Understand osteonecrosis: uncover the causes, recognize the symptoms, and explore treatment options for healthier bones and joints.
Osteonecrosis, or Avascular necrosis: This serious condition happens when blood stops flowing to the bones, causing them to die. It’s important to understand osteonecrosis, especially for those at risk or seeing joint degeneration. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, treatments, and ways to prevent this condition in this article.
Key Takeaways
- Osteonecrosis affects 20,000 to 30,000 people each year in the U.S.
- It is characterized by the disruption of blood flow leading to bone death.
- Avascular necrosis can lead to severe pain and deterioration of joints.
- Early diagnosis is key in managing this condition effectively.
- Treatment options vary and may include medication, therapy, or surgery.
- Awareness of risk factors plays a crucial role in prevention.
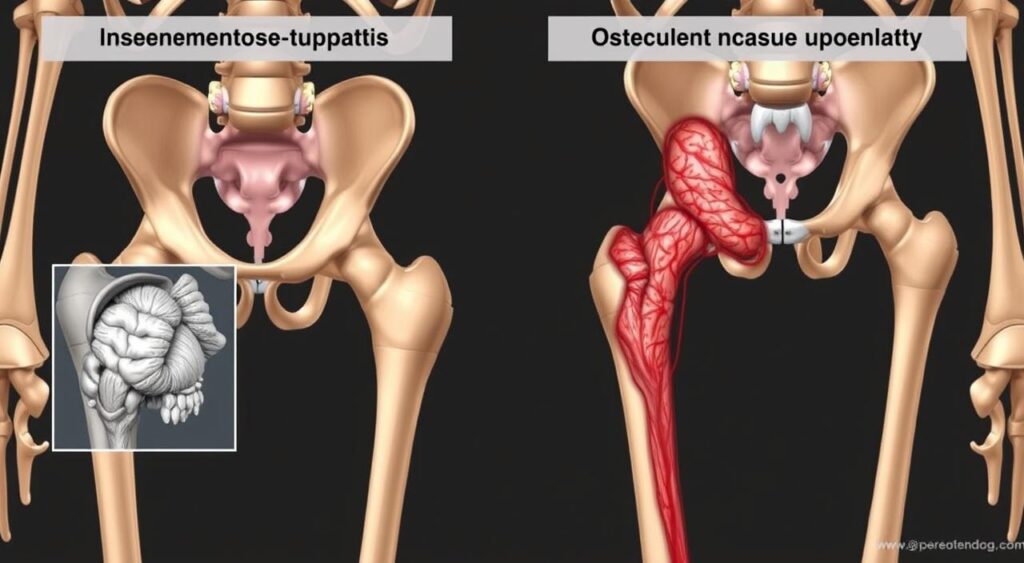
What is Osteonecrosis?
Osteonecrosis is a serious health problem where bone tissue dies because it doesn’t get enough blood. This leads to necrotic lesions that harm bone health. The hip, knee, and shoulder joints are often affected, causing a lot of pain and making it hard to move.
Knowing what osteonecrosis is is key to catching it early. When bones don’t get enough blood, cells start to die. This creates necrotic lesions that make bones weak. Getting medical help quickly can help ease pain and stop the damage from getting worse.
Things that can cause osteonecrosis include injuries and health issues that mess with blood flow. Knowing about these can help keep bones healthy. Scientists are always looking for ways to stop osteonecrosis and improve life for those who have it.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Death of bone tissue due to lack of blood supply |
| Affected Areas | Hip, knee, shoulder joints |
| Symptoms | Pain, limited mobility, joint stiffness |
| Importance of Early Detection | Prevents further degeneration and maintains joint health |
Understanding Avascular Necrosis
Avascular necrosis (AVN) is a type of bone death caused by a lack of blood flow. It harms joint health, causing pain and disability. The hip, knee, and shoulder are common places it affects, but other bones can be involved too.
The problem with AVN is that it stops bones from getting the blood they need. This can happen for many reasons, like:
- Corticosteroid use
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Medical conditions such as lupus or diabetes
- Previous joint or bone injuries
Knowing about avascular necrosis helps stop joint damage. Early treatment can make a big difference in someone’s life. Finding and treating the causes of this condition is key to managing it well.
| Risk Factor | Effect on Joint Health |
|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Can weaken bone tissue and diminish blood supply |
| Alcohol | Interferes with blood flow and bone repair |
| Underlying medical conditions | May predispose individuals to reduced circulation |
| Previous fractures | Can disrupt blood supply to bone |
Causes of Osteonecrosis
Understanding what causes osteonecrosis is key to preventing and treating it. Many factors lead to this condition, especially trauma and its effect on bones. An injury can cut off blood flow to bones, which is vital for their health.
Other risk factors, like certain demographics and conditions like osteoporosis, also play a big role. These factors make some people more likely to get osteonecrosis.
Trauma and Its Impact on Bone Health
Trauma is a major cause of osteonecrosis. High-impact injuries, especially in the hip or other joints, can harm bone blood supply. When bones get fractures or dislocations, the blood flow can stop, leading to necrosis if not treated right.
People who have had such injuries should watch their bone health closely.
Risk Factors: Who is Most Affected?
Some groups are more at risk for osteonecrosis. People aged 30-50 are more likely to get it. Heavy drinking or using steroids also raises the risk.
Medical conditions like lupus or sickle cell disease also increase the risk. Knowing these risks is important for preventing osteonecrosis.
Link to Osteoporosis and Bone Health
Osteoporosis makes bones weak and brittle, raising the risk of osteonecrosis. Less bone density means less blood supply, leading to necrotic lesions. Keeping bones healthy is crucial in preventing osteonecrosis and ensuring good health for a long time.
Symptoms of Osteonecrosis
Spotting the signs of osteonecrosis is key to getting help fast. The first sign is often joint pain, which feels dull or throbbing. This pain gets worse when you move but might feel a bit better when you rest.
Identifying Joint Pain
The first signs of joint pain from osteonecrosis can be hard to notice. You might feel a dull ache or tenderness in your hip, knee, or shoulder. Not paying attention to these osteonecrosis symptoms can make it harder to get treatment on time.
Stages of Osteonecrosis Symptoms
The symptoms of osteonecrosis go through different stages. It starts with mild pain that gets worse over time. As the bone damage gets more serious, you might feel:
- More pain when you move
- Stiffness in the joint
- Less ability to move your joint
- Swelling around the joint
This shows you need to see a doctor sooner rather than later.
Understanding Bone Death in Context
Bone death from osteonecrosis can cause more than just pain. It can also affect how well you can move and your overall quality of life. Knowing how osteonecrosis relates to chronic pain helps doctors take a better care of you.
| Stage | Symptoms | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early | Mild joint pain, tenderness | Minimal impact on daily activities |
| Mid | Increased joint pain, stiffness | Limitations in movement |
| Advanced | Severe pain, significant dysfunction | Chronic pain and disability |
Diagnosis of Osteonecrosis
Diagnosing osteonecrosis starts with a detailed clinical evaluation. This step involves looking at the patient’s medical history. It checks for any past injuries or conditions that could harm the bones.
Next, imaging tests are key to confirming the diagnosis. They help see how far the condition has spread. Common tests include:
| Imaging Test | Purpose | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray | Initial assessment of bone structure | Quick and widely available |
| MRI | Detailed view of bone and surrounding tissues | Highly sensitive to early bone changes |
| CT Scan | Cross-sectional images for precise evaluation | Useful for complex cases and surgical planning |
These imaging tests give important details for a correct diagnosis. By combining clinical evaluation and imaging, doctors can create a specific treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Osteonecrosis
Treating osteonecrosis involves different approaches based on the condition’s severity and the patient’s needs. Early treatments often include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Medications for Pain Relief and Inflammation
Medications are key in treating osteonecrosis early on. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce pain and inflammation. For severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to slow bone damage.
The right medication depends on the patient’s health and needs.
Physical Therapy as a Treatment Approach
Physical therapy is vital for osteonecrosis patients. It aims to improve joint mobility and strengthen muscles. Techniques like stretching and ultrasound therapy help manage pain and improve function.
Regular therapy helps manage symptoms and supports long-term recovery.
Surgical Options: When is Total Joint Replacement Necessary?
If other treatments fail, surgery may be needed. Total joint replacement is often chosen for advanced osteonecrosis. Surgeons consider age, activity level, and health before surgery.
This surgery aims to restore function and relieve pain, improving life quality.
Living with Osteonecrosis
Living with osteonecrosis brings its own set of challenges. Finding effective ways to cope is key. By managing daily life well, you can better handle the symptoms of osteonecrosis. This includes finding ways to reduce pain and keep moving, all while adjusting to new lifestyle habits.
Managing Symptoms in Daily Life
There are practical steps you can take to improve your life with osteonecrosis. Pacing yourself during the day helps avoid too much fatigue and pain. Using tools like canes or walkers can make moving around safer and more stable.
It’s also important to protect your joints. This means not putting too much stress on them. Doing so helps you stay independent and mobile.
Importance of Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Regular health checks and monitoring are crucial for managing osteonecrosis. These visits help track how the disease is progressing. They also allow for adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
These regular assessments are key to avoiding serious complications. Neglecting them can lead to bigger problems down the line.
| Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pacing Activities | Balancing tasks to avoid fatigue | Improves energy levels and reduces pain |
| Assistive Devices | Using tools for mobility support | Enhances stability and safety |
| Joint Protection | Avoiding stress on affected joints | Maintains independence and prevents injury |
| Regular Check-ups | Frequent evaluations by healthcare professionals | Tracks progress and adjusts treatment |
Preventing Osteonecrosis
To prevent osteonecrosis, we need a plan that covers nutrition and exercise. Eating foods high in calcium and vitamin D is crucial. It helps keep bones strong and lowers the risk of osteonecrosis.
Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing activities, is also key. These lifestyle changes boost fitness and bone density. Walking, running, and strength training are great options.
It’s important to watch how much alcohol you drink. Too much can harm your bones. Also, try to avoid using corticosteroids for a long time. They can increase the risk of osteonecrosis.
In short, eating right, exercising, and making smart lifestyle choices can help prevent osteonecrosis. By taking these steps, you can protect your bones for the long run.
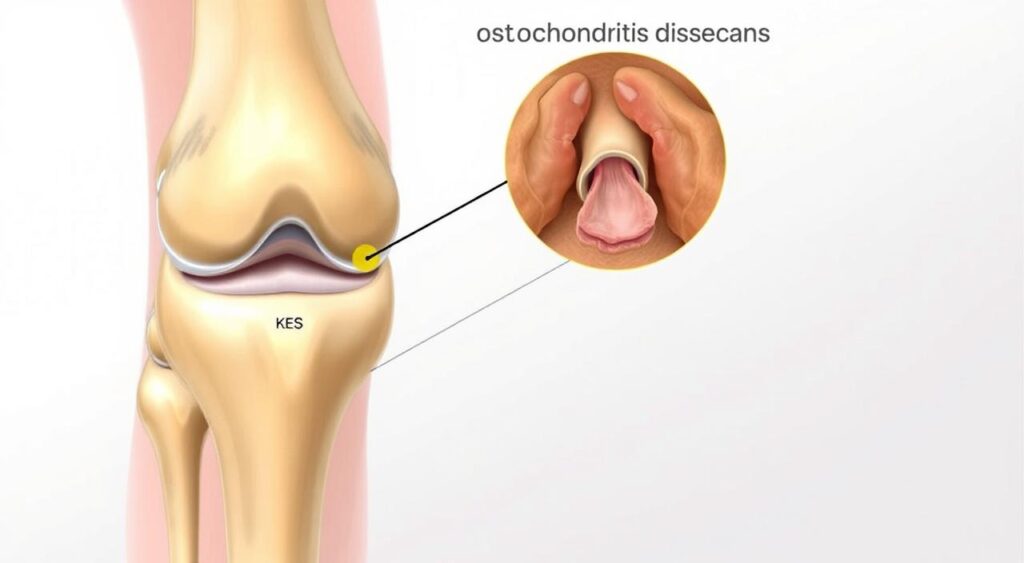
Related Conditions: Osteochondritis Dissecans
Osteochondritis dissecans is a serious issue that affects bones and cartilage. It happens when a bone part loses blood supply, causing pain and joint problems. Many people show symptoms similar to osteonecrosis, so it’s key to know about both.
In osteochondritis dissecans, the bone might become loose and move into the joint. This can lead to more issues like swelling and stiffness. Knowing about this condition helps spot early signs and get medical help fast.
It’s important to watch for signs of joint problems and get medical advice. Learning about osteochondritis dissecans and other joint issues helps improve bone health. People with joint problems should see doctors regularly for early treatment.
The Role of Nutrition in Bone Health
Nutrition is key to keeping bones healthy. It helps prevent diseases like osteonecrosis. Eating the right foods boosts bone density and strength, which is vital for joint health.
Essential Nutrients for Strong Bones
To keep bones strong, you need to eat certain nutrients:
- Calcium: It’s essential for building strong bones.
- Vitamin D: Helps your body absorb calcium and supports bone health.
- Protein: It helps maintain bone density and strength.
- Magnesium: Important for bone formation.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium to strengthen bone structure.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Living a healthy lifestyle also helps prevent osteoporosis and osteonecrosis. Here are some tips:
- Regular Exercise: Activities that make your bones work harder help strengthen them.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of foods to get all the vitamins and minerals you need.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol: These can harm your bones.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being too thin can increase bone loss risk.
Research and Future Directions in Osteonecrosis Treatment
Osteonecrosis research is growing, showing the need for new treatments. Studies now focus on ways to fix blood flow and heal bones. This includes stem cell therapy and better bone grafting.
Scientists say we need treatments that fit each patient’s needs. This means not just medicine, but also changes in lifestyle to help heal and stop the disease from getting worse.
The future of osteonecrosis treatment looks promising. It will involve working together from many fields. This teamwork will help find better ways to manage the disease and improve life for those affected.
| Research Focus | Potential Treatment Advancements |
|---|---|
| Stem Cell Therapy | Regeneration of Bone Tissue |
| Bone Grafting Techniques | Improved Bone Repair |
| Combination Therapies | Enhanced Healing Processes |
| Patient-Centered Approaches | Tailored Treatment Plans |
Conclusion
Osteonecrosis is a serious condition that affects bone health. This summary shows why it’s key to know its causes and symptoms. This way, people can spot early signs and get the right medical help.
Being aware of health risks is important, especially for those at risk. Making healthy choices like eating well, staying active, and getting regular check-ups helps a lot. For those with osteonecrosis, treatments like medicine and physical therapy can help keep joints working well.
Knowing about osteonecrosis helps people take control of their health. By learning about it, they can make smart health choices. This leads to a better life quality.
FAQ
Q: What is osteonecrosis?
A: Osteonecrosis, also known as avascular necrosis, is when blood stops flowing to the bone. This causes the bone to die. It can lead to joint damage and severe pain.
Q: What causes avascular necrosis?
A: Many things can cause avascular necrosis. These include injuries, long-term use of corticosteroids, heavy drinking, and certain diseases. These factors can block blood flow to the bone.
Q: What are the symptoms of osteonecrosis?
A: Symptoms include pain in the joint that gets worse with movement, stiffness, and less ability to move. As it gets worse, the pain and mobility problems can become severe.
Q: How is osteonecrosis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use a few ways to diagnose osteonecrosis. They look at your medical history and do tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. These help see how much damage there is.
Q: What treatment options are available for osteonecrosis?
A: There are several treatments. Doctors might give you pain medicine and anti-inflammatory drugs. Physical therapy can also help. In serious cases, surgery like a joint replacement might be needed.
Q: How can I manage symptoms of osteonecrosis in daily life?
A: To manage symptoms, pace yourself and use aids if needed. Physical therapy and joint protection can also help. These steps can keep you independent and active.
Q: Can osteonecrosis be prevented?
A: Not all cases can be prevented, but you can lower your risk. Eating well, exercising, not drinking too much, and avoiding long-term corticosteroids can help.
Q: What lifestyle changes promote bone health?
A: To keep your bones healthy, eat foods with calcium and vitamin D. Do exercises that make your bones strong. Avoid smoking and drinking too much. These habits can harm your bones.
Q: Is there ongoing research in osteonecrosis treatment?
A: Yes, there’s always new research. Scientists are working on treatments like stem cell therapy and better surgery methods. These could lead to better care for people with osteonecrosis.
