Did you know 1 in 100 people will get hyperparathyroidism? It’s a condition where the parathyroid gland makes too much hormone. This messes up the body’s calcium balance. The parathyroid gland is key to keeping calcium levels right. Any problem here can hurt your bones and overall health.
Hyperparathyroidism messes with the parathyroid gland’s job. This gland keeps calcium levels in check. Calcium is important for strong bones, teeth, and muscles. Knowing about hyperparathyroidism helps keep you healthy, especially when it comes to calcium and bones.
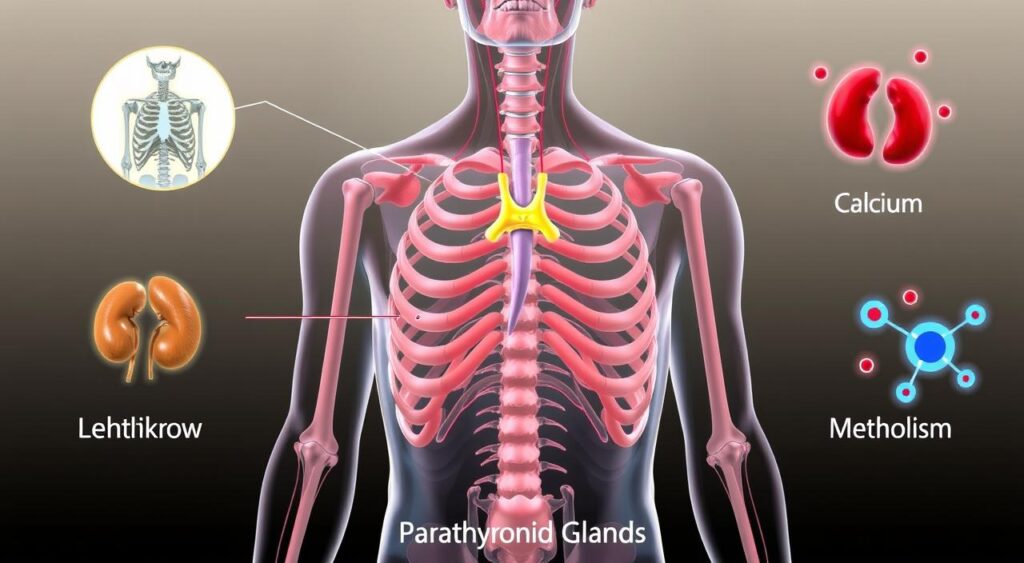
Ignoring hyperparathyroidism can lead to big problems. It’s important to spot its signs and symptoms. By understanding hyperparathyroidism, you can manage it better. This helps avoid serious damage to your parathyroid gland and calcium balance.
Key Takeaways
- Hyperparathyroidism affects 1 in 100 people, making it a relatively common condition.
- The parathyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating calcium levels in the body.
- Understanding hyperparathyroidism is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing long-term damage.
- Hyperparathyroidism can have significant effects on the body’s calcium balance and bone health.
- Recognizing the signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism is vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Proper management of hyperparathyroidism can help prevent long-term consequences and improve overall health.
Understanding Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition that affects the parathyroid gland. It leads to high calcium levels in the blood. The parathyroid gland is key in keeping calcium levels right. Its problems can cause bone loss.
The parathyroid gland makes parathyroid hormone (PTH). This hormone helps control calcium levels. If the gland makes too much PTH, calcium levels rise, and bones can weaken.
What is the Parathyroid Gland?
The parathyroid gland is small and located in the neck. It’s near the thyroid gland. It’s vital for keeping calcium levels healthy.
Role of Calcium Regulation
Calcium is important for strong bones, teeth, and muscles. The parathyroid gland helps manage calcium levels. It does this by making PTH, which helps release calcium from bones and improves its absorption from food.
Types of Hyperparathyroidism
There are several types of hyperparathyroidism. Primary hyperparathyroidism is the most common. It happens when one or more parathyroid glands work too much. Secondary hyperparathyroidism occurs when the gland works too much because of low calcium or vitamin D. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism happens when the gland works too much due to long-term low calcium or vitamin D.
Knowing the different types of hyperparathyroidism is key to effective treatment. It helps prevent serious problems like bone loss. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can help avoid severe consequences.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Primary hyperparathyroidism is a common endocrine disorder. It affects the parathyroid glands, which are key in regulating calcium levels. When these glands work too hard, they make too much parathyroid hormone. This leads to primary hyperparathyroidism.
Genetic disorders, like multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1, and radiation exposure are common causes. Women are also more likely to get it, especially after menopause.
- Family history of primary hyperparathyroidism
- Previous radiation therapy to the head or neck
- Presence of other endocrine disorders
Knowing the causes and risk factors is key for early diagnosis and treatment. Primary hyperparathyroidism is an endocrine disorder. It needs a detailed treatment plan to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Hyperparathyroidism shows up in many ways, making it key to spot them early. This condition often leads to high calcium levels in the blood. Symptoms include bone pain, kidney stones, and a higher chance of breaking bones.
It also affects your mind and feelings, like feeling down, tired, and having trouble focusing. Knowing these signs is important. A doctor can check these symptoms and run tests to find out if you have hyperparathyroidism.
Physical Symptoms
- Bone pain and osteoporosis
- Kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
- Increased risk of fractures
Mental and Emotional Signs
- Depression and anxiety
- Fatigue and weakness
- Difficulty concentrating and memory loss
Spotting the signs of hyperparathyroidism and knowing about high calcium risks is crucial. It helps people get medical help fast. This can stop serious problems and make treatment better.
Diagnosis Process and Testing
Diagnosing hyperparathyroidism involves several tests. These tests check the blood levels of calcium and parathyroid hormone. Testing for hyperparathyroidism starts with a physical check-up and looking at the patient’s health history. Blood tests then measure calcium, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone levels.
High levels of parathyroid hormone and calcium in the blood usually confirm hyperparathyroidism. Sometimes, imaging like ultrasound or CT scans help find and check the parathyroid glands. Here are some important tests:
- Blood tests to measure calcium, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone levels
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans to locate the parathyroid glands
- Urinalysis to measure the level of calcium in the urine
During the diagnosis process, patients go through many tests. It’s key to work with a healthcare provider to find the right treatment for hyperparathyroidism.
Knowing about the diagnosis and testing for hyperparathyroidism helps patients manage their condition. It’s important to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve health outcomes.
Treatment Options for Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism treatment varies based on the condition’s severity and the patient’s health. The main aim is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance quality of life. Treatment options include surgery, medication, and lifestyle changes.
For those with severe hyperparathyroidism, parathyroid surgery might be needed. This surgery removes the affected gland. It helps reduce symptoms and prevents long-term issues.
Surgical Interventions
- Removal of the affected parathyroid gland
- Minimally invasive surgery for reduced recovery time
- Monitoring for potential complications
Medication Management
Medications can help manage symptoms like calcium levels and bone density. It’s crucial to regularly check treatment effectiveness and watch for any signs of problems.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Parathyroid Surgery | Removal of the affected gland |
| Medication Management | Management of symptoms and calcium levels |
Complications and Long-term Effects
Hyperparathyroidism can cause serious problems if not treated. These include osteoporosis, kidney stones, and heart disease. These complications of hyperparathyroidism can greatly affect a person’s life.
Some long-term effects of hyperparathyroidism are:
- Osteoporosis, which makes bones more likely to break
- Kidney stones, causing severe pain and other symptoms
- Cardiovascular disease, raising the risk of heart attack and stroke
Getting an early diagnosis and treatment is key to avoiding these complications of hyperparathyroidism. Knowing the long-term effects helps people manage their symptoms. It also helps them lower their risk of these complications.
Working closely with a healthcare provider is crucial. They can help create a treatment plan that meets your specific needs. This plan aims to reduce the risk of complications of hyperparathyroidism.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | A condition characterized by brittle and porous bones |
| Kidney Stones | Small, hard deposits that can cause severe pain and other symptoms |
| Cardiovascular Disease | A condition that can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke |
Living with Hyperparathyroidism
Managing hyperparathyroidism is key to a good life. Effective management means eating right, living smart, and exercising well. These steps help control symptoms and avoid serious problems.
It’s crucial to know about calcium and vitamin D when living with hyperparathyroidism. Eating foods high in these nutrients helps keep hormone levels in check. Drinking plenty of water and cutting down on alcohol also helps with symptoms.
Dietary Considerations
- Eat foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and leafy greens
- Include vitamin D-rich foods, such as fatty fish and fortified dairy products
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid sugary drinks
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle can also help manage hyperparathyroidism. Stress-reducing activities like meditation and yoga are helpful. So is getting enough sleep. Regular, gentle exercise, like walking or swimming, boosts health and happiness.
Exercise Guidelines
Exercise is vital for managing hyperparathyroidism. Gentle activities, like yoga or tai chi, improve balance and flexibility. Avoiding hard activities that strain bones and joints is also important.
By following these tips and working with a healthcare provider, you can manage hyperparathyroidism well. This approach helps reduce symptoms and prevents serious issues. With the right living with hyperparathyroidism and management strategies, a better life is possible.
| Dietary Considerations | Lifestyle Modifications | Exercise Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium and vitamin D intake | Stress management and sleep schedule | Gentle exercises, such as yoga or tai chi |
| Hydration and limited alcohol consumption | Regular exercise and physical activity | Avoid high-impact activities |
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Hyperparathyroidism can’t always be stopped, but there are ways to lower your risk. Prevention steps include eating well, drinking lots of water, and avoiding some medicines that raise calcium levels.
To lower your risk of hyperparathyroidism, try these:
- Eat a balanced diet full of calcium and vitamin D
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Stay away from medicines like lithium that can raise calcium levels
By following these tips, you can help reduce the risk of hyperparathyroidism and stay healthy. Always talk to your doctor for advice on prevention and how to lower your risk.

Early detection and treatment are key for better outcomes with hyperparathyroidism. By focusing on prevention and taking steps to reduce the risk of hyperparathyroidism, you can manage your health and well-being.
| Prevention Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Maintaining a healthy diet | Reduces risk of hyperparathyroidism |
| Staying hydrated | Helps regulate calcium levels |
| Avoiding certain medications | Decreases risk of increased calcium levels |
Support Resources and Patient Care
Living with hyperparathyroidism can be tough. Having the right support is key to managing it. Support for hyperparathyroidism patients is out there, through healthcare providers, support groups, and online communities.
Finding the right medical care is crucial. Look for healthcare providers who know a lot about endocrine disorders. They can give you personalized care and advice on handling hyperparathyroidism. Here are some ways to find them:
- Ask your primary care doctor or other healthcare pros for recommendations.
- Check with groups like the Endocrine Society for specialists in your area.
- Search online for doctors who focus on endocrine disorders.
Support groups and online communities also offer help. They let you connect with others who understand what you’re going through. You can get valuable tips and advice from people who live with the condition.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Hyperparathyroidism Support Group | A online community for people living with hyperparathyroidism to connect and share their experiences |
| Endocrine Society | A professional organization that provides information and resources on endocrine disorders, including hyperparathyroidism |
By using these resources, people with hyperparathyroidism can get the support they need. This can help them manage their condition better and improve their health and happiness.
Conclusion: Managing Your Parathyroid Health
Hyperparathyroidism is a complex condition that needs careful attention. Understanding the parathyroid gland’s role and recognizing symptoms is key. Seeking timely medical care helps prevent long-term complications.
Regular checkups and staying alert to changes in your body are crucial. Working with healthcare providers to create a treatment plan is also important. This plan might include surgery, medication, or lifestyle changes to balance calcium levels and improve your life.
Being informed and involved in your care helps manage hyperparathyroidism. Remember, your parathyroid health is essential for your overall well-being. Prioritize it and seek support when needed.
FAQ
Q: What is Hyperparathyroidism?
A: Hyperparathyroidism is when the parathyroid glands in the neck make too much hormone. This hormone helps control calcium levels in the blood. Too much of it can cause high calcium levels, known as hypercalcemia.
Q: What is the role of the parathyroid gland?
A: The parathyroid gland makes parathyroid hormone (PTH). This hormone is key for keeping calcium and phosphorus levels balanced in the body. It helps by releasing calcium from bones and improving calcium absorption from food.
Q: What are the different types of Hyperparathyroidism?
A: There are two main types of Hyperparathyroidism: 1. Primary Hyperparathyroidism: This is the most common form. It happens when one or more parathyroid glands grow too big or work too hard, making too much PTH. 2. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: This type occurs when another issue, like kidney disease or vitamin D deficiency, makes the parathyroid glands work too hard to try to fix low blood calcium levels.
Q: What are the common causes and risk factors of Hyperparathyroidism?
A: The main cause of Hyperparathyroidism is primary hyperparathyroidism. This is usually due to a benign tumor or gland enlargement. Other risk factors include: – Being older, especially over 50 – Neck or head radiation – Certain genetic conditions – Chronic kidney disease – Vitamin D deficiency
Q: What are the symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism?
A: Symptoms of Hyperparathyroidism vary but can include: – Bone pain or weakness – Kidney stones – Feeling tired or weak – Depression or memory problems – Nausea, vomiting, or loss of appetite – Increased thirst and urination If not treated, Hyperparathyroidism can cause serious problems like osteoporosis and heart disease.
Q: How is Hyperparathyroidism diagnosed?
A: Doctors use blood tests and imaging studies to diagnose Hyperparathyroidism. The main tests are: – Blood tests to check calcium and PTH levels – Neck imaging tests, like ultrasound or sestamibi scan, to find the affected gland(s) – Sometimes, a biopsy is done to confirm the diagnosis.
Q: What are the treatment options for Hyperparathyroidism?
A: Treatment for Hyperparathyroidism varies based on the condition’s severity and the person’s health. Options include: – Surgery to remove the affected gland(s) – Medication to manage calcium and PTH levels – For mild cases, monitoring and lifestyle changes, like diet and exercise, may be recommended.
Q: What are the potential complications of Hyperparathyroidism?
A: Untreated Hyperparathyroidism can lead to serious complications, including: – Osteoporosis and increased fracture risk – Kidney stones – Heart disease, like high blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms – Neurological issues, such as depression and memory problems – Gastrointestinal problems, like peptic ulcers and pancreatitis
Q: How can I prevent or reduce the risk of Hyperparathyroidism?
A: While you can’t always prevent Hyperparathyroidism, there are ways to lower your risk: – Eat a healthy diet with enough calcium and vitamin D – Stay hydrated and limit sodium and alcohol – Avoid certain medications that raise calcium levels – Get regular check-ups and screenings, especially if you have a family history or other risk factors.
Q: Where can I find support and resources for living with Hyperparathyroidism?
A: There are many resources for those living with Hyperparathyroidism, including: – Finding healthcare providers who specialize in endocrine disorders – Joining support groups or online communities – Accessing educational materials from reputable medical organizations and patient advocacy groups.
