Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis: Explore this rare joint disorder, including its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment approaches.
About 1 in 1.8 million people have pigmented villonodular synovitis. It’s a rare joint disorder. It causes noncancerous tumors in the joint lining, leading to pigmented synovitis. This condition, also known as pvns, can cause a lot of pain and swelling.
If not treated, it can also damage joints severely. Knowing about pvns is key for early diagnosis and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis is a rare joint disorder that affects the synovium.
- Pvns can cause significant pain, swelling, and joint damage if left untreated.
- Early diagnosis is crucial for effective management of pigmented synovitis.
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis can be managed with proper treatment and care.
- Understanding pvns is essential for individuals who are at risk of developing this condition.
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent long-term damage.
Understanding Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS) is a rare joint disorder. It causes a noncancerous tumor to grow in the joint lining. This leads to joint disease. It often happens in the knee but can affect any joint.
Knowing PVNS is a noncancerous tumor helps us understand its impact. Joint disease from PVNS can cause a lot of pain and swelling. It’s important to know the different types of PVNS to get the right treatment.
Definition and Basic Concepts
PVNS is a rare joint disorder that affects the synovial lining. It leads to the growth of a noncancerous tumor. This can cause severe symptoms and limit mobility.
Types of PVNS
There are two main types of PVNS: localized and diffuse. Localized PVNS has a single tumor. Diffuse PVNS has multiple tumors in the joint.
Who is Most Affected
PVNS can affect anyone, but it’s more common in adults between 20 and 50. The exact cause is still unknown. If symptoms last, it’s important to see a doctor.
Understanding PVNS is key to recognizing symptoms and getting the right treatment. By knowing about its definition, types, and who it affects, we can manage the condition better. This helps prevent further problems.
| Type of PVNS | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Localized PVNS | Single tumor growth |
| Diffuse PVNS | Multiple tumor growths |
The History and Medical Background of PVNS
Pigmented villonodular synovitis, or pvns, is a joint disease known for decades. Medical experts have studied it, gaining insights into its causes and effects. PVNS involves inflammation of the synovium, a tissue in joints and tendons, leading to pigmented synovitis.
Advances in diagnosis and treatment have helped us better understand pvns. Early detection and intervention are key to managing the condition and preventing joint damage. Here are important points about pvns:
- Joint disease: pvns affects the synovium, causing inflammation and pain.
- Pigmented synovitis: It leads to the formation of pigmented nodules in the synovium, damaging the joint.
- Treatment options: Various treatments are available, including surgery, medication, and physical therapy.
Knowing the history and medical background of pvns is crucial for effective treatment. Recognizing its signs and symptoms allows medical professionals to provide timely care. This helps patients manage their condition and maintain their quality of life.
As research into pvns continues, staying updated is essential. This helps us improve our understanding of the disease and develop better treatments for those with pigmented synovitis.
| Aspect of PVNS | Description |
|---|---|
| Causes | Unknown, but may be related to trauma or genetic factors |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the affected joint |
| Treatment | Surgery, medication, and physical therapy |
Common Signs and Symptoms
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS) affects the joints, causing various symptoms. These can make daily life harder. Common pvns symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and limited movement. These symptoms can get worse over time.
Early signs of PVNS might be mild pain and swelling in a joint. As it gets worse, symptoms can lead to more pain and less mobility. Treatment options for PVNS exist, and catching it early is key to avoid lasting damage and better treatment results.
Early Warning Signs
- Mild pain in the affected joint
- Swelling or inflammation
- Warmth or redness in the affected area
Progressive Symptoms
- Increased pain and stiffness
- Decreased range of motion
- Locking or catching of the joint
Knowing the common signs and symptoms of PVNS is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment options. Spotting early signs and getting medical help can prevent long-term damage. This improves quality of life.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Joint Pain | Pain or discomfort in the affected joint |
| Swelling | Inflammation or swelling in the affected joint |
| Limited Range of Motion | Decreased ability to move the affected joint |
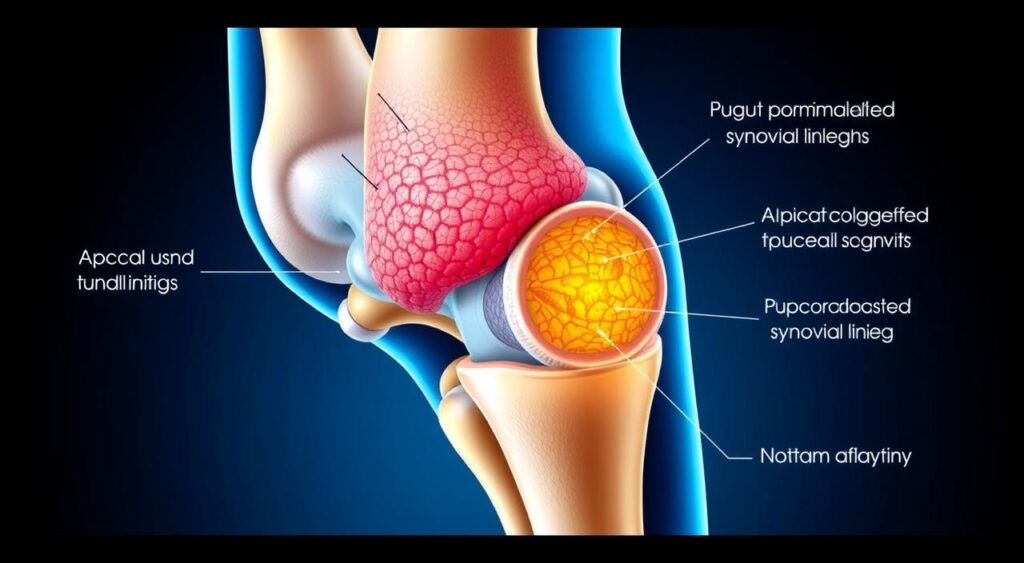
Anatomical Structures Affected by PVNS
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS) is a rare joint disorder. It mainly affects the synovium, the lining of the joints. This disease can cause noncancerous tumors to grow in the synovium, leading to symptoms and complications. Knowing which parts of the body are affected is key to finding the right treatment.
The synovium is important for joint health. It makes fluid that helps the joints move smoothly. When PVNS hits the synovium, it can cause inflammation and harm to nearby tissues. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and trouble moving the joint.
These parts can get damaged or inflamed because of the tumors in the synovium. This can cause long-term pain and make it hard to move. Doctors can create better treatment plans by knowing which parts PVNS affects.
PVNS is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive treatment approach, taking into account the specific anatomical structures affected.
Understanding how PVNS affects the synovium and nearby tissues helps people manage their condition better. With the right treatment, it’s possible to lessen symptoms and keep joints healthy.
| Anatomical Structure | Effect of PVNS |
|---|---|
| Synovium | Inflammation and damage |
| Joint cartilage | Degradation and loss |
| Bone tissue | Erosion and damage |
Risk Factors and Potential Causes
Pigmented villonodular synovitis (pvns) is a noncancerous tumor found in the joints. The exact cause is still a mystery. But, some risk factors and conditions are linked to it. These include genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, and other medical issues.
Some key risk factors for pvns are:
- Genetic mutations that affect the synovial lining of joints
- Environmental triggers, such as joint trauma or inflammation
- Associated medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis
Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing and managing pvns. By understanding the causes, people can lower their risk. This improves their joint health.
More research is needed to fully grasp pvns causes and find better treatments. Yet, by recognizing genetic and environmental roles, people can manage their joint health. This reduces the risk of getting pigmented villonodular synovitis.
Diagnostic Process and Testing Methods
The process to diagnose Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS) includes a physical exam, imaging tests, and sometimes a biopsy. Getting an accurate pvns diagnosis is key. It helps choose the right treatment options for the best results.
The steps to diagnose PVNS are:
- Physical exam to check joint movement and pain
- Imaging tests like X-rays and MRI to see the joint and tissues
- Biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and check for other conditions
Imaging tests are very important in pvns diagnosis. They show signs of PVNS, like joint swelling and thickened synovium. By using physical exams, imaging, and biopsy, doctors can create a good treatment options plan for each person.
Getting a diagnosis early is vital to avoid long-term joint damage. It also helps improve treatment results. Knowing about the diagnostic process and tests helps people with PVNS make informed choices about their care.
Medical Imaging Techniques for PVNS
Medical imaging is key in diagnosing and managing Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS). It helps doctors see how big the tumor is and how much of the joint it affects. This info is crucial for making treatment plans.
Imaging helps spot PVNS symptoms like joint pain and swelling. It shows how bad the condition is.
Accurate diagnosis is vital for managing joint diseases. Imaging like MRI, X-ray, and CT scans gives important details. MRI is especially good at showing how big the tumor is and how much of the joint it affects. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Common Imaging Modalities
- MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including tumors and joint structures
- X-ray: Helps assess bone health and detect any joint damage or deformities
- CT scan: Offers detailed images of bones, joints, and surrounding tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of PVNS
These imaging methods help doctors understand PVNS better. They can then create treatment plans to manage symptoms and slow joint disease.
Interpreting Imaging Results
Doctors need to be experts to understand imaging results. They look for any signs of tumors or joint damage. They then use this info to make a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Treatment Options and Approaches
There are several treatment options for pvns. The main goal is to lessen symptoms, stop joint damage, and boost life quality. Treatments might include surgery, physical therapy, or medication.
The treatment options for pvns include:
- Surgical intervention: This may involve removing the affected synovial tissue or repairing any damaged joints.
- Physical therapy: This can help improve joint mobility and strength, reducing pain and stiffness.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
Talking to a healthcare professional is key to finding the right treatment options for pvns. Knowing the different treatment options helps people make informed choices. This way, they can manage their condition effectively.
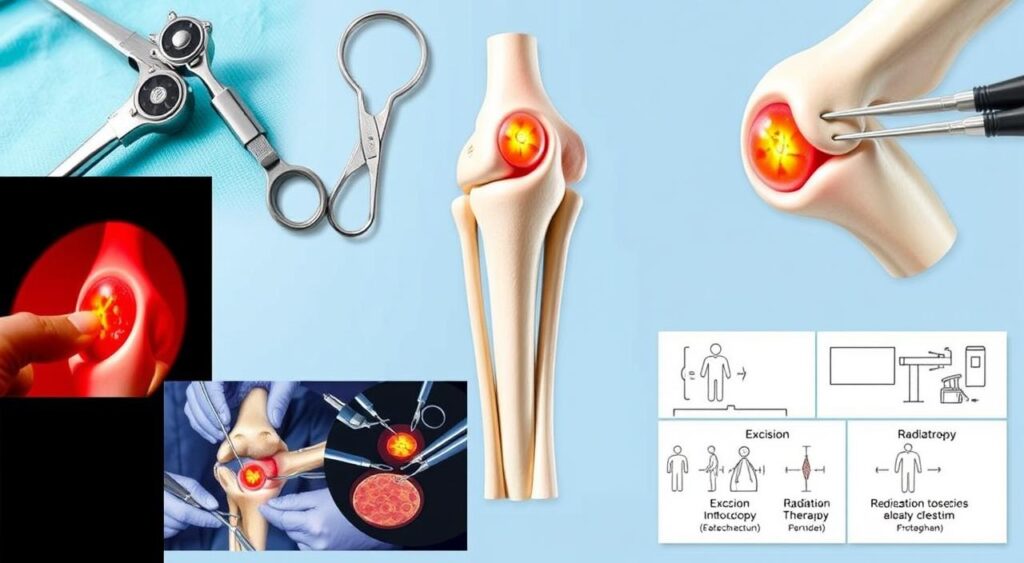
Surgical Interventions for PVNS
Surgery is often needed to remove the tumor and fix damaged joint tissue in PVNS patients. This is done when other treatments don’t work. The surgery aims to take out the bad tissue and protect the joint.
There are two main ways to treat PVNS: open surgery and minimally invasive methods. Open surgery uses a big cut to get to the joint. Minimally invasive methods use small cuts and special tools. The choice depends on the case and how bad the condition is.
Types of Surgical Interventions
- Traditional open surgery: This is for severe cases where a lot of tissue needs to be removed.
- Minimally invasive techniques: These are for milder cases, where small cuts can remove the bad tissue.
After surgery, care and rehab are key for recovery. Patients must follow a rehab plan to get their joint strong and mobile again. With the right treatment, PVNS patients can see big improvements in their symptoms and life quality. It’s important to work with a healthcare team to create a treatment plan that includes surgery and other options.
Recovery and Rehabilitation Process
After treatment for pvns, a type of joint disease, recovery and rehabilitation are key. This stage is vital for getting joints to work right again. It involves physical therapy and exercises made just for you.
Some important parts of the recovery process are:
- Rest and ice to reduce inflammation and pain
- Range of motion exercises to improve joint mobility
- Strengthening exercises to build muscle around the affected joint
Rehabilitation is a big part of treating joint diseases like pvns. By sticking to a good rehab plan, you can get your joints moving better, feel less pain, and live better overall.
It’s important to work with a healthcare expert to make a rehab plan that fits you. With the right plan and effort, people with pvns can get better and move their joints well again.
Rehabilitation is not just about recovering from treatment, but also about learning to manage and cope with the condition to prevent future complications.
Understanding the role of rehabilitation in treating joint diseases like pvns helps you take charge of your recovery. This way, you can aim for the best results possible.
Living with PVNS: Lifestyle Modifications
Managing pvns symptoms needs a whole approach. This includes medical treatment options and changes in lifestyle. After getting a pvns diagnosis, people can take steps to better their life.
Physical Activity Guidelines
Regular exercise keeps joints healthy and lessens pvns symptoms. It’s key to talk to a doctor to make a workout plan that fits you.
Pain Management Strategies
Good pain management strategies help people with PVNS handle their symptoms better. This might include medicine, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Support Resources
Dealing with PVNS can be tough, but there are support resources to help. These include support groups, counseling, and online help.
By changing your lifestyle and getting support, people with PVNS can live better. They can manage their pvns symptoms well.
Conclusion
Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS) is a rare and complex joint disorder. But, it can be managed effectively with the right approach. Understanding PVNS, seeking medical help early, and working with healthcare providers are key steps.
Living well with PVNS starts with early diagnosis and proper treatment. Patients should be active in their healthcare. They can work with orthopedic specialists to create a plan that meets their needs.
Many people with PVNS regain mobility and reduce pain. They can improve their quality of life through surgery, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
The medical community is making progress in treating PVNS. Patients can stay hopeful by staying informed and connecting with others. There are many resources and a community of healthcare professionals ready to help.
FAQ
Q: What is Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (PVNS)?
A: PVNS is a rare joint disorder. It causes noncancerous tumors to grow in the synovium, the lining of joints.
Q: What are the different types of PVNS?
A: PVNS comes in two types: localized and diffuse. Localized PVNS is in one area of the joint. Diffuse PVNS spreads to more of the joint.
Q: Who is most affected by PVNS?
A: PVNS can happen in any joint. But it’s most common in the knee.
Q: What are the common symptoms of PVNS?
A: Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and limited movement. Early signs are mild pain and swelling. Later, pain and mobility worsen.
Q: How is PVNS diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis uses a physical exam, imaging tests (like X-rays and MRI), and sometimes a biopsy. This confirms the presence of noncancerous tumors.
Q: What are the treatment options for PVNS?
A: Treatment may include surgery to remove tumors. Physical therapy helps restore function. Medication can manage symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Q: What is the recovery and rehabilitation process after PVNS treatment?
A: Rehabilitation is key to getting back joint function and strength. It includes physical therapy, exercises, and gradually returning to normal activities.
Q: What lifestyle modifications can help manage PVNS?
A: Lifestyle changes can help manage PVNS. These include following activity guidelines, managing pain, and using support resources. They improve quality of life for those with PVNS.
