Imagine a small organ, no bigger than a human hand, controlling your digestive system. This is pancreatitis, a serious condition affecting 300,000 Americans yearly. It causes inflammation in the pancreas, which is key for digestion and hormone production. A simple meal can become a nightmare with pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis has two types: acute and chronic. Each has its own causes, symptoms, and treatments. Knowing about pancreatitis is vital, as it can be deadly if not treated. This guide will help you understand pancreatitis, its signs, and how to manage it.
Key Takeaways
- Pancreatitis is a condition marked by inflammation of the pancreas, a small but vital organ in the digestive system.
- It can manifest as acute pancreatitis, a sudden onset of symptoms, or chronic pancreatitis, a persistent and progressive form of the disease.
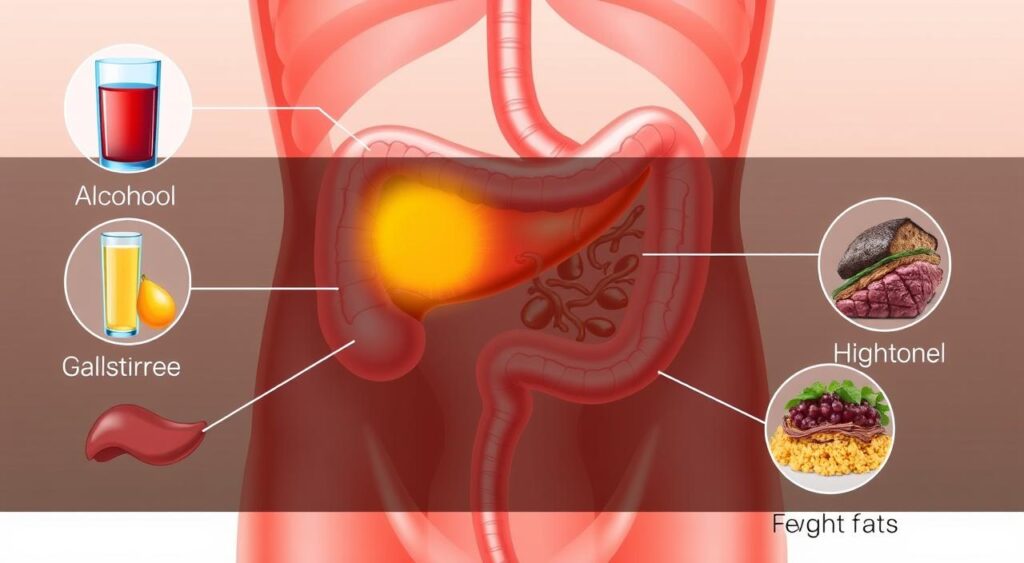
- Common causes include gallstones, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications, while symptoms range from severe abdominal pain to nausea and vomiting.
- Prompt medical attention is crucial, as pancreatitis can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated.
- Treatment options may include pain management, dietary changes, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
Understanding Pancreatitis: An Overview
The pancreas is a key organ behind the stomach. It helps break down food into nutrients. When it gets inflamed, it can cause many digestive problems.
The Role of the Pancreas in Digestive Health
The pancreas makes enzymes to digest food. These enzymes are vital for breaking down proteins, fats, and carbs. It also makes hormones like insulin to control blood sugar.
Types of Pancreatic Inflammation
Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is sudden and severe, often from gallstones or too much alcohol. Chronic is long-term, causing lasting damage and digestive issues.
Impact on Overall Health
Pancreatitis affects health greatly. It can cause severe pain, nausea, and malnutrition. In bad cases, it can lead to organ failure and death. Getting medical help quickly is crucial.
| Condition | Symptoms | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Pancreatitis | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting | Gallstones, excessive alcohol consumption |
| Chronic Pancreatitis | Persistent abdominal pain, maldigestion, malnutrition | Alcohol abuse, genetic factors, autoimmune disorders |
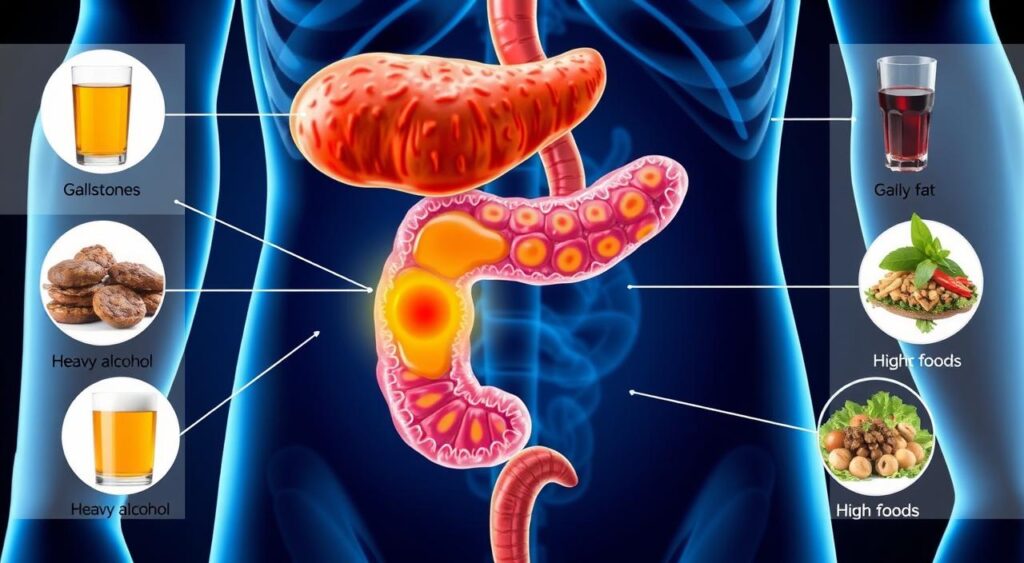
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is a painful and serious condition. It happens when the pancreas gets inflamed. Several common factors can cause this inflammation.
Gallstones are a leading cause of acute pancreatitis. These hard deposits can block the pancreatic duct. This prevents digestive enzymes from flowing properly, causing inflammation. Drinking too much alcohol is also a major risk factor. It can irritate the pancreas and disrupt its function.
Certain medications, like some antibiotics and cancer treatments, can increase the risk of acute pancreatitis. People with a family history of hereditary pancreatitis are also at higher risk due to genetics.
Other causes include abdominal trauma, viral infections, and certain medical conditions. These include high triglyceride levels or diabetes. The abdominal pain from these causes can be very severe and needs quick medical help.
| Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Gallstones | Hard deposits that form in the gallbladder and can block the pancreatic duct, leading to inflammation. |
| Alcohol Consumption | Excessive alcohol intake can irritate the pancreas and disrupt its normal function. |
| Medications | Certain medications, such as antibiotics, corticosteroids, and cancer treatments, have been associated with an increased risk of acute pancreatitis. |
| Hereditary Pancreatitis | Individuals with a family history of pancreatitis may have a genetic predisposition to the condition. |
Knowing the common causes and risk factors of acute pancreatitis is key. It helps in early diagnosis and effective management. Healthcare providers can then develop targeted treatments. They can also guide patients to reduce the risk of future episodes.
Recognizing Chronic Pancreatitis: Signs and Development
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-lasting condition where the pancreas keeps getting inflamed. It’s different from acute pancreatitis because it doesn’t always get better with treatment. Knowing the early signs and how symptoms develop is key to managing it well.
Early Warning Signs
In the early stages, people might feel pain in the upper abdomen or back. This pain can happen after eating fatty or heavy foods. It might also cause nausea, vomiting, or indigestion. As it gets worse, the pain can become more constant and severe.
Progressive Symptoms
As chronic pancreatitis gets worse, more symptoms appear. These include unintentional weight loss, malnutrition, and steatorrhea (excess fat in the stool). This is because the pancreas can’t work right, making it hard to absorb nutrients. Autoimmune pancreatitis, a specific type, might also cause jaundice and high antibody levels.
Complications Over Time
If not treated, chronic pancreatitis can cause serious problems. These include strictures, stones, and pseudocysts in the pancreas. These issues can make digestion worse, leading to malabsorption, diabetes, and a higher risk of pancreatic cancer.
It’s important to catch chronic pancreatitis early and manage it well. Working with healthcare providers can help. This way, people can control their symptoms, keep their digestive system healthy, and avoid serious complications.
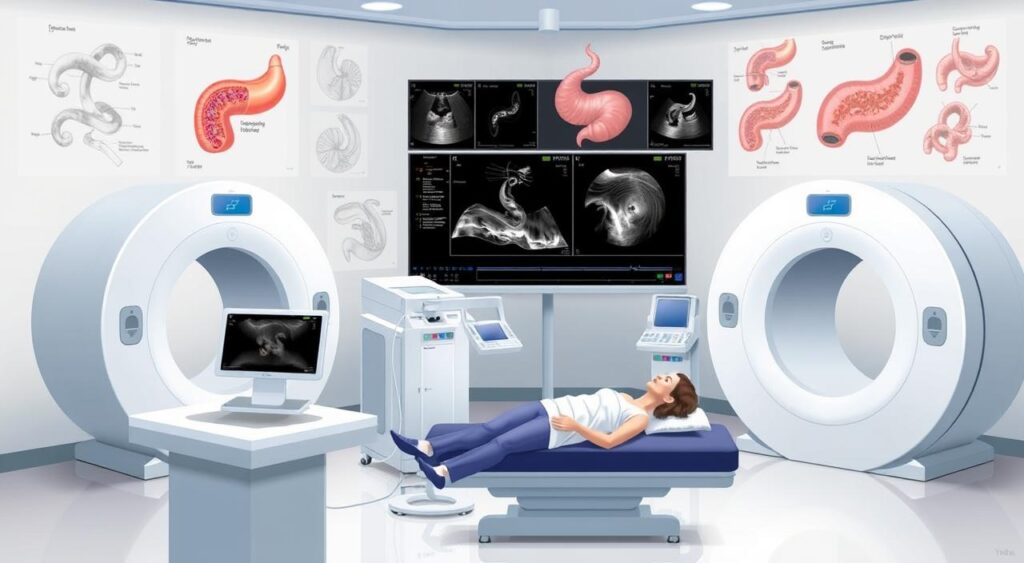
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
To diagnose pancreatitis, doctors use many tests. These help tell pancreatitis apart from other stomach problems. They also find out why someone is in pain.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are a first step in diagnosing pancreatitis. Doctors check for high levels of pancreatic enzymes like amylase and lipase. These tests show if the pancreas is inflamed and how bad it is.
Imaging Studies
Doctors also use imaging tests to look at the pancreas and nearby areas. These include:
- Abdominal ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the pancreas and other organs. It helps find any problems or changes.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan makes detailed pictures of the abdomen with X-rays. It shows how much the pancreas is inflamed or damaged.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to make clear pictures of the pancreas and tissues around it. It gives important information about the organ’s condition.
Functional Assessments
Doctors might also do tests to see how well the pancreas works. Tests like the secretin stimulation test or the pancreatic function test help find the cause of pancreatitis. They help decide the best treatment.
| Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood Tests | Measure pancreatic enzyme levels to confirm pancreatitis |
| Abdominal Ultrasound | Visualize the pancreas and surrounding structures for abnormalities |
| CT Scan | Generate detailed images of the abdomen to assess pancreatic inflammation and damage |
| MRI | Provide high-resolution images of the pancreas and surrounding tissues |
| Functional Tests | Evaluate the pancreas’s ability to produce and secrete digestive enzymes |
By using these tests together, doctors can accurately diagnose pancreatitis. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the person’s needs.
Medical Treatment Options for Acute Cases
Managing acute pancreatitis requires a variety of treatments. Doctors use emergency care, pain relief, and special diets to help patients get better. Each treatment is chosen based on the patient’s specific needs.
Emergency Interventions
In serious cases of acute pancreatitis, doctors take quick action. They give fluids through an IV, use pancreatic enzyme therapy, and sometimes stop eating to help the pancreas heal.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain is a big problem in acute pancreatitis. Doctors use medicines like opioids and NSAIDs to help with pain. They also try other methods like nerve blocks for more severe pain.
Dietary Modifications
Changing what you eat is key in treating acute pancreatitis and gastrointestinal diseases. Doctors suggest eating less fat and protein to ease the pancreas’s work. Sometimes, pancreatic enzyme therapy is needed to help digest food better.
| Treatment Approach | Objectives | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Interventions | – Stabilize patient condition – Support pancreatic healing | – Intravenous fluid administration – Pancreatic enzyme therapy – Temporary cessation of oral intake |
| Pain Management Strategies | – Alleviate discomfort – Promote patient comfort | – Analgesics (opioids, NSAIDs) – Nerve blocks – Interventional radiology procedures |
| Dietary Modifications | – Reduce pancreatic workload – Support healing process | – Low-fat, low-protein diet – Pancreatic enzyme therapy |
Doctors use a mix of emergency care, pain relief, and special diets to fight acute pancreatitis. This approach helps patients recover well.
Managing Chronic Pancreatitis Long-term
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-lasting and often painful digestive disorder. It needs ongoing care to lessen symptoms and avoid more problems. Good long-term care includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and pancreatic enzyme therapy.
At the heart of managing chronic pancreatitis is pancreatic enzyme supplements. These medicines replace the missing digestive enzymes. They help break down and absorb nutrients better. This can ease malabsorption, reduce pain, and improve digestive health.
| Pancreatic Enzyme Therapy Benefits | Importance for Chronic Pancreatitis |
|---|---|
| Improved nutrient absorption | Addresses malabsorption issues and malnutrition |
| Reduced abdominal pain and discomfort | Enhances quality of life and daily functioning |
| Prevention of weight loss and deficiencies | Maintains optimal nutritional status |
People with chronic pancreatitis might also need to change their diet. Eating less fat and more protein can help. It’s important to check with a doctor to make sure you’re getting the right nutrients.
Changing your lifestyle is also key in managing chronic pancreatitis. Giving up alcohol and quitting smoking are crucial. These habits can make pancreatitis worse. Regular exercise and finding ways to reduce stress can also help.
By taking a full approach to managing chronic pancreatitis, people can live better lives. This includes using medicines, changing diets, and making lifestyle changes. Together, these steps can help manage the condition and protect pancreatic health.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention Strategies
Managing pancreatitis, a common gastrointestinal disease, needs a mix of lifestyle changes. By making healthier choices, people can ease symptoms and stop future digestive disorder episodes.
Dietary Guidelines
Changing what you eat is key in handling pancreatitis. Doctors suggest eating low-fat, low-protein foods that are whole and unprocessed. This lightens the pancreas’s load and cuts down inflammation. Drinking plenty of water and eating small meals often helps digestion too.
Alcohol and Smoking Cessation
Drinking alcohol and smoking raise the risk of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Giving up these habits can greatly boost the pancreas’s health and lower digestive disorder risks. Getting help from doctors or support groups can make quitting easier.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular exercise is good for those with pancreatitis. Activities like walking, swimming, or light yoga can ease pain and boost well-being. Stress management, like through relaxation or counseling, also helps manage pancreatitis.
By making these lifestyle changes, people with pancreatitis can improve their health. This can lead to a better life and lower digestive disorder risks.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
While traditional medicine is key for pancreatitis management, some people find relief in alternative and complementary therapies. These methods, when added to standard care, can help ease abdominal pain. They also support the well-being of those with pancreatitis, including autoimmune pancreatitis.
Herbal supplements are a popular alternative. Research shows that turmeric and ginger might have anti-inflammatory effects. This could help lessen pancreatitis-related pain. But, it’s important to talk to a doctor before trying herbal remedies. They might affect other medicines you’re taking.
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory compounds, turmeric may help alleviate abdominal pain associated with pancreatitis.
- Ginger: This versatile root has been used for centuries to soothe digestive issues, including the symptoms of pancreatitis.
Mind-body practices like meditation and yoga are also promising. They can help manage stress and anxiety linked to pancreatitis. These practices promote relaxation and may reduce inflammation, making them a good addition to traditional treatments.
“Integrating alternative therapies with conventional medical care can provide a more holistic approach to managing pancreatitis and improving overall quality of life.”
It’s vital to remember that the effectiveness and safety of these treatments for pancreatitis are still being studied. Always talk to your healthcare provider before adding any complementary therapies to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pancreatitis is a serious condition that needs quick diagnosis and right treatment. It can be acute or chronic. The key is to know the causes, spot the symptoms, and get medical help.
Regular health checks, making lifestyle changes, and following diet advice can help a lot. By tackling the main causes like too much alcohol or gallstones, people can lower their risk of pancreatitis. This might also slow down chronic pancreatitis.
Managing pancreatitis is tough, but a mix of medical care, diet changes, and other therapies can help. It can ease symptoms, stop complications, and make life better. Always get medical advice if you have ongoing or getting worse pancreatitis symptoms.
FAQ
Q: What is pancreatitis?
A: Pancreatitis is when the pancreas, a key organ for digestion, gets inflamed. This can happen suddenly (acute) or last a long time (chronic).
Q: What are the different types of pancreatitis?
A: There are two main types. Acute pancreatitis is sudden and severe. Chronic pancreatitis lasts a long time and can damage the pancreas.
Q: What are the common causes of pancreatitis?
A: Common causes include gallstones, too much alcohol, certain meds, and high triglycerides. Sometimes, the cause is unknown.
Q: What are the symptoms of pancreatitis?
A: Severe abdominal pain is the main symptom. It can spread to the back. Other signs are nausea, vomiting, fever, and a fast heartbeat. Chronic pancreatitis can also cause weight loss and digestive problems.
Q: How is pancreatitis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use physical exams, blood tests, and imaging like CT scans to diagnose pancreatitis. These help find the cause and how severe it is.
Q: What are the treatment options for pancreatitis?
A: Treatment varies based on the severity and cause. For acute pancreatitis, treatment might include hospital care, IV fluids, and pain relief. Chronic pancreatitis treatment includes diet changes, enzyme therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Q: Can pancreatitis be prevented?
A: While you can’t avoid pancreatitis completely, healthy habits can lower your risk. Eating well, drinking less alcohol, and managing health issues can help.
Q: What is the role of pancreatic enzymes in the treatment of pancreatitis?
A: Pancreatic enzymes are key in treating pancreatitis, especially chronic cases. They help digest food and improve nutrient absorption, easing symptoms and preventing complications.
Q: Can pancreatitis lead to other health complications?
A: Yes, pancreatitis can cause malnutrition, diabetes, and serious issues like pancreatic necrosis or organ failure. Quick medical care and following treatment plans are crucial to avoid these problems.
