About 20 out of every 100,000 people worldwide have myasthenia gravis. It’s a rare autoimmune disorder that makes simple movements hard. This disease attacks the connection between nerves and muscles, causing unpredictable weakness.
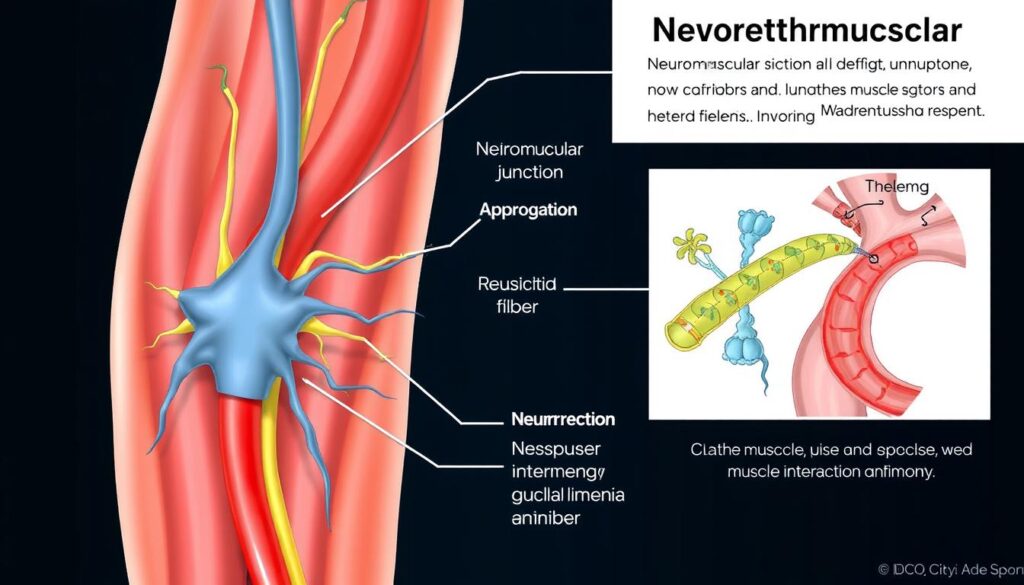
Myasthenia gravis affects muscle function deeply. It makes the immune system attack the communication between nerves and muscles. People with this condition often face muscle weakness that can change in strength. Even simple tasks like climbing stairs or holding a coffee mug can become hard.
Understanding myasthenia gravis requires insight into how the body’s defense can turn against it. It involves genetic and environmental factors. This makes myasthenia gravis a complex medical puzzle for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Key Takeaways
- Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder affecting neuromuscular function
- Muscle weakness can vary in intensity and impact daily activities
- The condition disrupts communication between nerves and muscles
- Genetic and environmental factors can contribute to disease development
- Early diagnosis and management are critical for improving quality of life
Understanding Myasthenia Gravis: An Overview
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a complex autoimmune disorder. It affects the body’s neuromuscular system. This condition makes it hard for patients to move their muscles and communicate between nerves and muscles.
The Role of the Immune System in MG
In Myasthenia Gravis, the immune system attacks the body’s healthy tissues. It targets the acetylcholine receptors, which are crucial for muscle movement. This attack disrupts the communication between nerves and muscles, causing muscle weakness.
- Immune system mistakenly targets neuromuscular junctions
- Acetylcholine receptor antibodies block muscle signal transmission
- Nerve-muscle communication becomes impaired
Key Characteristics of the Disease
MG presents unique challenges for patients. The main symptom is muscle weakness that gets worse with activity and better with rest. The muscles most affected are those controlling eye movement, facial expressions, and breathing.
| MG Characteristic | Impact |
|---|---|
| Muscle Weakness | Varies in intensity throughout the day |
| Neuromuscular Signal Disruption | Prevents effective muscle contraction |
| Autoimmune Response | Targets own neuromuscular connections |
Who Is Most Affected?
Myasthenia Gravis can affect anyone, but some groups are more likely to get it. Women under 40 and men over 60 are often diagnosed. People with a family history of MG or other autoimmune conditions are also at higher risk.
“Understanding Myasthenia Gravis is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life.” – Neuromuscular Research Institute
Common Signs and Symptoms
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) brings unique symptoms that can really affect a person’s daily life. It mainly messes with muscle function, making everyday tasks hard for those who have it.
People with MG face several key symptoms. These symptoms set MG apart from other muscle and nerve problems:
- Ptosis: Eyelids droop, causing vision problems and uneven faces
- Diplopia: Double vision happens because eye muscles are weak
- Dysphagia: Swallowing is tough, making eating and drinking hard
- Muscle weakness in different parts of the body
“Understanding these symptoms early can lead to more effective management of Myasthenia Gravis.” – Neurology Research Institute
Respiratory issues are a big deal in MG. Weak muscles in the lungs can make breathing hard. This can lead to serious problems if not treated.
| Symptom Category | Specific Manifestations | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ocular Symptoms | Ptosis, Diplopia | Vision impairment, eye muscle fatigue |
| Muscular Symptoms | Generalized weakness | Reduced physical functionality |
| Respiratory Symptoms | Breathing difficulties | Potential medical emergencies |
Spotting these symptoms early helps patients team up with doctors. Together, they can create plans to manage MG better.
The Science Behind Neuromuscular Junction Dysfunction
Myasthenia gravis is a complex neuromuscular disease. It disrupts communication between nerves and muscles at the cellular level. Acetylcholine receptor antibodies play a key role in muscle weakness.
How Acetylcholine Receptors Work
Acetylcholine receptors are vital for muscle movement. They sit on muscle cell surfaces, ready to receive chemical signals. In a healthy nervous system, these receptors ensure smooth communication between nerves and muscles.
- Receptors receive neurotransmitter signals
- Chemical messages trigger muscle movement
- Precise communication ensures muscle function
The Impact on Muscle Function
When neuromuscular disease disrupts this communication, muscle weakness follows. The breakdown of signal transmission means muscles can’t respond well to nerve impulses.
| Communication Stage | Normal Function | Myasthenia Gravis Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Nerve Signal Transmission | Smooth and Complete | Interrupted and Weakened |
| Muscle Response | Strong and Immediate | Delayed and Reduced |
Understanding Antibody Attack
In myasthenia gravis, the immune system makes antibodies that attack acetylcholine receptors. This autoimmune response blocks nerve signals to muscles. It leads to progressive weakness.
“The immune system’s misguided attack transforms a normal communication pathway into a battlefield of cellular dysfunction.” – Neurology Research Team
Researchers are working to understand these antibody attacks. They aim to find better treatments for this challenging neuromuscular disease.
Triggers and Risk Factors
Understanding myasthenia gravis triggers and risk factors is key. It helps both patients and doctors manage this complex autoimmune disorder. While the exact cause is still unknown, several factors contribute to its development and progression.
Genetic and environmental factors are crucial in myasthenia gravis. Researchers have found important risk factors that can increase someone’s chance of getting this autoimmune disorder.
- Age: Most common in women under 40 and men over 60
- Genetic predisposition
- Underlying thyroid conditions
- Chronic stress
- Viral infections
Certain medical conditions can trigger or worsen myasthenia gravis symptoms. These include:
- Autoimmune thyroid diseases
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
“Understanding your personal risk factors can be crucial in managing myasthenia gravis effectively.”
| Risk Category | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Increased susceptibility to autoimmune response |
| Hormonal Changes | Potential symptom fluctuation |
| Chronic Stress | Potential symptom intensification |
Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to identify and manage individual risk factors for myasthenia gravis.
Diagnostic Process and Testing Methods
Diagnosing Myasthenia Gravis (MG) needs a detailed and accurate method. Doctors use many tests to find acetylcholine receptor antibodies and check muscle weakness.
Finding MG involves important steps. These help doctors understand this neuromuscular disorder better.
Physical Examination Techniques
Doctors start by doing special physical exams. They check muscle weakness and neurological issues. Key tests include:
- Repetitive muscle movement testing
- Assessing eye muscle function
- Checking muscle strength and fatigue patterns
- Evaluating facial muscle responses
Blood Tests and Imaging
Testing is key to finding acetylcholine receptor antibodies. These are important signs of MG. Important tests and scans are:
- Acetylcholine receptor antibody blood test
- Thyroid function screening
- Chest CT scan to examine thymus gland
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
Specialized Diagnostic Procedures
Advanced tests give deeper insights into muscle and nerve issues. They help doctors understand muscle weakness and immune system problems.
- Electromyography (EMG) – measures electrical activity in muscles
- Nerve conduction studies
- Edrophonium (Tensilon) test
“Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective management of Myasthenia Gravis.” – Neurology Research Institute
These detailed tests help doctors create the right treatment plans. They focus on muscle weakness caused by Myasthenia Gravis.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing myasthenia gravis needs a detailed plan. Doctors create treatment plans based on each patient’s needs and how severe their symptoms are.

- Medications to improve neuromuscular transmission
- Immunosuppressants to reduce immune system attacks
- Surgical interventions
- Lifestyle management techniques
Immunosuppressants are key in fighting this disease. They control the immune system’s wrong actions. This helps lessen muscle weakness and stops it from getting worse.
“Effective treatment requires a multifaceted approach tailored to each patient’s unique condition.” – Neurology Research Institute
Here are some important medical treatments:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: Help nerves talk to muscles better
- Corticosteroids: Keep the immune system in check
- Plasma exchange: Removes bad antibodies from blood
- Intravenous immunoglobulin: Temporarily changes how the immune system works
Thymectomy surgery is also a big help. It removes the thymus gland. This can make symptoms less severe and might even lead to long-term recovery for some.
Living with Myasthenia Gravis: Daily Challenges
Dealing with Myasthenia Gravis (MG) every day is tough. People with muscle weakness need to find ways to keep living well and stay independent.
Managing Physical Activities
To make daily life easier, those with MG can:
- Do hard tasks when they have the most energy
- Take breaks often
- Use tools to help them
- Save energy for important things
“Adaptation is not about limitation, but about finding innovative ways to accomplish your goals.” – MG Support Network
Emotional and Social Impact
MG can also affect how you feel. People might feel:
- Upset by not being able to do things
- Left out because they can’t join in
- Worried about how their health will change
Getting help from a therapist can really help. It’s key to staying strong and feeling good mentally.
Workplace Accommodations
At work, people with MG can ask for changes like:
- Being able to choose their hours
- Working in a comfortable space
- Working from home
- Doing less physically demanding tasks
Knowing your rights and talking to your boss can make work better, even with muscle weakness.
Emergency Situations and Crisis Management
People with myasthenia gravis need to know about emergency situations, especially those that affect breathing. A myasthenic crisis is a serious situation that needs quick help from doctors.
“Recognizing early warning signs can be life-saving for individuals managing myasthenia gravis.” – Neurology Research Institute
Respiratory problems can get worse fast. It’s important to be aware and ready. Look out for these urgent signs:
- Severe muscle weakness affecting breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Sudden respiratory distress
- Pronounced fatigue with breathing challenges
Managing emergencies for myasthenia gravis patients involves special medical steps. Doctors use intensive care to keep breathing stable and avoid more problems.
| Emergency Sign | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Breathing Difficulty | Immediate Medical Evaluation |
| Muscle Weakness | Respiratory Support Assessment |
| Choking Sensation | Emergency Room Consultation |
Being ready is crucial for dealing with breathing problems linked to myasthenia gravis. Patients should have an emergency contact list, carry medical ID, and make a crisis plan with their doctor.
- Create an emergency medical information card
- Practice breathing exercises
- Keep emergency contact numbers accessible
- Schedule regular medical check-ups
Knowing these emergency steps helps patients act fast in critical times. This can stop serious breathing problems linked to myasthenia gravis.
Support Systems and Resources
Living with a neuromuscular disease like myasthenia gravis can be tough. But, there are many support systems and resources to help. They make managing this complex condition easier for patients and their families.
Patient Support Groups
Meeting others who face similar challenges can be very empowering. Support groups offer many benefits:
- Emotional support and shared experiences
- Practical coping strategies
- Latest treatment information
- Opportunities for social interaction
“Finding community makes the journey with myasthenia gravis less isolating.” – MG Patient Advocate
Professional Care Networks
Getting the right care for myasthenia gravis means working with a team. Key professionals include:
- Neurologists specializing in neuromuscular diseases
- Occupational therapists
- Psychiatric counselors
- Physical rehabilitation specialists
Educational Resources
Knowing as much as you can about your disease is powerful. Patients can find helpful information through:
- Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America online resources
- Specialized medical websites
- Webinars and patient education programs
- Academic medical center publications
Using these support systems can greatly improve life and disease management for those with myasthenia gravis.
Research and Future Treatments
Research on myasthenia gravis is moving fast, bringing new hope for this complex disease. Scientists are looking into new ways to understand and treat it. This could change how we manage this autoimmune disorder.
Right now, researchers are working on several new treatment ideas:
- Targeted Immunotherapy
- Gene Therapy Techniques
- Advanced Biological Interventions
New treatments are being developed that go beyond what we have now. Precision medicine is being used to tailor treatments to each patient. This is based on their genetic makeup and the specific antibodies they have.
“The future of myasthenia gravis treatment lies in understanding the intricate mechanisms of the immune system’s attack on neuromuscular junctions.” – Neuroscience Research Institute
Some of the biggest breakthroughs are happening in these areas:
| Research Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Molecular Targeting | Reduced Immune System Attacks |
| Regenerative Medicine | Muscle Function Restoration |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Neurological Repair Potential |
New technologies in neuromuscular disease research offer hope for patients. Clinical trials are testing new treatments. These could greatly improve the lives of those with myasthenia gravis.
Conclusion
Understanding myasthenia gravis is key for patients, caregivers, and doctors. This complex autoimmune disorder causes muscle weakness. It can greatly affect daily life.
Despite the challenges, new medical research and treatments offer hope. They help improve the quality of life for those affected.
Patients with this condition are not alone. They have support systems, medical care, and ongoing research to help. Early detection and personalized treatment are crucial.
These steps help manage the condition’s complexities. They make it easier to live with myasthenia gravis.
The treatment for myasthenia gravis is getting better. Researchers are finding new therapies to reduce muscle weakness. This could lead to better outcomes for patients.
As we learn more about the disorder, there’s hope for the future. New treatments might make managing the disease easier.
Knowledge is the most powerful tool for those with myasthenia gravis. By staying informed and working with healthcare providers, they can lead fulfilling lives. They can also manage their symptoms effectively.
FAQ
Q: What exactly is Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a condition where the immune system attacks the nerves and muscles. This causes muscle weakness and fatigue. It makes it hard to move even simple parts of the body.
Q: What are the most common symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Symptoms include drooping eyelids and double vision. It also causes trouble swallowing and facial muscle weakness. Muscle fatigue gets worse with activity.
Q: Who is most likely to develop Myasthenia Gravis?
A: MG can affect anyone but is more common in women under 40 and men over 60. People with a family history or other autoimmune diseases are at higher risk.
Q: How is Myasthenia Gravis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use physical exams, blood tests, and tests like electromyography (EMG). They might also look at the thymus gland with imaging tests.
Q: Can Myasthenia Gravis be cured?
A: There’s no cure for MG yet. But treatments can manage symptoms and improve life quality. Options include medicines, plasma exchange, surgery, and targeted therapies.
Q: What triggers Myasthenia Gravis symptoms?
A: Symptoms can be triggered by stress, fatigue, and certain medications. Physical exertion and lack of sleep can also make symptoms worse.
Q: Are there any emergency situations associated with Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Yes, myasthenic crisis is a serious condition where breathing is compromised. It needs immediate medical attention and can involve respiratory support.
Q: How can patients manage daily life with Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Patients should follow their treatment plan and get enough rest. Managing stress and avoiding triggers helps. Working with healthcare providers and using support groups can also improve life quality.
Q: Is exercise safe for people with Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Gentle exercise is safe for MG patients. Activities like walking and swimming help maintain strength. Always check with a neurologist and listen to your body to avoid overexertion.
Q: What ongoing research is happening for Myasthenia Gravis?
A: Research aims to develop better treatments and understand the disease. It includes immunotherapies, stem cell therapy, and finding ways to manage the autoimmune response.
