Explore the symptoms, causes, and effective treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis, aiding in better management and quality of life.
Rheumatoid arthritis: This chronic condition affects not just joints but also other body tissues. Knowing about rheumatoid arthritis is key for early detection and treatment. We’ll look at symptoms, causes, and treatment options in this article. By the end, you’ll understand more about living with this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Rheumatoid arthritis affects approximately 1.5 million Americans.
- RA is a chronic condition that primarily impacts joints.
- Understanding symptoms aids in early diagnosis.
- Effective treatment options are crucial for managing RA.
- Support from healthcare providers enhances quality of life.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
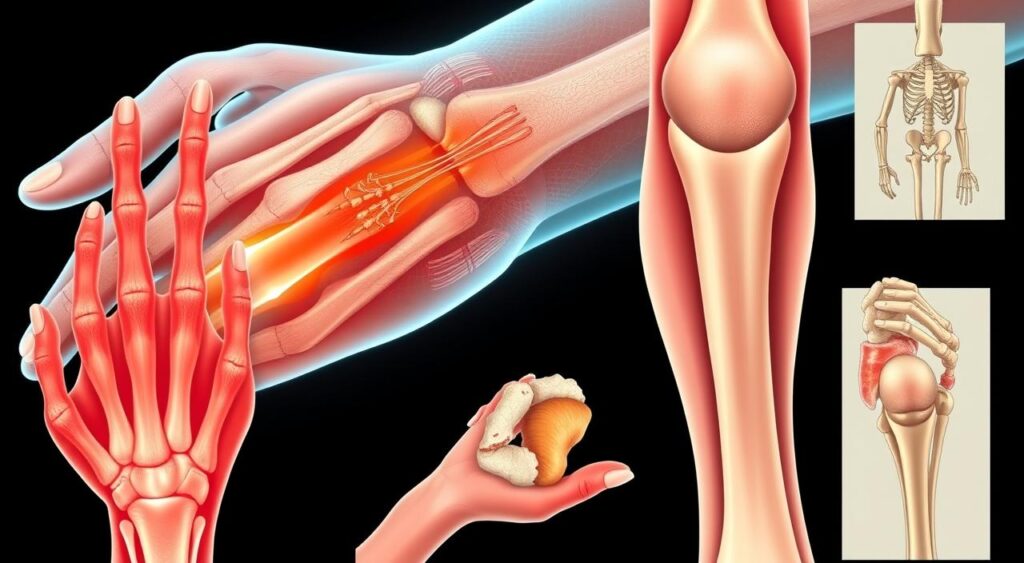
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a major autoimmune disease affecting millions worldwide. It causes chronic inflammation, mainly in the joints. In RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, especially in the joints, causing damage to the joint linings.
This damage leads to pain and swelling in patients. Understanding this helps us grasp the severity of their condition.
Chronic inflammation is key in RA’s progression. It can cause lasting damage, impacting mobility and quality of life. It’s important to know the difference between RA and other arthritis types, like osteoarthritis, as their causes and treatments differ.
Learning more about RA helps both patients and doctors manage this tough disease. Better understanding leads to earlier diagnosis and more effective treatments. This improves patient outcomes significantly.
| Characteristic | Rheumatoid Arthritis | Other Types of Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Autoimmune disease | Degenerative or inflammatory |
| Joint Involvement | Symmetrical | Can be asymmetrical (e.g., osteoarthritis) |
| Causes | Immune system malfunction | Wear and tear, infection |
| Chronic Inflammation | Present | Varies by type |
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of rheumatoid arthritis early. Catching it early helps manage it better and improves life quality. Here are some common symptoms to watch out for.
Common Symptoms to Look For
The most common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Joint Pain: Often the first sign, it mainly affects hands and feet.
- Swelling: Inflammation around joints causes visible swelling.
- Stiffness: More noticeable in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired all the time adds to discomfort.
- Symmetric Joint Involvement: Both sides of the body are usually affected, especially later on.
Early Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Spotting early signs of RA might mean noticing body-wide effects, such as:
- Mild Anemia: Can happen due to ongoing inflammation.
- Fever: A low-grade fever shows the body’s inflammatory response.
- Loss of Appetite: Some people might eat less.
These symptoms can make daily tasks hard. So, knowing and diagnosing them early is key to managing the condition well.
| Symptom | Description | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Pain | Discomfort in joints, often worsening with movement. | Limits functionality, affecting work and personal activities. |
| Stiffness | Mornings and inactivity lead to restricted movement. | Hinders getting out of bed or starting the day. |
| Fatigue | Chronic tiredness unrelated to physical exertion. | Decreases motivation and energy for daily tasks. |
| Swelling | Visible inflammation around joints. | Causes discomfort and limits range of motion. |
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis has many causes. Knowing these can help find who is at risk. It also helps in finding ways to prevent it.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a big role in getting rheumatoid arthritis. Scientists have found certain genes that increase the risk. If your family has it, you might have these genes too.
This shows how important genetics are. It also gives clues for future treatments.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors also matter a lot. Lifestyle choices and exposures can start the disease in people who are already at risk. Some common triggers include:
- Smoking, which notably raises the risk
- Exposure to specific pathogens that may initiate inflammatory responses
- Occupational exposures to certain toxins
These environmental factors work with genetics. This shows how both are key to understanding rheumatoid arthritis.
| Factor Type | Examples | Impact on Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic | Gene markers (e.g., HLA-DRB1) | Increases susceptibility |
| Environmental | Smoking Pathogen exposure Toxins | May trigger disease onset |
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Getting a correct diagnosis for rheumatoid arthritis is key to treating it well. The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Doctors look at how symptoms affect daily life.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors check for swelling, pain, and tenderness in joints during the physical exam. They also ask about family history and past health issues. This helps understand the patient’s condition better.
- Family history of rheumatoid arthritis
- Any recent infections or illnesses
- Past injuries or surgeries
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests are then used to confirm the diagnosis. Tests like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are common. They check for inflammation by measuring C-reactive protein (CRP) and sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Rheumatoid factor (RF)
- Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA)
- C-reactive protein (CRP) and sedimentation rate (ESR) to indicate inflammation
These tests help understand the immune response and inflammation levels. They are important for the overall diagnosis.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies help see joint damage from rheumatoid arthritis. X-rays and MRI show the condition of joints and inflammation levels. These studies give crucial information on the disease’s progression.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a mix of treatments to ease symptoms and improve life quality. Starting treatment early is key to avoid joint damage and better outcomes.
The main aim of treatment is to reduce inflammation and pain while keeping joints working. Here are some common strategies:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs help with pain and swelling. Corticosteroids and DMARDs are crucial in slowing the disease.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy boosts flexibility, strength, and mobility. It helps improve joint function and eases discomfort.
- Lifestyle Modifications: A healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management helps manage the condition.
- Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers keep a close eye on progress. They adjust treatments as needed for the best results.
Adding therapies like acupuncture or yoga can also help. Working closely with healthcare professionals is vital to create a treatment plan that meets individual needs.
| Treatment Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Includes NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs. | Reduces pain, inflammation, and slows disease progression. |
| Physical Therapy | Customized exercises and stretches to improve mobility. | Enhances joint function and reduces stiffness. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Involves regular exercise and a nutritious diet. | Supports overall health and boosts immune function. |
| Complementary Therapies | Methods like acupuncture and yoga. | May alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. |
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis medications are key in managing symptoms and slowing disease growth. There are three main types: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs. Each has its own role. Knowing about these can help patients choose the best treatment for them.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, like ibuprofen and naproxen, help with pain and swelling. They block enzymes that cause inflammation. These drugs can greatly improve life quality for many patients.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, offer quick relief during flare-ups. They quickly reduce inflammation and calm the immune system. But, long-term use can cause side effects like weight gain and infections. It’s important to watch for these issues closely.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs, including methotrexate and sulfasalazine, are vital in fighting rheumatoid arthritis. They aim to slow the disease and protect joints. Regular tests are needed to check for side effects, keeping patients safe while treating.

Rheumatoid Arthritis Management Strategies
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a mix of lifestyle changes and healthcare support. This approach helps reduce symptoms and improve life quality.
Lifestyle Changes
Key lifestyle adjustments are crucial for managing rheumatoid arthritis. Here are some strategies to help you:
- Balanced Diet: Eating more fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins can lower inflammation.
- Maintain Healthy Weight: A healthy weight reduces joint pressure, helping with mobility and comfort.
- Physical Activity: Regular, low-impact exercise keeps joints flexible and reduces stiffness.
Support from Healthcare Providers
Healthcare support is vital for managing rheumatoid arthritis. Working with a team of professionals offers comprehensive care:
- Rheumatologists: They diagnose and create treatment plans based on your needs.
- Physical Therapists: They design exercise plans to boost strength and mobility.
- Nutritionists: They offer advice on diets that help manage symptoms.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Exercises
Regular physical activity is key in managing rheumatoid arthritis. Doing exercises for RA can improve joint function and overall health. Low-impact workouts are great because they don’t strain joints too much. They’re especially good for people with RA.
Low-Impact Activities
Low-impact workouts are gentle on the joints but still keep you moving. Activities like:
- Swimming
- Walking
- Cycling
- Yoga
These activities help keep a healthy weight, which is good for your joints. Doing them regularly is a big part of managing RA.
Stretching and Strengthening
Stretching and strengthening exercises also help with joint health. They make your muscles stronger and more flexible, which helps with stiffness. Good exercises include:
- Gentle stretches for major muscle groups
- Resistance training using light weights
- Balance exercises to improve stability
Being consistent is important. Adding these exercises to your daily routine can really help with managing RA.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Swimming | Full body workout, low joint stress | 3-4 times a week |
| Walking | Improves cardiovascular health, increases endurance | Daily |
| Cycling | Strengthens legs, enhances joint mobility | 3-5 times a week |
| Yoga | Enhances flexibility, reduces stress | 2-3 times a week |
Rheumatoid Arthritis Prevention Tips
Preventing rheumatoid arthritis is possible with proactive steps. Healthy habits and regular checkups are key. They help spot issues early.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Changing your lifestyle can lower rheumatoid arthritis risk. Here are some healthy habits to consider:
- Quitting smoking: Smoking increases rheumatoid arthritis risk. Quitting boosts your health.
- Eating an anti-inflammatory diet: Eat foods rich in omega-3s like fish, nuts, and seeds. Also, include lots of fruits and veggies.
- Regular exercise: Exercise keeps joints working well and improves health.
- Stress management: Use meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to reduce stress. Stress can cause inflammation.
Regular Medical Checkups
Regular checkups are vital for those at risk of rheumatoid arthritis. They help catch symptoms early and start treatments. This keeps joints healthy.
At checkups, doctors can:
- Check your joint health and movement.
- Look at your family history and risk factors.
- Give advice to improve your overall health.

Complementary and Alternative Therapies
For those with rheumatoid arthritis, trying RA complementary therapies can help. These methods can boost traditional care and make you feel better. Always talk to your doctor before trying new treatments to make sure they won’t harm your current care.
Acupuncture is a well-liked option. It uses needles to help with pain and swelling. Many people find it helpful, showing it can be a good addition to their treatment.
Yoga is another great choice. It combines gentle exercises with deep breathing and meditation. Studies show it can help reduce pain and improve your quality of life.
Dietary supplements like omega-3 fatty acids are also worth considering. They can help fight inflammation, which is good for people with rheumatoid arthritis. Adding these to your routine might offer natural relief.
It’s important to use these therapies with your regular medical care. Keep an eye on how they work for you. Talking to your doctor regularly helps make sure these treatments fit your needs.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with RA is tough and requires good coping strategies and daily management. People often face chronic pain and fatigue, which can change their life a lot. It’s important to take care of both physical and emotional health.
Support groups are key for social and emotional support. Talking to others who understand helps a lot. Also, getting help from mental health professionals can help deal with the emotional side of chronic illness.
Managing RA daily means staying productive and organized. Keeping track of symptoms, meds, and triggers helps doctors understand better. Technology, like apps and devices, also helps track illness and meds.
Good ways to cope with RA include:
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact activities help keep moving and reduce stiffness.
- Prioritizing Rest: Taking breaks during the day helps fight fatigue.
- Healthy Eating: Eating well helps overall health and might reduce inflammation.
Using these strategies every day can make living with RA better. It can lead to a better quality of life.
| Coping Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Support Groups | Enhanced emotional support and connection with others. |
| Mental Health Resources | Professional guidance to tackle emotional challenges. |
| Exercise | Improved mobility and reduced pain levels. |
| Healthy Diet | Potential reduction of inflammation and pain. |
| Technology Aids | Efficient symptom and medication tracking. |
Conclusion
This article has given a detailed look at rheumatoid arthritis. It shows how important it is to know the symptoms and causes. It also talks about different ways to treat it.
Rheumatoid arthritis can really change your life. But, knowing what to do and taking action can help a lot. This way, people can handle their RA better.
Working closely with doctors is key for RA patients. This helps create treatment plans that fit each person’s needs. Making lifestyle changes, going for regular check-ups, and taking the right medicines can improve life with RA.
It’s vital to stay informed and take charge of your health. By focusing on your well-being and following good RA management practices, you can stay strong. This helps you live a better life, even with rheumatoid arthritis.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often causes joint pain and swelling. It also leads to stiffness, especially in the morning. Feeling tired is another common symptom.
Early signs might show the same joints on both sides of the body are affected. You might also feel feverish or have mild anemia.
Q: What causes rheumatoid arthritis?
A: RA is caused by genes and environmental factors. Some people are more likely to get it because of their genes. Smoking and exposure to toxins can also play a role.
Q: How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use a detailed medical history and physical exam to diagnose RA. They also run tests like rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA). X-rays help check for joint damage.
Q: What treatment options are available for rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Treatment for RA includes medicines, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Starting treatment early is key to prevent damage and improve outcomes. Common medicines include NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs.
Q: What types of medications are prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Medicines for RA include NSAIDs for pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids help during flare-ups. DMARDs, like methotrexate, slow the disease’s progress. It’s important to watch for side effects.
Q: Can lifestyle changes impact rheumatoid arthritis management?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes can help manage RA. Eating well, staying at a healthy weight, and exercising are important. Getting support from healthcare providers is also crucial.
Q: What types of exercises are recommended for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Low-impact activities like swimming and walking are good for RA. They keep joints moving without too much strain. Stretching and strengthening exercises also help with flexibility and muscle support.
Q: What preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Preventive measures include quitting smoking and eating anti-inflammatory foods. Managing stress is also important. Regular check-ups can help catch RA early.
Q: Are there any complementary therapies that can benefit those with rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Yes, therapies like acupuncture, yoga, and omega-3 fatty acids may help with RA. It’s important to talk to your doctor before trying these.
Q: How can individuals cope with the challenges of living with rheumatoid arthritis?
A: Coping with RA includes managing pain and fatigue. Taking care of your emotional health is also key. Support groups and mental health resources can help with daily challenges.
