Explore expert-backed tips for healthily managing mixed hyperlipidemia and reducing cardiovascular risks.
Mixed hyperlipidemia is a common one, with high cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. It’s a big risk for heart health, so managing it well is key.
Managing mixed hyperlipidemia needs a full plan. This includes changing your lifestyle, diet, and sometimes medicine. We’ll look into what mixed hyperlipidemia is, its causes, symptoms, and how to treat it. Plus, we’ll share tips for keeping it under control.

Introduction to Mixed Hyperlipidemia
Knowing about mixed hyperlipidemia is the first step to managing it. It can lead to heart disease, so it’s important to keep your lipid levels in check. By learning more about mixed hyperlipidemia, you can take charge of your health.
Key Takeaways
- Mixed hyperlipidemia is a common lipid disorder that affects millions of Americans.
- Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Managing mixed hyperlipidemia requires a comprehensive approach, involving lifestyle modifications and medical treatment.
- Dietary changes and regular exercise can help reduce lipid levels and improve overall health.
- Regular monitoring and testing are essential for tracking progress and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
- By understanding the causes and symptoms of mixed hyperlipidemia, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition and reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease.
Understanding Mixed Hyperlipidemia and Its Impact on Health
Mixed hyperlipidemia means you have too much cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. Knowing how these lipids work is key to managing this condition. Cholesterol helps make cell membranes, and triglycerides are our main energy source.
This condition can harm your health a lot. Too much cholesterol and triglycerides can cause plaque in your arteries. It’s crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms of mixed hyperlipidemia to avoid serious damage.
The Role of Cholesterol and Triglycerides
Cholesterol and triglycerides are important lipids in our bodies. Cholesterol helps make hormones and vitamin D. Triglycerides store energy. But too much of them can cause health issues.
How Mixed Hyperlipidemia Affects Your Body
Mixed hyperlipidemia can harm your body in many ways. It can:
- Make you more likely to get heart disease and stroke
- Damage your blood vessels and arteries
- Reduce blood flow to important organs
Common Risk Factors and Causes
Some things can make you more likely to get mixed hyperlipidemia. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Family history | A history of high cholesterol or triglycerides in the family |
| Obesity | Being overweight, especially around the waist |
| Physical inactivity | Not exercising regularly or being active enough |
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of mixed hyperlipidemia early. High lipid levels can cause health problems like dyslipidemia. Spotting common signs like high cholesterol and triglycerides is key to getting help fast.
Here are some common signs of mixed hyperlipidemia:
- High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
- Low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
- Elevated triglycerides
- Family history of high cholesterol or heart disease
People with mixed hyperlipidemia might not feel sick. But, regular health checks are vital for catching it early. Knowing the signs helps you manage your lipid levels and lower your risk of dyslipidemia and other health problems.
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to managing mixed hyperlipidemia. A healthcare provider will order a blood test to check your lipid profile. This test looks at total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides in your blood.
Knowing your lipid profile is important for your heart health. It shows if you have high LDL cholesterol, which can lead to heart disease. By keeping an eye on your lipid levels, you can lower your heart disease risk.
Key Components of a Lipid Profile
- Total Cholesterol: The total amount of cholesterol in the blood.
- LDL Cholesterol: Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, high levels can increase cardiovascular risk.
- HDL Cholesterol: Known as “good” cholesterol, high levels can help reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Triglycerides: A type of fat found in the blood, high levels can also increase cardiovascular risk.
It’s important to regularly check your lipid levels if you have mixed hyperlipidemia. How often you need to get tested depends on your risk factors and medical history. Working with your healthcare provider, you can create a plan to manage your lipid profile and lower your heart disease risk.
Frequency of Monitoring
If you have mixed hyperlipidemia, talk to your healthcare provider about how often to check your lipid levels. They might suggest regular blood tests and lifestyle changes to help manage your lipid levels and heart disease risk.
The Connection Between Mixed Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Disease
Mixed hyperlipidemia can raise the risk of atherosclerosis. This is when plaque builds up in the arteries, causing heart disease. It’s important to treat lipid levels well to lower heart disease risk.
Some key factors to consider in the connection between mixed hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular disease include:
- High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
- Low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
- High levels of triglycerides
Managing mixed hyperlipidemia through lipid treatment and lifestyle changes can help. It’s key to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan.
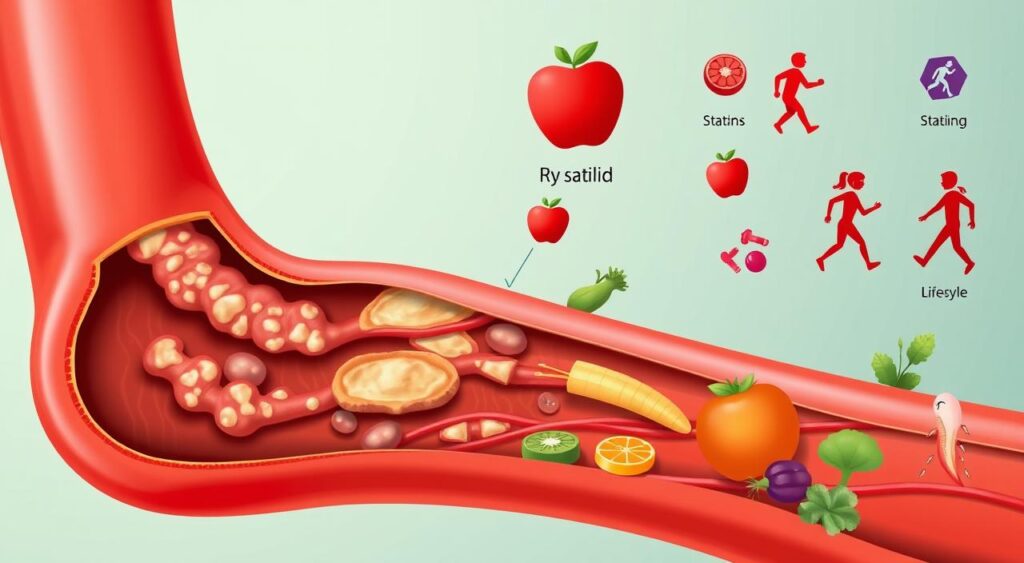
Understanding the link between mixed hyperlipidemia and heart disease helps. People can take steps to manage their condition. This reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Atherosclerosis | Buildup of plaque in the arteries |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels |
Medical Treatment Options
People with mixed hyperlipidemia, a condition affecting cholesterol and triglycerides, have treatment options. These include lifestyle changes and prescription drugs. A mix of both is often used in treatment plans.
There are different types of prescription drugs for mixed hyperlipidemia. These include statins, fibrates, and bile acid sequestrants. Each type works differently and can have different side effects. It’s important to know how each drug affects lipid levels for effective treatment.
Prescription Medications
- Statins: These medications block cholesterol production in the liver, lowering overall cholesterol levels.
- Fibrates: Fibrates help lower triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol levels.
- Bile acid sequestrants: These drugs bind to bile acids in the gut, removing excess cholesterol from the body.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
It’s crucial to regularly check lipid levels and overall health. This ensures the treatment is working and makes any needed changes. Working closely with a healthcare provider helps manage mixed hyperlipidemia and lowers the risk of heart disease.
Dietary Strategies for Managing Lipid Levels
Keeping lipid levels in check is key to avoiding heart disease. A balanced diet is vital for healthy cholesterol and triglycerides. It’s important to know how different foods impact lipid levels and make smart choices.
A healthy diet should include a mix of foods from all groups. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods like oily fish are high in omega-3s, which can lower triglycerides. Also, avocados and nuts are good for overall lipid health because of their healthy fats.
Here are some tips for managing lipid levels:
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables for nutrients and fiber
- Include lean proteins like poultry and fish in your meals
- Choose whole grains over refined ones, like brown rice and quinoa
- Reduce saturated and trans fats to lower cholesterol
By sticking to these dietary tips and living a healthy lifestyle, you can manage your lipid levels. This helps lower the risk of heart disease.

| Food Group | Effect on Lipid Levels |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Help lower cholesterol and triglycerides levels |
| Whole Grains | Help improve overall lipid profiles |
| Lean Proteins | Help lower triglycerides levels |
Essential Lifestyle Modifications
Managing lipid levels and preventing dyslipidemia needs a full plan. This plan includes regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. These habits help lower the risk of heart disease and boost overall health.
Exercise is key for healthy lipid levels. Physical activity boosts “good” cholesterol and lowers “bad” cholesterol. The American Heart Association suggests at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
Exercise Recommendations
- Do aerobic exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for 30 minutes daily
- Add strength-training to build muscle and speed up metabolism
- Try to walk 10,000 steps a day for more activity
Managing stress is also vital for healthy lipids. Stress can increase “bad” cholesterol and lower “good” cholesterol. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help.
Stress Management Techniques
Getting enough sleep is also key for lipid health. Poor sleep can mess with hormones that control hunger and metabolism, leading to weight gain and dyslipidemia risk. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night to help keep lipid levels in check.
| Lifestyle Modification | Benefits for Lipid Levels |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Increases HDL cholesterol, reduces LDL cholesterol |
| Stress Management | Reduces cortisol levels, decreases LDL cholesterol |
| Adequate Sleep | Regulates appetite and metabolism, reduces risk of dyslipidemia |
Natural Supplements and Alternative Treatments
Managing mixed hyperlipidemia often requires a mix of medical treatment and lifestyle changes. Besides diet and exercise, some natural supplements and alternative treatments can help. Always talk to a healthcare provider before trying new supplements, as they can affect medications or cause problems in some people.
Some natural supplements that may help with lipid profile include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids, which can lower triglycerides
- Plant sterols and stanols, which can reduce LDL cholesterol
- Soluble fiber, which can lower LDL cholesterol and improve overall lipid profile
Alternative treatments like acupuncture and stress management might also help. They can improve overall health and reduce inflammation. But, more research is needed to fully understand their effects on mixed hyperlipidemia.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to find the best treatment for mixed hyperlipidemia. By combining medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and natural supplements or alternative treatments, people can manage their lipid profile and lower their risk of heart disease.
Prevention Strategies for High-Risk Individuals
People with a family history of mixed hyperlipidemia face a higher risk of atherosclerosis. This condition is when plaque builds up in the arteries. To lower this risk, it’s crucial to eat well, exercise regularly, and consider lipid treatment if needed.
High-risk individuals should focus on:
- Keeping a healthy weight to lower atherosclerosis risk
- Doing regular physical activities like walking or jogging to boost heart health
- Eating a balanced diet that’s low in bad fats and high in fruits, veggies, and whole grains
- Seeing a healthcare provider regularly to check lipid levels and adjust lipid treatment if necessary
By taking these steps, high-risk people can lower their chance of getting atherosclerosis and heart diseases. It’s also key to remember that lipid treatment must fit each person’s needs and health. It should be checked often to make sure it works well.
In the end, a mix of lifestyle changes and lipid treatment can help high-risk folks avoid atherosclerosis and heart diseases.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Managing mixed hyperlipidemia needs teamwork between patients and healthcare providers. A lipid disorder is complex. Working with a healthcare provider is key to creating a treatment plan that fits you.
A healthcare provider will explain your lipid profile and help you manage it. They might suggest lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. They may also recommend medication.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor progress
- Open communication about symptoms, concerns, and treatment goals
- Collaboration with other healthcare professionals, such as dietitians or cardiologists, if necessary
Together, patients and healthcare providers can manage mixed hyperlipidemia well. This can lower the risk of heart disease. A well-managed lipid disorder can greatly improve your health and happiness.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Mixed Hyperlipidemia Journey
Managing mixed hyperlipidemia is a long-term effort. Understanding the need for healthy cholesterol and triglyceride levels is key. This helps lower your risk of cardiovascular disease and boosts your health.
It’s important to keep an eye on your lipid profile and work with your doctors. They can help you find the right treatment. This might include prescription medications, changing your diet, or making lifestyle changes. Sticking to your treatment plan is crucial for good lipid levels.
Start your journey by focusing on prevention. Deal with any risk factors and make choices that are good for your heart. With hard work and a solid plan, you can manage your mixed hyperlipidemia and look forward to a healthier life.
FAQ
Q: What is mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Mixed hyperlipidemia is when you have too much cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. This can raise your risk of heart disease.
Q: What are the common risk factors and causes of mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Genetics, being overweight, diabetes, not being active, and bad eating habits can cause it. Some medicines and health issues also play a part.
Q: How is mixed hyperlipidemia diagnosed and tested?
A: Doctors use a blood test to find out if you have it. This test checks your cholesterol and triglycerides levels. It’s important to keep an eye on these numbers.
Q: What is the connection between mixed hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular disease?
A: It’s a big risk factor for heart disease. High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Managing it well is key to avoiding these serious problems.
Q: What are the medical treatment options for mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Doctors might prescribe statins, fibrates, or other medicines. They’ll work with you to find the right mix of treatments for your cholesterol and triglycerides.
Q: How can dietary and lifestyle strategies help manage mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Eating right, staying active, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can help. These habits can lower your risk of heart disease.
Q: What role do natural supplements and alternative treatments play in managing mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Supplements and alternative treatments might help, but talk to your doctor first. They can affect your medicines or have side effects.
Q: How can high-risk individuals prevent the development of mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: If you’re at high risk, get regular check-ups and follow a healthy lifestyle. Work with your doctor to prevent it.
Q: Why is it important to work with healthcare providers when managing mixed hyperlipidemia?
A: Doctors, cardiologists, and dietitians are key to managing it. They help create a treatment plan, track your progress, and make changes as needed.
