Explore the key details about hyperparathyroidism, including its symptoms, diagnosis process, and effective management strategies.
1 in 100 people will get hyperparathyroidism. This is when the body makes too much parathyroid hormone. This hormone helps control calcium in the blood. Too much of it can harm your health.
Hyperparathyroidism is a common condition. It’s important to know its symptoms, how to diagnose it, and how to manage it.
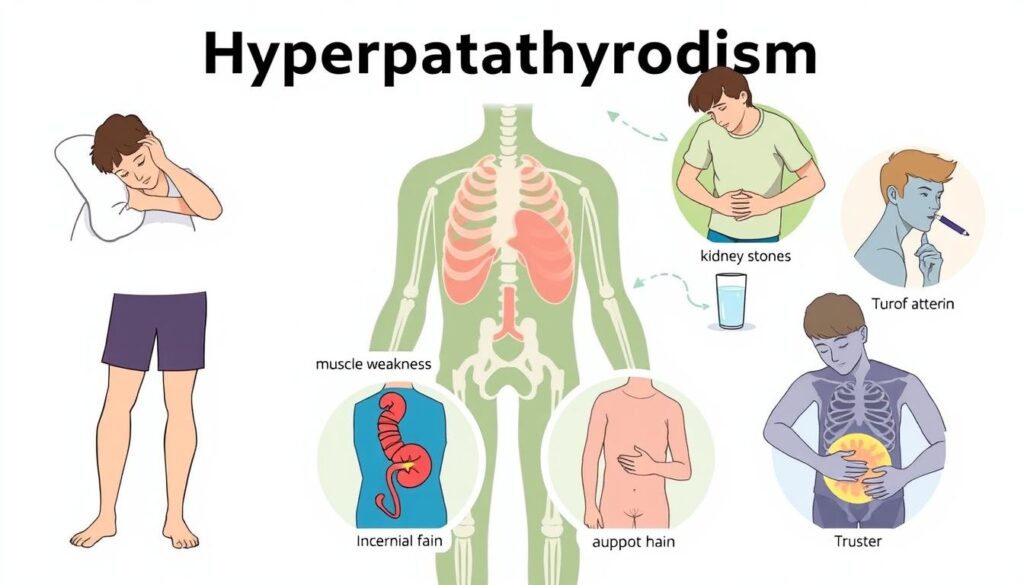
Hyperparathyroidism can cause problems like weak bones and kidney stones. Finding it early and treating it is key. Knowing the symptoms is the first step to managing it.
This article will explain hyperparathyroidism. We’ll cover its symptoms, how to diagnose it, and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Hyperparathyroidism affects 1 in 100 people, making it a relatively common condition.
- The overproduction of parathyroid hormone leads to an array of symptoms of hyperparathyroidism.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effective management of hyperparathyroidism.
- Hyperparathyroidism can lead to bone health problems and kidney stones if left untreated.
- Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for managing hyperparathyroidism.
- Recognizing the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism is vital for prompt medical attention.
What is Hyperparathyroidism?
Hyperparathyroidism happens when one or more parathyroid glands work too much. They make too much parathyroid hormone (PTH). This hormone is key for keeping calcium levels right in the blood.
The parathyroid gland helps keep calcium levels balanced. It does this by releasing calcium from bones, helping the gut absorb more calcium, and reducing urine calcium. This ensures the body has enough calcium for important functions.
When the parathyroid gland makes too much PTH, it can upset calcium levels. This leads to primary hyperparathyroidism. Symptoms include bone pain, kidney stones, and feeling very tired.
The Role of Parathyroid Glands
The parathyroid glands are four small glands near the thyroid gland in the neck. They make PTH, which controls calcium levels in the blood. These glands are crucial for keeping calcium levels stable, and any problem can cause hyperparathyroidism.
Types of Hyperparathyroidism
There are two main types of hyperparathyroidism: primary and secondary. Primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common. It’s usually caused by a benign tumor on a parathyroid gland. Secondary hyperparathyroidism happens when calcium levels are low, often due to vitamin D deficiency or chronic kidney disease.
Impact on Calcium Regulation
In hyperparathyroidism, too much PTH messes with calcium levels. This can cause problems like osteoporosis, kidney stones, and heart disease. Knowing about the parathyroid gland and the different types of hyperparathyroidism is key to diagnosing and treating it.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Hyperparathyroidism is a complex condition. It can be caused by several factors, including benign tumors on the parathyroid gland and hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands. Knowing these causes and risk factors is key for early detection and treatment.
Some common causes of hyperparathyroidism include:
- Benign tumors (adenomas) on the parathyroid glands
- Hyperplasia (an increase in the number of cells) of the parathyroid glands
- Parathyroid cancer (rarely)
Risk factors for hyperparathyroidism include a family history, radiation to the head and neck, and certain genetic disorders. Being aware of these risk factors helps individuals monitor their health and seek medical help if symptoms appear.
It’s important to recognize the signs of hyperparathyroidism and get medical help if symptoms last. By understanding the common causes and risk factors, individuals can manage their health better. They can work with their healthcare provider to create an effective treatment plan.
Recognizing the Signs of Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism shows itself in many ways. It’s key to spot its signs early for quick diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms fall into physical and mental categories. Knowing these symptoms helps in finding the right treatment.
Physical signs include bone pain, kidney stones, and stomach issues. These can start off mild but get worse if not treated. Mental symptoms like depression and fatigue are also common. If you notice any of these, seeing a doctor is important.
Physical Symptoms
- Bone pain
- Kidney stones
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal cramps
Psychological Symptoms
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Fatigue
Spotting these signs early can lead to better treatment and a better life. Knowing the symptoms and treatment options is the first step to managing the condition.
If you notice any symptoms, see a doctor right away. They can guide you to the best treatment. With the right care, you can manage hyperparathyroidism and live better.
The Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing hyperparathyroidism requires a few steps. First, a doctor will do a physical check-up and ask about your medical history. They will also run some tests to see if your parathyroid glands are making too much hormone. This hormone can upset the balance of calcium in your body.
Doctors will look for signs that might point to hyperparathyroidism. They’ll do blood tests to check your calcium and hormone levels. They might also use imaging like ultrasound or CT scans to find the parathyroid glands and see if they’re working right.
The steps to diagnose include:
- Blood tests to measure calcium and parathyroid hormone levels
- Imaging studies to locate the parathyroid glands and identify any abnormalities
- Physical examination and medical history to identify any symptoms or signs of hyperparathyroidism
It’s important for patients to know about the diagnosis process. This way, they can understand their condition better. By working with their doctor, patients can get the right diagnosis and start a treatment plan to manage their hyperparathyroidism.
In some cases, a sestamibi scan is used. It helps find the overactive parathyroid gland(s). Knowing where the problem is helps doctors choose the best treatment. This ensures patients get the care they need.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood tests | Measure calcium and parathyroid hormone levels |
| Imaging studies | Locate the parathyroid glands and identify any abnormalities |
| Physical examination and medical history | Identify any symptoms or signs of hyperparathyroidism |
Understanding Blood Tests and Imaging
Diagnosing hyperparathyroidism requires blood tests and imaging. Blood tests check calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels. High levels of these can show primary hyperparathyroidism.
Imaging, like ultrasound and CT scans, helps see the parathyroid glands. It spots any issues. Parathyroid hormone levels are also checked to confirm the diagnosis.
Here are the main tests and imaging for diagnosing hyperparathyroidism:
- Calcium level testing: measures the level of calcium in the blood
- Parathyroid hormone testing: measures the level of PTH in the blood
- Imaging techniques: such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, to visualize the parathyroid glands
Blood tests and imaging are key in diagnosing hyperparathyroidism. They help doctors see the parathyroid glands and confirm the diagnosis. This way, they can plan the best treatment.
| Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Calcium level testing | Measures the level of calcium in the blood |
| Parathyroid hormone testing | Measures the level of PTH in the blood |
| Imaging techniques | Visualize the parathyroid glands to identify abnormalities |
Treatment Options for Hyperparathyroidism
There are several treatment options for hyperparathyroidism. The main one is surgery for hyperparathyroidism, where the affected gland is removed. This is often recommended for those with symptoms or certain criteria.
When choosing a treatment, several factors are considered:
- Severity of symptoms
- Level of calcium elevation
- Bone density
- Overall health of the patient
In some cases, just watching and waiting might be the best plan. This involves checking calcium and PTH levels and bone density regularly. It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare provider about the best treatment options for you.

Knowing about surgery for hyperparathyroidism and other options helps patients make informed choices. This way, they can manage their condition more effectively.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgery | Removal of affected parathyroid gland(s) |
| Watchful Waiting | Regular monitoring of calcium and PTH levels, and assessment of bone density |
Surgical Management Approaches
Surgery is a common treatment for hyperparathyroidism when meds don’t work. The main goal is to remove the overactive parathyroid gland causing the issue. There are two main ways to do this: minimally invasive surgery and traditional methods.
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery, like focused parathyroidectomy, is preferred. It uses smaller incisions, causes less pain, and has a quicker recovery. This method is chosen when the affected gland is clearly seen on imaging tests.
Traditional Surgical Methods
Traditional surgery involves a bigger incision in the neck. It’s used when the gland’s location is unclear or when more than one gland is affected.
After surgery, patients must watch their calcium levels to make sure they’re normal. It’s also important to manage any complications, like low calcium levels. The parathyroid gland helps control calcium, and surgery aims to balance this.
Talking to a healthcare professional is key to figuring out the best surgery for hyperparathyroidism.
Medication and Non-Surgical Treatments
For those with hyperparathyroidism who can’t or don’t want to have surgery, there are other treatment options. These non-surgical methods can help control the condition and ease symptoms.
Some medications used include:
- Cinacalcet to lower parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels
- Bisphosphonates to improve bone density
- Calcimimetics to reduce PTH secretion
It’s also important to get enough vitamin D and calcium. These non-surgical treatments are often for patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism or those with primary hyperparathyroidism who are not showing symptoms. By looking into these treatment options, people with hyperparathyroidism can manage their condition better and live a better life.
Living with Hyperparathyroidism
Managing daily life with hyperparathyroidism means making some changes. You need to balance your calcium and vitamin D intake. Also, making lifestyle changes can improve your health.
People living with hyperparathyroidism must watch their parathyroid hormone and calcium levels. This helps avoid serious problems. Regular visits to your doctor are key to keep your treatment on track.
Dietary Considerations
- Maintaining adequate calcium and vitamin D intake
- Possibly limiting calcium-rich foods if calcium levels are very high
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular exercise to improve bone density and overall health
Regular Monitoring
It’s important to regularly check your calcium and parathyroid hormone levels. Also, bone density tests are crucial. By making these changes and staying informed, you can manage living with hyperparathyroidism well. This can greatly improve your life quality.

Prevention and Long-term Management
Effective prevention and long-term management of hyperparathyroidism are key to avoiding complications. Regular health check-ups, monitoring of calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, and a healthy lifestyle are vital. These steps are crucial for managing the condition over time.
Some important strategies for prevention and long-term management include:
- Early detection and treatment to reduce the risk of long-term complications
- Regular monitoring of calcium and PTH levels to ensure effective management
- Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle to support overall well-being
Studies have shown that good long-term management can greatly improve outcomes. It can also lower the risk of problems like osteoporosis, kidney stones, and heart disease. By focusing on prevention and long-term management, patients with hyperparathyroidism can live active and healthy lives.
It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to create a personalized plan for prevention and long-term management. This way, patients can actively manage their condition and lower the risk of future complications.
| Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular monitoring of calcium and PTH levels | Ensures effective management and reduces the risk of complications |
| Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle | Supports overall well-being and reduces the risk of long-term complications |
Complications if Left Untreated
Hyperparathyroidism can cause serious problems if not treated early. One major issue is bone health issues, like osteoporosis, which raises the chance of fractures. This happens because too much calcium in the blood weakens bones.
Another concern is kidney problems, such as kidney stones or chronic kidney disease. High calcium levels can also harm the heart, leading to high blood pressure and heart disease. Knowing these risks is key to managing hyperparathyroidism and avoiding serious damage.
Bone Health Issues
- Osteoporosis, increasing the risk of fractures
- Pain and discomfort in the bones and joints
- Decreased bone density, making bones more susceptible to breaks
Kidney Problems
- Formation of kidney stones
- Development of chronic kidney disease
- Increased risk of kidney failure
It’s vital to know the risks of hyperparathyroidism to act quickly and avoid long-term harm. By understanding these risks, people can take steps to manage their condition and lower the chance of these problems.
Conclusion
Hyperparathyroidism is a complex condition that needs a careful approach to diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and effects helps people take charge of their health. They can work closely with their doctors to manage it well.
Early detection and proper diagnosis are key. They help doctors create a personalized management plan for each patient. This plan might include surgery, medication, diet changes, and lifestyle adjustments. The goal is to balance the body and improve overall health.
It’s important to stay informed and advocate for your health. Keeping open communication with doctors is crucial. By educating patients and working together, we can help those with hyperparathyroidism manage their condition. This way, they can live happy and fulfilling lives.
FAQ
Q: What is hyperparathyroidism?
A: Hyperparathyroidism is when the parathyroid glands make too much hormone. This hormone helps control calcium in the blood.
Q: What are the types of hyperparathyroidism?
A: There are two main types. Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by a tumor on a gland. Secondary hyperparathyroidism happens when calcium levels are low, often due to vitamin D deficiency or kidney disease.
Q: What are the common causes and risk factors for hyperparathyroidism?
A: Common causes include tumors, gland cell increase, and rare cancer. Risk factors include family history, head and neck radiation, and genetic disorders.
Q: What are the symptoms of hyperparathyroidism?
A: Symptoms include bone pain, kidney stones, and mood swings. Other signs are nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
Q: How is hyperparathyroidism diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam, medical history, and blood tests. Imaging like ultrasound or CT scans also help find gland issues.
Q: What are the treatment options for hyperparathyroidism?
A: Surgery to remove glands is the main treatment. Medications can also help. For mild cases, watching closely is an option.
Q: What are the potential complications of untreated hyperparathyroidism?
A: Untreated cases can cause osteoporosis, kidney stones, and kidney disease. They also raise heart disease risks.
Q: How can hyperparathyroidism be prevented and managed long-term?
A: Managing it involves surgery, medication, or both. Regular blood tests and a healthy lifestyle are key. Treating underlying conditions also helps.
