS and open thoracotomy depends on the severity and complexity of the individual case.”
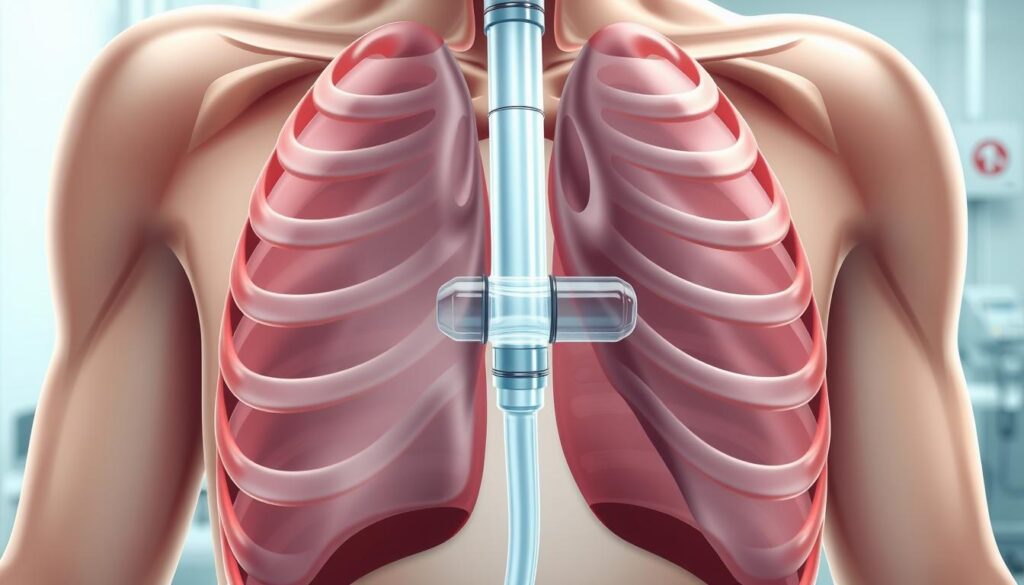
Chest Tube Drainage and Management
Empyema and complicated pleural effusions often need chest tube drainage. This procedure is key in managing these conditions. It removes fluid and controls infection.
A chest tube is inserted under local anesthesia. The tube is placed between the ribs to drain the pleural space. This helps relieve pressure and improve lung function.
Managing the chest tube is vital. The drainage must be watched closely. The fluid is checked regularly for signs of improvement or complications. The tube may stay in for days or weeks, depending on the condition and patient response.
While chest tube drainage is safe and effective, it has risks. These include pain, bleeding, infection, and lung injury. Careful monitoring and quick action are key to a good outcome.
“Chest tube drainage is a critical component in the management of empyema and complicated pleural effusions, but it requires meticulous care and diligence to ensure the best possible results for the patient.”
In conclusion, chest tube drainage is a valuable treatment for empyema and pleural effusions. Understanding the procedure and its management helps healthcare providers improve patient outcomes and support recovery.
Prevention Strategies and Long-term Outlook
Empyema is a serious lung infection that happens in the pleural space. It’s important to take steps to prevent it. Knowing how to prevent and recover from empyema can help keep your lungs healthy.
Preventive Measures
One way to fight empyema is to treat infections like pneumonia quickly. Getting vaccinated against flu and pneumococcal pneumonia can also help. Regular health check-ups and early treatment of any health issues are key.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
The time it takes to recover from empyema depends on how severe it is and the treatment. Surgery, like VATS or open thoracotomy, means a longer recovery, often weeks to months. You might need physical therapy and lung exercises to get back to normal.
Those treated with antibiotics and chest tubes might recover faster, in a few weeks to a month. It’s important to stick to your treatment plan and any lifestyle changes to avoid complications.
| Recovery Timeline | Conservative Treatment | Surgical Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Several weeks to a month | Several weeks to several months |
| Key Milestones | Antibiotics and chest tube drainage Return to normal activities | Surgical procedure (VATS or thoracotomy) Physical therapy and respiratory rehabilitation |
Understanding how to prevent and manage empyema can protect your lungs. This knowledge helps improve your life quality and health.
Recent Advances in Empyema Treatment
New breakthroughs in empyema treatment are changing how doctors handle this serious condition. These advancements include new surgical methods and better fibrinolytic agents. They are making a big difference in patient care and changing thoracic surgery.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a big step forward. It’s a less invasive way to treat empyema compared to old methods. With VATS, doctors can fix the problem through small cuts, cutting down on pain and recovery time.
The field of fibrinolytic therapy has also seen big improvements. New, stronger fibrinolytic agents can break down the tough adhesions in empyema better. This means patients often need less surgery, leading to better results.
Doctors are also trying new ways to tackle tough empyema cases. They’re using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) to get a clearer picture of the infection. This helps them create treatment plans that are just right for each patient.
These new developments in empyema treatment are promising. With ongoing research and teamwork, we can expect even better care for patients. As thoracic surgery keeps getting better, patients will have more options and better health outcomes.
Conclusion
Empyema is a serious lung infection that needs quick diagnosis and the right treatment. Knowing the causes, risk factors, and stages helps doctors treat it better.
Spotting pleural effusion early is key. It lets doctors act fast and improve patient results. With the right mix of treatments, patients can get better and avoid serious problems.
As treatments for empyema get better, it’s important for everyone to stay up to date. Patients and doctors working together can tackle this health issue. By focusing on prevention and using new treatments, we can improve life for those with empyema and keep lungs healthy.
FAQ
Q: What is Empyema?
A: Empyema is a serious condition. It happens when pus builds up in the pleural space. This is the area between the lungs and the chest wall.
Q: What causes Empyema?
A: Empyema often comes from a lung infection, like pneumonia. It can also be caused by trauma, cancer, or other health issues.
Q: What are the symptoms of Empyema?
A: Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever. You might also cough and feel tired. In bad cases, it can cause serious breathing problems.
Q: How is Empyema diagnosed?
A: Doctors use imaging tests like CT scans or ultrasounds. They also take fluid samples through thoracentesis to find Empyema and its cause.
Q: What are the treatment options for Empyema?
A: Treatment might include antibiotics and chest tube drainage. Fibrinolytic therapy and surgery, like VATS, might also be needed.
Q: How can Empyema be prevented?
A: Preventive steps include treating infections quickly and getting vaccinated. Keeping healthy and treating pleural effusions early can also help.
Q: What is the long-term outlook for patients with Empyema?
A: Most patients get better with the right treatment. But, not treating it fast enough can lead to serious problems.
Q: What are the recent advancements in Empyema treatment?
A: New treatments include better surgery methods, like VATS. There are also stronger fibrinolytic agents and new ways to handle complex cases.
