Osteochondritis dissecans affects 15% of all joint disorders. It damages cartilage and bone, causing pain and limited movement in joints like the knee and elbow. It’s a big worry for athletes, as it can hurt their performance and life quality. Knowing about osteochondritis dissecans is key to managing it well.
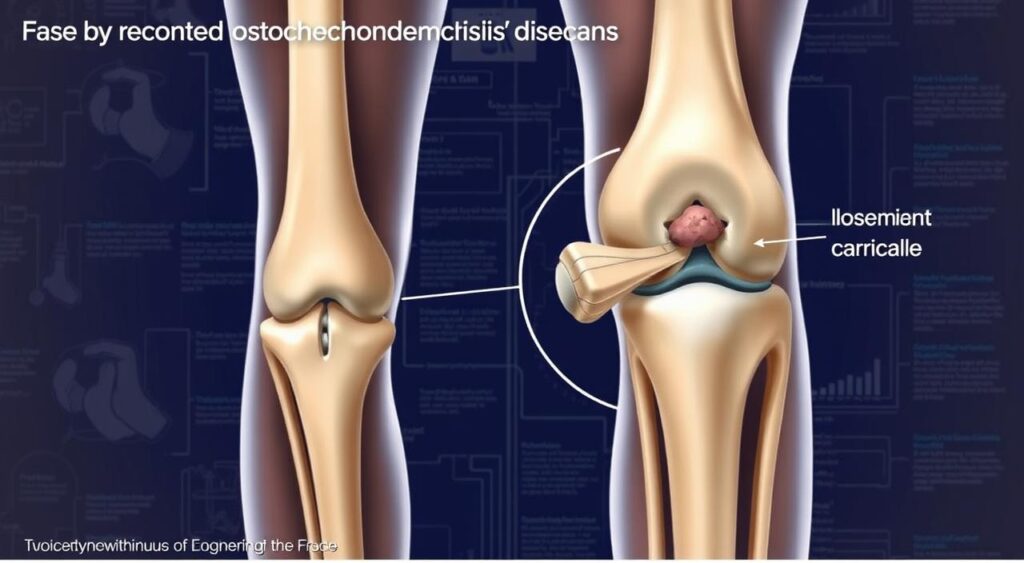
Understanding osteochondritis dissecans is vital for recovery. It can happen in many joints, but the knee, elbow, and ankle are most common. We’ll explore what it is, its history, and how it affects joints in this article.
Key Takeaways
- Osteochondritis dissecans is a joint disorder that affects the cartilage and bone, leading to pain and limited mobility.
- This condition is commonly found in the knee, elbow, and ankle joints.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for osteochondritis dissecans is crucial for effective management and recovery.
- Osteochondritis dissecans can impact an individual’s quality of life and performance in sports or physical activities.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term damage and improve outcomes for individuals with osteochondritis dissecans.
- Osteochondritis dissecans is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management and recovery.
Understanding Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis Dissecans is a joint condition that affects the cartilage and bone. It leads to cartilage damage and knee pain. To understand this condition, we need to know its definition and basic concepts.
The term “Osteochondritis Dissecans” means a piece of cartilage and bone gets damaged or dies. This happens because it doesn’t get enough blood.
The history of Osteochondritis Dissecans goes back to the 19th century. Many studies have been done to find out what causes it and how to treat it. Knowing about the joint’s structure and function is key to understanding the condition. Cartilage damage can cause knee pain and other symptoms.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Osteochondritis Dissecans is when a piece of cartilage and bone gets damaged or dies. This leads to cartilage damage and knee pain. It can happen in any joint, but it often affects the knee, elbow, and ankle.
Historical Background
Since the 19th century, research on Osteochondritis Dissecans has been ongoing. Many studies have helped us understand the condition better. We now know more about its causes and how to treat it.
Anatomical Considerations
The joint’s structure and function are affected by Osteochondritis Dissecans. The condition can cause cartilage damage and knee pain. It’s important to know about the joint’s anatomy and how it relates to the condition.
Understanding Osteochondritis Dissecans is key to managing and preventing it. By knowing its definition, history, and anatomy, we can take steps to prevent cartilage damage and knee pain. This helps improve our joint health overall.
Common Locations and Impact on Joint Health
Osteochondritis Dissecans can happen in many joints, but it’s most common in the knee, elbow, and ankle. It can really hurt joint health, causing pain, instability, and making it hard to move.
Sports injuries often lead to Osteochondritis Dissecans, especially in young athletes playing high-impact sports. Knowing where it usually happens and how it affects joint health is key to preventing and treating it. Here are some common places where Osteochondritis Dissecans occurs:
- Knee
- Elbow
- Ankle
To prevent sports injuries and Osteochondritis Dissecans, it’s important to take steps. Wear the right protective gear, warm up before you start exercising, and don’t push yourself too hard. These actions can help keep your joint health in check and lower the chance of getting this condition.
Risk Factors and Causes
Osteochondritis Dissecans is a complex condition. Several risk factors contribute to its development. Genetic predisposition is a big factor, as those with a family history are more likely to get it. The condition also affects adolescents and young adults more often.
Sports that involve repetitive trauma or stress on the joint can also increase the risk. Here are some common risk factors:
- Family history of Osteochondritis Dissecans
- Participation in high-impact sports, such as football or basketball
- Repetitive trauma or stress on the joint
- Age, with adolescents and young adults being more commonly affected
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and managing Osteochondritis Dissecans. By understanding the causes and taking steps to reduce risk, individuals can help prevent this condition.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Family history of Osteochondritis Dissecans |
| Sports-Related Factors | Repetitive trauma or stress on the joint |
| Age | Adolescents and young adults are more commonly affected |
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
It’s important to know the signs and symptoms of Osteochondritis Dissecans. This helps you get medical help quickly and find the right treatment. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and trouble moving the joint. You might also feel the joint lock or catch, which means a piece of cartilage or bone is loose.
Some key signs and symptoms to watch for include:
- Pain in the affected joint, especially during or after activity
- Swelling or inflammation in the affected joint
- Locking or catching of the joint
- Limited mobility or stiffness in the affected joint
Knowing these signs and symptoms is key to finding the right treatment. By spotting them early, you can get help fast. This can stop more damage and make treatment work better.
It’s also crucial to understand the treatment options. Working with a healthcare professional, you can create a plan that fits your needs. This helps you manage your condition well.
| Signs and Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Pain and swelling | Medication, physical therapy |
| Locking or catching of the joint | Surgical intervention, rehabilitation exercises |
| Limited mobility or stiffness | Physical therapy, lifestyle modifications |
Diagnostic Process and Evaluation Methods
Diagnosing Osteochondritis Dissecans involves several steps. These include a physical check-up, imaging tests, and lab work. This thorough check is key to create a good treatment plan. Sometimes, this plan might include surgery.
The first step is a physical exam. It looks for signs of joint problems or limited movement. Here are the main ways to check the condition:
- Physical examination to assess joint mobility and stability
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to provide detailed images of the joint
- Laboratory tests to rule out other conditions or assess overall health
In severe cases, surgery might be needed. The diagnostic process helps find the best treatment. It’s important for a good outcome.
Knowing about the diagnostic process helps people understand their treatment options. It’s a key step in managing Osteochondritis Dissecans. It helps prevent more problems.
Classification and Staging System
Osteochondritis Dissecans is divided into stages based on its severity. This is key for choosing the right treatment and predicting results. The classification and staging system look at the lesion’s size, location, and the bone and cartilage’s condition.
Knowing the classification and staging system is vital for a good treatment plan. It helps doctors understand the damage’s extent and recovery chances. This way, they can tailor care to improve bone health.

The staging system has several stages, from mild to severe. Each stage has its symptoms and damage levels. Accurate staging helps doctors choose the best treatments and advise on bone health and preventing more damage.
Treatment Options and Approaches
Osteochondritis Dissecans needs a detailed treatment plan. This plan considers the condition’s severity and the person’s health. The main goal is to ease symptoms, help the joint heal, and stop further damage.
Choosing the right treatment options is key. The plan might include non-surgical methods, surgery, and rehabilitation exercises. This mix helps ensure the best recovery.
Conservative Management
For mild cases, non-surgical methods are often suggested. This can include:
- Rest and physical therapy to ease joint stress
- Pain relief through medication or other non-surgical ways
- Using ice, heat, or ultrasound to aid healing
Surgical Interventions
For severe cases, surgery might be needed. It aims to fix or remove the damaged cartilage and bone. Surgical options include:
- Drilling or microfracture to boost healing
- Osteochondral autograft transplantation to replace damaged tissue
Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehabilitation exercises are vital for recovery. They help regain strength, flexibility, and joint movement. A good rehab program might include:
| Exercise | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Range of motion exercises | 3-4 times a day | 10-15 minutes |
| Strengthening exercises | 2-3 times a week | 20-30 minutes |
| Flexibility exercises | 3-4 times a week | 10-15 minutes |
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Knowing the recovery timeline for Osteochondritis Dissecans is key. It helps set realistic goals and aids in a smooth recovery. The time it takes to recover depends on how severe the condition is and the treatment used. Generally, people can expect to fully recover in a few months to a year after treatment.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about getting better. This means understanding that recovery can take a long time. It also involves ongoing rehabilitation and follow-up care. A typical recovery timeline includes:
- Initial treatment and rehabilitation phase (2-6 months)
- Strengthening and conditioning phase (3-6 months)
- Return to normal activities phase (6-12 months)
By knowing the recovery timeline and expectations, people can prepare better. They can work closely with their healthcare provider for a successful recovery.
Prevention Strategies and Joint Protection
To prevent Osteochondritis Dissecans, we need a mix of prevention strategies and protective equipment. People in high-impact sports should wear knee pads or elbow pads. This can help lower the risk of getting the condition.
Here are some good prevention strategies:
- Modifying activities to avoid high-impact movements
- Wearing protective equipment such as knee pads or elbow pads
- Strengthening exercises to improve joint stability
Using these prevention strategies and protective equipment can greatly lower the risk of Osteochondritis Dissecans. It also helps keep joints healthy.

| Prevention Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity Modification | Modifying activities to avoid high-impact movements |
| Protective Equipment | Wearing protective gear such as knee pads or elbow pads |
| Strengthening Exercises | Exercises to improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury |
Long-term Prognosis and Complications
The outlook for Osteochondritis Dissecans is mostly positive. However, it can cause complications if not treated properly or on time. Knowing about these complications helps in making the right treatment choices and achieving the best results.
Some possible complications of Osteochondritis Dissecans include:
- Chronic pain
- Limited mobility
- Degenerative joint disease
It’s important to tackle these complications to get the best outcome.
Early diagnosis and treatment greatly improve the long-term prognosis. By understanding and addressing potential complications, people with Osteochondritis Dissecans can reduce long-term damage. This helps in keeping the joint healthy.
Living with Osteochondritis Dissecans: Lifestyle Adjustments
Managing osteochondritis dissecans means making lifestyle adjustments to protect your joint. You need to change how you do daily activities to avoid too much stress on the joint. These changes help keep your joint healthy and reduce the condition’s impact on your life.
Managing daily activities well is key to dealing with osteochondritis dissecans. Here’s how:
- Avoid high-impact activities that stress the joint too much.
- Change your daily activities to lessen stress on the joint.
- Do low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to keep the joint moving and strong.
Also, follow sports participation guidelines to play safely. This might mean wearing protective gear or avoiding sports that stress the joint too much.
By adjusting your lifestyle and following these guidelines, you can lower the risk of problems and keep your joint healthy. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional to create a plan that fits your needs and helps your joint stay healthy.
Conclusion
Osteochondritis dissecans is a complex joint condition that needs a deep understanding and specific treatment. We’ve learned a lot about its definition, causes, symptoms, and how to manage it. Knowing the risks, getting the right diagnosis, and using the right treatments can help those with osteochondritis dissecans recover and improve their joint health.
As we wrap up, it’s key to remember that osteochondritis dissecans can be managed well. With the right help and a proactive mindset, people can get back to their active lives. Following rehabilitation plans, making lifestyle changes, and talking to doctors can help patients get better and stay strong.
Remember, osteochondritis dissecans is treatable. With proper care and support, people can regain their joint mobility, lessen pain, and improve their life quality. Using the knowledge from this guide, you can protect your joint health and start a journey towards a more active and fulfilling life.
FAQ
Q: What is Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: Osteochondritis Dissecans is a joint disorder. It happens when a piece of cartilage and bone gets damaged or separates from the bone. This can cause pain, instability, and limited movement in the joint.
Q: What are the most common locations for Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: It often affects the knee, elbow, and ankle joints. This condition can seriously impact joint health, leading to pain, instability, and limited mobility.
Q: What are the risk factors for developing Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: Risk factors include genetic predisposition and sports-related injuries. It’s also more common in adolescents and young adults.
Q: What are the typical signs and symptoms of Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: Symptoms include pain, swelling, and limited mobility. Some people may also experience joint locking or catching, indicating a loose fragment.
Q: How is Osteochondritis Dissecans diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging studies, and lab tests. Sometimes, surgery is needed to diagnose and treat it.
Q: How is Osteochondritis Dissecans classified and staged?
A: It’s classified into stages based on severity. This helps doctors choose the best treatment and predict outcomes.
Q: What are the treatment options for Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: Treatments include rest, physical therapy, and pain management. Surgery like drilling or microfracture may also be needed. Rehabilitation exercises are crucial for recovery.
Q: What is the recovery timeline and expectations for Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: Recovery time varies based on the condition’s severity and treatment. Most people can recover fully in several months to a year. Ongoing rehabilitation and follow-up care are often necessary.
Q: How can Osteochondritis Dissecans be prevented?
A: Prevention involves modifying activities, using protective gear, and strengthening exercises. Wearing protective equipment and improving joint stability can help prevent it.
Q: What is the long-term prognosis and potential complications of Osteochondritis Dissecans?
A: The prognosis is generally good, but untreated or delayed treatment can lead to complications. These can include chronic pain, limited mobility, and degenerative joint disease.
Q: How can individuals living with Osteochondritis Dissecans make lifestyle adjustments?
A: Lifestyle adjustments are needed to promote joint health and prevent complications. This includes managing daily activities, following sports guidelines, and maintaining a healthy diet and staying hydrated.
