Did you know over 1 million people in the United States get diagnosed with pleural effusion every year? This serious condition happens when too much fluid builds up around the lungs. It can really hurt your breathing and overall health. Knowing what causes it, its symptoms, and how to treat it is key to dealing with this serious issue.
Key Takeaways
- Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space around the lungs.
- It can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, including heart failure, pneumonia, and cancer.
- Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and a persistent cough.
- Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to manage the condition and prevent complications.
- Treatment options may include medications, drainage procedures, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause.
Understanding Pleural Effusion and Its Impact on Respiratory Health
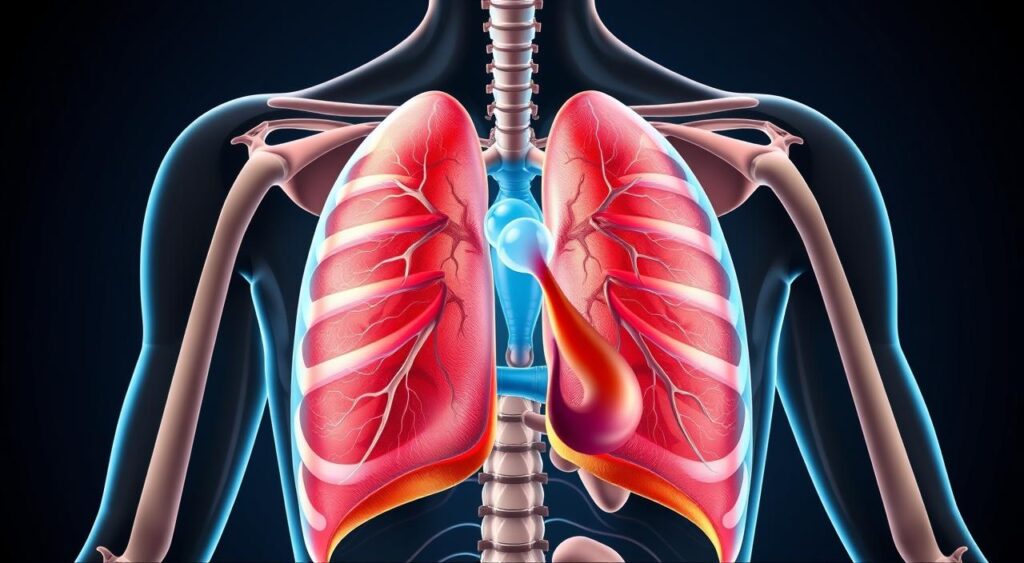
Pleural effusion is a condition where too much fluid builds up in the pleural cavity. This can greatly affect your breathing. It’s important to know how this happens and what it means for your lungs.
Anatomy of the Pleural Space
The pleural space is a thin, fluid-filled area. It’s between the visceral pleura (covering the lungs) and the parietal pleura (lining the chest wall). This space is key for breathing, letting the lungs move in and out.
Normal vs. Abnormal Fluid Accumulation
Usually, a small amount of fluid helps the lungs move smoothly. But too much fluid can cause pleural effusion. This can lead to serious lung problems and breathing issues.
Types of Pleural Effusions
Pleural effusions can be different based on the fluid’s makeup and cause. There are transudative and exudative effusions. Knowing the type helps doctors find the right treatment.
Fluid buildup in the pleural space can make it hard for the lungs to expand. This can cause breathing problems, chest pain, and make it hard to exercise. It’s vital to treat pleural effusion quickly to keep your lungs healthy.
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion is when fluid builds up in the pleural space. It can come from many medical conditions. Knowing what causes it helps in preventing and treating it.
Infection is a main cause, like pneumonia or tuberculosis. Viral infections can also cause it. These infections lead to inflammation and fluid buildup. Cardiovascular diseases like heart failure can also cause fluid to gather. This is because of changes in fluid and pressure.
Cancers like lung or breast cancer can cause pleural effusions. They can spread to the pleural space or block lymphatic drainage. This leads to fluid buildup. Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also cause inflammation and fluid buildup.
Other risks include liver disease, kidney disease, and exposure to harmful substances. People with these conditions or exposures are more likely to get pleural effusion.
Knowing the causes and risks helps doctors in pulmonary medicine. They can better manage and prevent fluid buildup. This improves lung health outcomes.

“Pleural effusions can be a significant indicator of underlying health issues, and understanding their causes is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.”
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion is when fluid builds up around the lungs. It can cause various symptoms. Knowing these signs is key to getting the right treatment quickly.
Primary Symptoms to Watch For
The main symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and a cough that won’t go away. People might find it hard to breathe, especially when they’re active. This is because the fluid makes it hard for the lungs to expand.
Chest pain can feel sharp and stabbing. It happens because the lining around the lungs gets inflamed.
Emergency Warning Signs
Sometimes, pleural effusion can cause serious respiratory distress. This is an emergency. Signs like fast breathing, severe chest pain, and coughing up blood are urgent.
Seeing a doctor right away is vital. Quick action can prevent serious problems and help you feel better.
Impact on Daily Activities
Pleural effusion can really affect your life. It makes it hard to do everyday things. You might struggle with simple tasks like walking or even breathing.
In severe cases, it can mess with your sleep. This leads to feeling tired all the time. It makes it hard to do anything.
Spotting the symptoms of pleural effusion early is crucial. It helps get the right treatment fast. Knowing the symptoms and how they affect your life can help you get help quickly.
Diagnostic Methods and Medical Evaluation
Pulmonary medicine experts use a detailed approach to diagnose pleural effusion. They start with a physical exam and look at the patient’s medical history. This helps find any underlying issues that might be causing the fluid buildup.
To find out the exact cause and how severe it is, doctors order several tests. These include:
- Thoracentesis: A small amount of pleural fluid is taken out for analysis.
- Imaging studies: Chest X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds to see the pleural space and the fluid.
- Lab tests: The fluid is analyzed to find the cause, like an infection, cancer, or heart failure.
These tests give important information to help manage the pleural effusion. Based on the results, the team might suggest more tests, medicine, or surgery to help the patient’s breathing.
“Diagnosing the underlying cause of pleural effusion is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach.”
Pulmonary medicine specialists combine physical exams, medical history, and advanced tests to understand the patient’s condition. This approach helps tailor the treatment plan. It ensures the best care for pleural effusion and related breathing problems.
Understanding Different Types of Pleural Fluid Analysis
In pulmonary medicine, knowing about pleural fluid is key for diagnosing and treating pleural effusions. This condition is when fluid builds up in the pleural cavity. It’s important to figure out if the fluid is transudative or exudative to find the cause and choose the right treatment.
Transudative vs. Exudative Effusions
Transudative effusions happen when there’s an imbalance in the pleural cavity’s pressures. This is often seen in heart failure or liver cirrhosis. On the other hand, exudative effusions are caused by inflammation, infection, or cancer making the pleural membrane more permeable.
Laboratory Testing Procedures
Testing the pleural fluid is crucial to understand the effusion’s nature. Tests include cell counts, protein and LDH levels, and looking for microorganisms or cancer cells. These tests help tell if it’s a transudative or exudative effusion, guiding the doctor’s diagnosis and treatment.
Imaging Studies and Their Importance
Imaging studies are also key in evaluating pleural effusions. Chest X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasound help see the fluid’s size, location, and characteristics. They also spot any lung or pleural problems that might be causing the effusion.
Understanding pleural fluid analysis and imaging studies helps healthcare providers manage pleural effusions better. This ensures patients get the right treatment for their respiratory health concerns.
| Characteristic | Transudative Effusion | Exudative Effusion |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Content | Low ( | High (>3.0 g/dL) |
| Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) | Low ( | High (>200 U/L) |
| LDH Ratio (Pleural/Serum) | ≥0.6 | |
| Specific Gravity | ≥1.015 |
“Accurate classification of pleural effusions as transudative or exudative is essential for determining the underlying cause and guiding appropriate treatment.”
Treatment Options and Medical Interventions
Dealing with pleural effusion needs a mix of medical treatments and lifestyle changes. The main goal is to find and fix the cause of the fluid buildup. This helps ease breathing problems.
Thoracentesis is a key treatment for pleural effusion. It involves removing extra fluid from the chest area. This helps patients breathe better and feel less pain. Sometimes, they need to have this done more than once.
For those with ongoing pleural effusions, more serious treatments are considered. These include diuretics to reduce fluid, corticosteroids to fight inflammation, or a special catheter for ongoing drainage.
| Treatment Approach | Intended Outcome |
|---|---|
| Thoracentesis | Drainage of excess fluid to relieve respiratory distress |
| Diuretic therapy | Reduction of fluid retention to prevent recurrent effusions |
| Corticosteroid administration | Addressing underlying inflammation and immune-related causes |
| Indwelling pleural catheter placement | Ongoing fluid drainage to manage chronic or recurrent effusions |
Changing your lifestyle is also important in treating effusion. Doctors might suggest eating less salt, exercising regularly, and managing health issues like heart or kidney disease.
The treatment plan is made just for each patient. It considers the cause, how bad the symptoms are, and the patient’s health. Working together with the pulmonary medicine team is key to managing respiratory distress well.
Thoracentesis and Other Surgical Procedures
When treatments for pleural effusion don’t work, doctors might suggest thoracentesis. This is a simple way to remove extra fluid from the space around the lungs. It helps ease symptoms and can help find the cause of the problem.
Preparation for the Procedure
Before thoracentesis, patients get checked thoroughly. They might have X-rays or ultrasounds to see how much fluid is there. Then, a local anesthetic numbs the area, and a thin needle or catheter is used to take out the fluid.
Recovery and Aftercare
After the procedure, patients usually go home the same day. They can start doing light things a few days later. But, they must follow their doctor’s advice for wound care and watch for any signs of trouble.
Potential Complications
Thoracentesis is usually safe, but there are risks. These include:
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pain or discomfort at the procedure site
It’s important to talk about these risks with your doctor. If you notice any problems, tell your doctor right away.
In some cases, more serious surgeries might be needed. These include VATS or open thoracotomy. These surgeries let doctors directly see and treat the problem in the pleural space.
| Procedure | Description | Typical Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracentesis | Minimally invasive fluid drainage from the pleural cavity | Same-day discharge, light activities within a few days |
| VATS | Keyhole surgery to inspect and treat pleural conditions | Hospitalization for 1-3 days, return to normal activities in 2-4 weeks |
| Open Thoracotomy | Surgical incision in the chest wall to access the pleural space | Hospitalization for 3-7 days, return to normal activities in 4-6 weeks |
It’s crucial for patients to work closely with their healthcare team. This ensures the best care for their pleural effusion.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Modifications
Keeping your respiratory health in check is key to avoiding lung complications like pleural effusion. By using pulmonary medicine tips, you can lower your risk of getting this condition or having it come back.
First, tackle any health issues that might lead to pleural effusion. This means managing chronic diseases like heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disease. Use the right meds, eat right, and keep up with your doctor’s advice.
- Quit smoking and stay away from secondhand smoke. Smoking can make breathing problems worse and up your chance of getting pleural effusion.
- Stay active to keep your heart and lungs healthy. This can help stop fluid from building up in your pleural space.
- Eat a diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains. This supports your immune system and breathing.
If you’ve had pleural effusion before, team up with your pulmonary medicine doctor. They can help you make a plan to watch your condition. This might include regular check-ups, scans, and quick action if you get fluid again.
| Prevention Strategy | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Quit Smoking | Reduces the risk of respiratory complications and lung complications |
| Manage Underlying Health Conditions | Addresses the root causes of pleural effusion and supports respiratory health |
| Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle | Promotes overall cardiovascular and pulmonary fitness, reducing the likelihood of fluid buildup |
By using these prevention tips and being proactive with pulmonary medicine, you can protect your respiratory health. This helps lower your risk of pleural effusion.
Conclusion
Pleural effusion is when too much fluid builds up in the pleural space. This can really affect how well you breathe. Knowing what causes it and how to spot the signs is key. Getting medical help quickly is also important.
Finding out what’s causing the fluid is the first step. Then, doctors can choose the best way to treat it. This might include simple procedures or more serious surgery. The goal is to get rid of the fluid and ease breathing problems.
Research is always finding new ways to deal with pleural effusions. Working with your doctor to try these new methods can help a lot. Taking care of your breathing can make a big difference in your life. It can help avoid serious problems too.
FAQ
Q: What is pleural effusion?
A: Pleural effusion is when too much fluid gathers in the pleural space. This space is between the lungs and the chest wall. This fluid can make it hard to breathe and cause distress.
Q: What are the common causes of pleural effusion?
A: Many things can cause pleural effusion, like infections and heart problems. Cancers and autoimmune diseases can also lead to it. Older people, those with health issues, and those exposed to certain dangers are at higher risk.
Q: What are the symptoms of pleural effusion?
A: Symptoms include shortness of breath and chest pain. You might also cough and feel tired. Severe breathing problems or a fast heart rate are emergencies that need quick help.
Q: How is pleural effusion diagnosed?
A: Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and tests to find pleural effusion. They might use imaging studies and analyze the fluid. These steps help figure out what’s causing it and how bad it is.
Q: What are the treatment options for pleural effusion?
A: Treatment aims to fix the cause, remove excess fluid, and ease symptoms. Doctors might use medicine, change your lifestyle, or do surgery. The best plan depends on your specific situation.
Q: What is the role of thoracentesis in the treatment of pleural effusion?
A: Thoracentesis is a way to remove fluid from the pleural space. A small needle or catheter is used to drain it. This can help you breathe better and feel relief. It’s important to prepare well, recover right, and watch for any problems.
Q: How can pleural effusion be prevented?
A: To prevent pleural effusion, manage your health, live a healthy lifestyle, and avoid harmful exposures. Regular doctor visits and catching problems early are key to prevention.
