Understand the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for otosclerosis, a leading cause of hearing loss.
A staggering 1 in 100 people suffer from otosclerosis, a type of ear bone disease. It can lead to hearing loss. Otosclerosis affects the middle ear, causing abnormal bone growth. This growth can block sound waves, leading to hearing loss.
This condition can make everyday activities a challenge. Understanding otosclerosis, its causes, symptoms, and management is key. It’s important for timely intervention and improving hearing health.
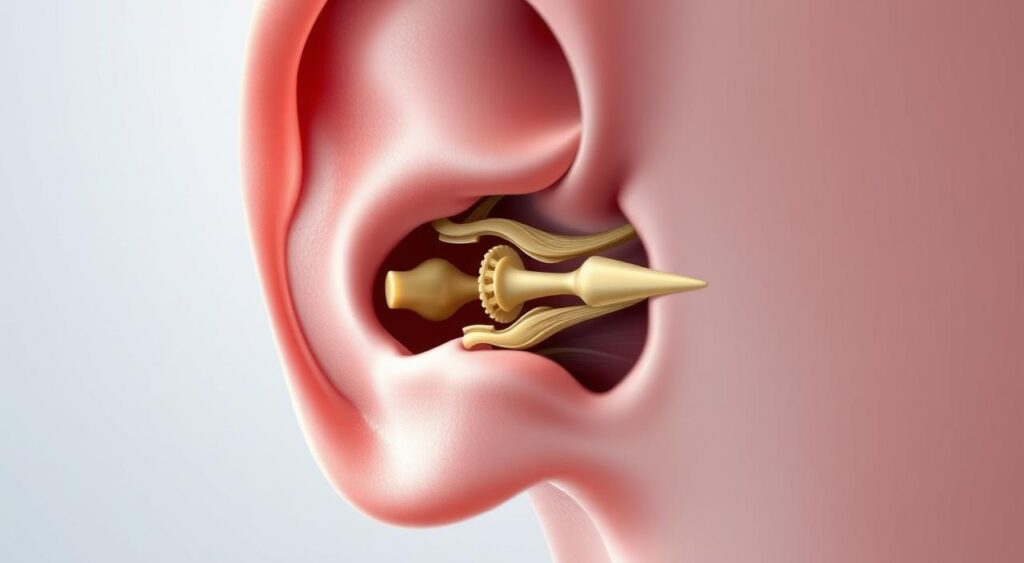
Otosclerosis is a complex condition that needs a comprehensive management approach. By knowing its causes, like genetic predisposition and hormonal influences, individuals can take proactive steps. Effective management includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and support systems.
In this article, we’ll explore otosclerosis. We’ll look at its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies. Our focus will be on hearing loss and ear bone disease.
Key Takeaways
- Otosclerosis is a type of ear bone disease that can cause hearing loss
- 1 in 100 people in the United States suffer from otosclerosis
- Understanding the causes of otosclerosis is crucial for effective management
- Genetic predisposition, hormonal influences, and environmental factors contribute to otosclerosis
- Effective management of otosclerosis involves medical treatment, lifestyle adaptations, and support systems
- Otosclerosis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life
- Early intervention and treatment can improve hearing health and mitigate the effects of otosclerosis
Understanding Otosclerosis: An Overview
Otosclerosis is a middle ear condition that leads to hearing loss. It’s linked to otospongiosis, affecting the ear bones. Knowing what it is, how common it is, and its impact on daily life is key.
Otosclerosis can greatly affect your daily life. Symptoms include:
- Hearing loss, from mild to severe
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears
- Balance problems
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy places
In the United States, about 1 in 100 people have otosclerosis. It’s more common in women, especially during pregnancy. The exact cause is still a mystery, but genetics and environment might play a role.
There’s no cure for otosclerosis, but treatments can help manage symptoms. Options include hearing aids, surgery, and medications. Understanding otosclerosis helps individuals manage their condition and improve their life quality.
The Anatomy of Hearing and How Otosclerosis Affects It
The human ear is a complex and delicate organ. It detects sound waves and sends them to the brain. The ossicles, three small bones in the middle ear, are key to sound conduction.
When sound waves hit the ear, they make the eardrum vibrate. This vibration moves the ossicles to vibrate too. These vibrations then go to the inner ear, where they become electrical signals sent to the brain.
Otosclerosis can harm the ossicles, causing conductive hearing loss. This hearing loss happens when sound can’t reach the inner ear right. In otosclerosis, abnormal bone growth in the middle ear fixes the ossicles, stopping them from vibrating. This makes it hard to hear speech and other sounds.
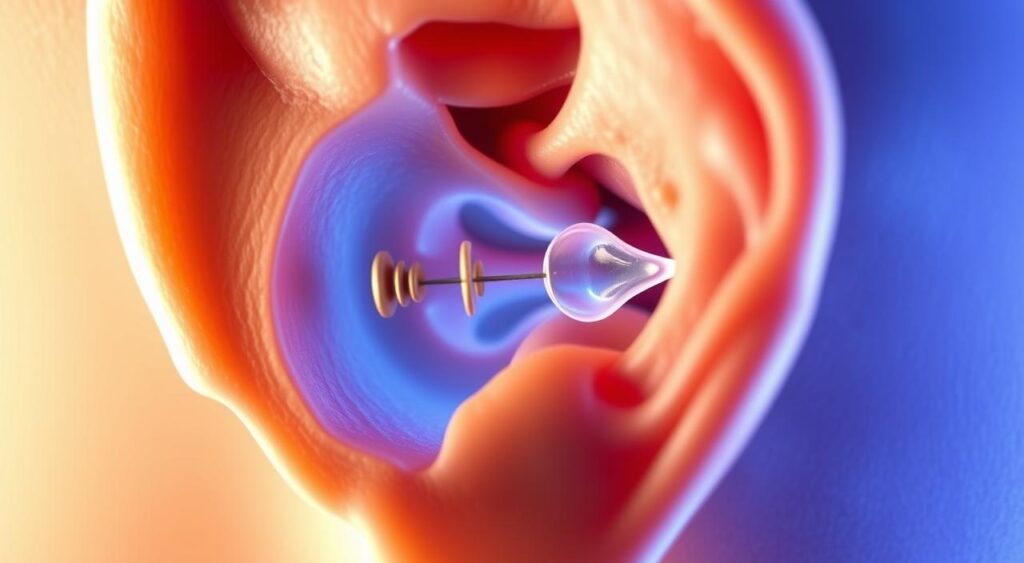
Knowing how the ear works and how otosclerosis affects it is key to treating it. Recognizing the ossicles‘ role in hearing helps those with otosclerosis manage their condition. They might need surgery to remove the abnormal bone or use hearing aids to boost sound.
With the right treatment and care, people with otosclerosis can improve their hearing. This helps reduce the impact of conductive hearing loss on their daily lives.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Otosclerosis is a complex condition. Researchers have found several factors that contribute to it. Genetic predisposition is a big factor, as people with a family history are more likely to get it. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or other times can also trigger it in some.
Studies show that otosclerosis is linked to genetics, hormones, and environment. For example, having otospongiosis can raise the risk. Here are some key risk factors:
- Family history of otosclerosis
- Pregnancy or hormonal changes
- Certain medical conditions, such as otospongiosis
- Exposure to loud noises or environmental toxins
Knowing the causes and risk factors of otosclerosis is key to managing it. Recognizing the role of genetic predisposition and hormonal influences helps. This way, people can take steps to lower their risk and prevent hearing loss.
Recognizing the Signs of Otosclerosis
Otosclerosis symptoms can vary from person to person. Hearing loss is the most common complaint. It can be gradual or sudden, and it may affect one or both ears.
Other symptoms include ringing or buzzing in the ears, balance problems, and a feeling of fullness in the ears.
Some people may experience hearing loss that worsens over time. Others may have stable hearing loss. It’s essential to recognize the signs of otosclerosis and seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
Here are some common signs of otosclerosis:
- Hearing loss that worsens over time
- Ringing or buzzing in the ears
- Balance problems
- A feeling of fullness in the ears
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a doctor or an audiologist. They can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further hearing loss.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Otosclerosis diagnosis uses physical exams, hearing tests, and imaging studies. It starts with a doctor checking for hearing loss signs. This is the first step in finding out if you have otosclerosis.
Hearing tests are crucial in diagnosing otosclerosis. They include pure tone audiometry and speech audiometry. These tests check how well you can hear sounds and understand speech. Sometimes, CT scans or MRI scans are used to see the middle ear bones. This helps confirm if you have otosclerosis.
- Hearing tests to assess the extent of hearing loss
- Imaging studies to visualize the bones in the middle ear
- Physical examination to check for signs of hearing loss or other related symptoms
Doctors use these tools together to accurately diagnose otosclerosis. This way, they can create a good treatment plan. It helps manage the condition and improve your hearing.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Otosclerosis treatment aims to improve hearing and reduce symptoms. A common surgery is stapedectomy. It removes part of the fixed stapes bone and replaces it with a prosthetic device. This surgery can greatly improve hearing in people with otosclerosis.
Non-surgical management strategies are also available. These include hearing aids and other assistive listening devices. They can help improve communication and reduce the impact of hearing loss on daily life.
Some benefits and risks associated with otosclerosis treatment options include:
- Improved hearing and communication
- Risks of surgical complications, such as infection or further hearing loss
- Cost and accessibility of treatment options
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for otosclerosis. They can help individuals understand the available options and make an informed decision about their care.
Living with Otosclerosis: Lifestyle Adaptations
People with otosclerosis can live full lives with some changes. Living with otosclerosis means being aware, using communication strategies, and having a strong support system. Knowing your condition helps manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Good communication strategies are key for those with otosclerosis. This includes speaking clearly and using visual aids. It also means avoiding loud places. Support systems are also crucial for emotional and social challenges. Joining groups, counseling, and having a close network of friends and family help a lot.
- Using assistive listening devices, such as hearing aids or cochlear implants
- Avoiding loud noises and protecting hearing
- Staying connected with friends and family through regular communication
- Seeking professional help when needed, such as counseling or speech therapy
With these strategies and a strong support network, people with otosclerosis can live active and full lives. Despite the challenges, they can thrive.
Prevention and Long-term Outlook
Otosclerosis prevention is a complex topic. The condition is largely unpredictable. However, research shows that early detection and treatment can slow hearing loss. People with a family history should protect their hearing by avoiding loud noises and getting regular check-ups.
The long-term outlook for otosclerosis varies. It depends on the condition’s severity and treatment success. With proper care, many people see big improvements in their hearing. It’s key to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan and keep up with follow-up appointments.
Several factors can affect the long-term outlook for otosclerosis:
- Age at diagnosis
- Severity of hearing loss
- Effectiveness of treatment
- Presence of other underlying health conditions
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are vital for managing otosclerosis. By working with a healthcare provider and taking steps to protect their hearing, individuals can improve their outlook. This helps maintain their quality of life.
Otosclerosis prevention and management need a comprehensive approach. This includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Understanding the condition’s progression and taking proactive steps can lead to a favorable long-term outlook. This results in improved hearing and overall well-being.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Hearing Health
As we wrap up our look at otosclerosis, remember you can control your hearing health. Otosclerosis may be tough, but with the right info and action, you can manage it well. This keeps your life quality high.
Knowing what causes otosclerosis and spotting early signs are key. Getting medical help early is also important. Regular check-ups and following your treatment plan help keep your hearing sharp.
Also, making lifestyle changes and finding ways to communicate better can help. Connecting with others who face similar issues is powerful. You’re not alone, and there’s help out there.
Keep up the good work in taking care of your hearing. With the right mindset and tools, you can beat otosclerosis’s challenges. Use this knowledge to improve your hearing and enjoy a better future.
FAQ
Q: What is otosclerosis?
A: Otosclerosis is a condition that affects the middle ear. It involves abnormal bone growth around the stapes, a tiny bone in the ear. This can cause hearing loss.
Q: How common is otosclerosis?
A: Otosclerosis is quite common, affecting 3% to 10% of people. It’s more common in Caucasians and often diagnosed between 15 and 45 years old.
Q: What are the symptoms of otosclerosis?
A: Symptoms include gradual hearing loss and tinnitus. You might also feel dizzy or have pressure in your ear.
Q: How does otosclerosis affect hearing?
A: It stops the stapes bone from vibrating. This makes it hard for sound to reach the inner ear, causing hearing loss.
Q: What causes otosclerosis?
A: The exact cause is unknown. But it’s thought to be influenced by genetics, hormones, and certain health conditions.
Q: How is otosclerosis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use physical exams, hearing tests, and imaging like CT scans to diagnose it.
Q: What are the treatment options for otosclerosis?
A: Treatments include surgery to replace the stapes bone and non-surgical options like hearing aids.
Q: How can I manage my daily life with otosclerosis?
A: Use amplification devices and communicate effectively. Workplace adjustments and support from loved ones can also help.
Q: What is the long-term outlook for individuals with otosclerosis?
A: Outcomes vary. Some see improvement, while others experience ongoing hearing loss. Regular check-ups are key to managing the condition.
