Did you know 1 in 5 people will face a coagulation disorder at some point? It’s a big deal to understand blood clotting issues. The coagulation cascade is key in making blood clots. If it goes wrong, it can cause serious health problems.
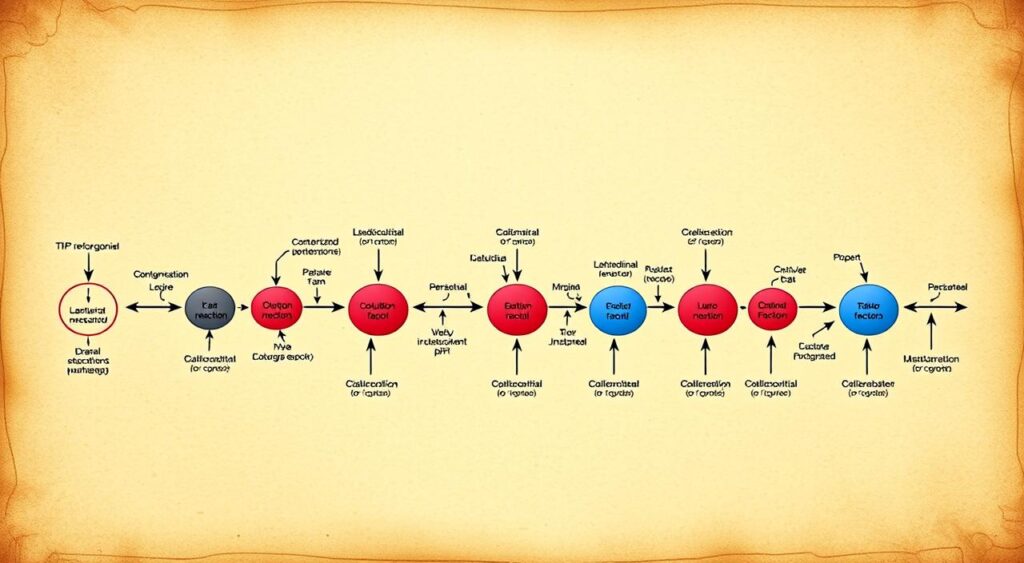
Coagulation disorders happen when blood can’t clot right. This leads to too much bleeding or clotting. The coagulation cascade is complex, involving many clotting factors. It’s important to know how it works to treat blood clotting disorders.
Key Takeaways
- Disorders of coagulation affect a significant portion of the population, emphasizing the need for awareness and education.
- Blood clotting disorders can be inherited or acquired, and understanding the coagulation cascade is vital for diagnosis and treatment.
- The coagulation cascade is a complex process involving multiple clotting factors that work together to form a blood clot.
- Coagulation disorders can lead to severe health issues, including excessive bleeding or clotting, if left untreated.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for coagulation disorders is essential for effective management and prevention.
- Early detection and diagnosis of blood clotting disorders can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life.
Understanding the Basics of Blood Coagulation
Blood coagulation is a complex process that prevents excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. At its core are platelets, which start the clotting process. Clotting factor deficiencies can disrupt this, leading to disorders.
Understanding how platelets work with other substances is key. It helps in diagnosing and managing coagulation disorders, including those related to platelet function.
The coagulation cascade is a series of chemical reactions that lead to clot formation. It involves the activation of various clotting factors. Hemostasis disorders, like those caused by clotting factor deficiencies, can disrupt this balance.
By knowing the normal hemostasis process, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage coagulation disorders. This includes those related to platelet function disorders.
The Role of Platelets in Blood Clotting
Platelets are the first to respond to a blood vessel injury. They play a critical role in starting the coagulation cascade. When a blood vessel is injured, platelets are activated.
They release chemical signals that attract other platelets and clotting factors. This leads to the formation of a blood clot, preventing excessive bleeding. However, platelet function disorders can disrupt this process, leading to bleeding or clotting complications.
Understanding the Coagulation Cascade
The coagulation cascade is a complex series of chemical reactions. It involves the activation of various clotting factors. This process can be disrupted by clotting factor deficiencies, leading to hemostasis disorders.
By understanding the coagulation cascade, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage coagulation disorders. This includes those related to platelet function disorders.
Common Disorders of Coagulation: An Overview
Coagulation disorders can be split into two main types: bleeding and clotting disorders. Bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, happen when there’s not enough clotting factors. This leads to bleeding that lasts too long or is too much. On the other hand, thrombophilia makes it easier for blood clots to form, which can be dangerous if not treated.
Von willebrand disease is another bleeding disorder. It’s caused by not having enough von Willebrand factor. People with this condition might bruise easily, get nosebleeds, or have heavy periods. Bleeding disorders can be passed down or happen later in life. Their symptoms can vary from mild to very serious.
- Thrombophilia
- Von Willebrand disease
- Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia
These conditions can really affect someone’s life. It’s very important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t go away or get worse.
| Disorder | Description |
|---|---|
| Thrombophilia | A condition characterized by an increased risk of blood clots |
| Von Willebrand disease | A bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency of von Willebrand factor |
| Bleeding disorders | Disorders that occur when there is a deficiency of one or more clotting factors |
Inherited Blood Clotting Disorders
Inherited coagulation disorders affect how blood clots. They can cause too much bleeding or blood clots. Knowing about the coagulation cascade is key for diagnosis and treatment.
The coagulation cascade involves many clotting factors. Disorders like hemophilia A and B disrupt this process. Von Willebrand disease also affects it, caused by a lack of von Willebrand factor.
Common Inherited Blood Clotting Disorders
- Hemophilia A: caused by a deficiency of clotting factor VIII
- Hemophilia B: caused by a deficiency of clotting factor IX
- Von Willebrand disease: caused by a deficiency of von Willebrand factor
- Factor V Leiden: a genetic mutation that increases the risk of blood clots
These disorders can greatly affect a person’s life. It’s important to understand them and find good treatments. Getting medical help early can prevent serious problems and improve health.
Early treatment is vital for inherited blood clotting disorders. Knowing how they affect the coagulation cascade helps manage them. This can reduce bleeding or clot risks.
| Disorder | Causes | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Hemophilia A | Deficiency of clotting factor VIII | Bleeding into joints, muscles, and internal organs |
| Hemophilia B | Deficiency of clotting factor IX | Bleeding into joints, muscles, and internal organs |
| Von Willebrand disease | Deficiency of von Willebrand factor | Nosebleeds, heavy menstrual bleeding, and bleeding into joints |
Acquired Coagulation Disorders
Acquired coagulation disorders happen later in life. They can come from another medical issue or treatment. These disorders can be caused by liver disease, kidney disease, or certain medicines. Knowing the cause is key to finding the right treatment.
These disorders can be triggered by liver disease. Liver disease can lead to a lack of clotting factors. This can make bleeding more likely, so managing the liver disease is crucial.
Some common reasons for acquired coagulation disorders include:
- Liver disease, such as cirrhosis
- Kidney disease, such as nephrotic syndrome
- Certain medications, such as anticoagulants
- Vitamin K deficiency
Managing these disorders involves treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. Working with a healthcare provider is important. They can create a treatment plan that addresses the root cause and prevents problems.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of acquired coagulation disorders helps manage them. With the right treatment and care, people with these disorders can live active and healthy lives.
| Disorder | Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Liver disease | Cirrhosis, hepatitis | Bleeding, bruising, jaundice |
| Kidney disease | Nephrotic syndrome, kidney failure | Bleeding, swelling, fatigue |
Recognizing Symptoms and Warning Signs
Coagulation disorders, like hemostasis disorders and bleeding disorders, show up in different ways. It’s key to spot the symptoms and warning signs early. This helps prevent serious problems and improves health outcomes.
People with these disorders might notice easy bruising, nosebleeds, or heavy periods. These signs can point to a bigger issue.
Knowing the difference between early signs and emergency symptoms is crucial. Early detection indicators include:
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Nosebleeds or bleeding gums
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
Emergency symptoms need quick medical help. These include severe bleeding, chest pain, or trouble breathing. If you see these signs, get help right away.
Spotting the warning signs of coagulation disorders helps manage the condition better. Being aware of symptoms and getting medical help when needed can lower risks. It also improves life quality.
| Disorder | Symptoms | Emergency Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Hemostasis disorders | Easy bruising, nosebleeds | Severe bleeding, chest pain |
| Thrombophilia | Blood clots, swelling | Difficulty breathing, chest pain |
| Bleeding disorders | Heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding gums | Severe bleeding, dizziness |
Diagnostic Approaches and Testing Methods
Diagnosing coagulation disorders needs a detailed approach. It involves different tests to see how blood clots. Knowing the coagulation cascade helps find issues with clotting factors and platelet function. Blood tests, like counts and clotting factor assays, are key to checking clotting ability.
Several tests help diagnose coagulation disorders, including:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check blood cell counts
- Prothrombin Time (PT) and Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) to check clotting factor function
- Clotting factor assays to find specific clotting factor deficiencies
Genetic testing can spot inherited coagulation disorders like hemophilia A and B, and von Willebrand disease. Imaging studies, like ultrasound and MRI, help see how much bleeding or clotting there is. By understanding the coagulation cascade and finding clotting issues, doctors can create good treatment plans.
It’s important to use a mix of these tests for accurate diagnosis and effective management of coagulation disorders. By combining these diagnostic methods, healthcare professionals can give personalized care and better patient outcomes.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment for disorders of coagulation, like blood clotting and hemostasis disorders, varies. It depends on the cause and how severe it is. Medications like clotting factor replacements are often used to manage these conditions.
Some common treatments for coagulation disorders include:
- Clotting factor replacements
- Anticoagulant medications
- Platelet transfusions
Changing your lifestyle can also help. Avoiding activities that might increase bleeding or clotting risk is key. Working closely with a healthcare provider is crucial to create a treatment plan that fits you.
Knowing about treatment options and management strategies helps those with coagulation disorders. It lets them manage their condition well and lower the risk of complications.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Clotting Factor Replacements | Medications that replace missing or defective clotting factors |
| Anticoagulant Medications | Medications that prevent blood clots from forming |
| Platelet Transfusions | Transfusions of platelets to replace missing or defective platelets |
Living with Coagulation Disorders: Lifestyle Modifications
People with thrombophilia, von Willebrand disease, or other inherited coagulation disorders need to make lifestyle changes. They should eat well and exercise regularly to lower the risk of problems.
Eating right is key to managing coagulation disorders. Foods like salmon and walnuts, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help. But, foods high in vitamin K, like leafy greens, might not be good with some medicines.
Diet and Exercise Guidelines
- Avoid foods that can increase the risk of bleeding or clotting, such as those high in sugar or saturated fats
- Incorporate physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to improve circulation and overall health
- Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized diet and exercise plan
Also, people with coagulation disorders should know what activities to avoid. This includes staying away from contact sports. Having a support system, like groups and counseling, can also help with emotional and psychological challenges.

Support Systems
Meeting others who understand what you’re going through can be very helpful. Support groups offer a sense of community and help with emotional and psychological issues.
| Support System | Description |
|---|---|
| Support Groups | Online or in-person groups where individuals can share their experiences and connect with others |
| Counseling | One-on-one therapy sessions to address emotional and psychological concerns |
Prevention and Risk Reduction Methods
Learning about the coagulation cascade is key to preventing bleeding and clotting disorders. People with bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, can avoid activities that might cause bleeding. Those with clotting disorders, such as thrombophilia, should steer clear of certain medicines or foods that might lead to clots.
Here are some ways to lower the risk of bleeding and clotting disorders:
- Avoiding contact sports or activities that may increase the risk of injury
- Taking medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Avoiding certain foods or substances that may increase the risk of clotting
- Getting regular check-ups and monitoring blood clotting factors
By following these steps, people with coagulation disorders can lower their risk of problems. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a plan that fits your needs. The coagulation cascade is complex and needs a tailored approach.
Understanding the coagulation cascade and taking preventive steps can help control health. This can improve life quality and reduce the chance of long-term harm.
Conclusion: Managing Coagulation Disorders Effectively
Managing disorders of coagulation needs a full plan. This includes diagnosis, treatment, and changes in lifestyle. Knowing the cause and how the coagulation cascade works is key. Working with a healthcare provider helps create a plan to lower risks and improve life quality.
Inherited disorders like hemophilia and von Willebrand disease need a special plan. This might include regular checks, medicine, and lifestyle changes. By being proactive and informed, people with these disorders can live full and happy lives.
Managing coagulation disorders is a long-term effort. It takes dedication, patience, and teamwork with healthcare experts. By focusing on health, people can lessen the effects of these conditions. This way, they can enjoy a better life, even with inherited disorders.
FAQ
Q: What are coagulation disorders and how do they affect the body?
A: Coagulation disorders, or blood clotting disorders, happen when the blood can’t form clots properly. This leads to too much bleeding or clotting. It makes it hard for the body to heal from injuries and raises the risk of bleeding problems.
Q: What is the coagulation cascade and how does it work?
A: The coagulation cascade is a complex process. It involves many clotting factors working together to form a blood clot. It starts when a blood vessel is injured and activates platelets and clotting factors to create a clot.
Q: What are the common types of coagulation disorders?
A: Common types include thrombophilia, von Willebrand disease, and bleeding disorders like hemophilia. These happen when there’s a lack of clotting factors or a problem with platelet function.
Q: What are the symptoms of coagulation disorders?
A: Symptoms include easy bruising, nosebleeds, heavy menstrual bleeding, and swelling. In severe cases, it can cause life-threatening bleeding or blood clots.
Q: How are coagulation disorders diagnosed?
A: Doctors use lab tests, like blood counts and clotting factor assays, and genetic testing to diagnose. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound and MRI, help check the extent of bleeding or clotting.
Q: What are the treatment options for coagulation disorders?
A: Treatment depends on the cause and severity. It may include medications like clotting factor replacements. Lifestyle changes, like avoiding activities that increase bleeding risk, are also important.
Q: Can coagulation disorders be prevented?
A: Some disorders, like bleeding disorders, can be prevented by avoiding activities that increase bleeding risk. Thrombophilia prevention involves avoiding certain medications or foods. Understanding the coagulation cascade is key to prevention and risk reduction.
Q: What are the lifestyle modifications that can help manage coagulation disorders?
A: Managing disorders includes diet and exercise guidelines and avoiding certain activities. Support groups and counseling help with the emotional and psychological aspects of living with a disorder.
Q: What is the role of inherited coagulation disorders in the development of coagulation disorders?
A: Inherited disorders, like hemophilia A and B, increase the risk of developing coagulation disorders. They are caused by a lack of clotting factors and can be passed down from parents.
Q: How do platelet function disorders affect coagulation?
A: Platelet function disorders impair clot formation. This increases bleeding risk and can be caused by medications or medical conditions.
Q: What is the relationship between coagulation disorders and hemostasis disorders?
A: Coagulation and hemostasis disorders are closely related. They both affect clot formation. Hemostasis disorders can lead to bleeding problems and are caused by various factors, including coagulation disorders and platelet function disorders.
