Discover the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for secondary hyperlipidemias. Get informed today.
Many cases are due to secondary hyperlipidemias. This condition is caused by medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors. Knowing what causes secondary hyperlipidemias is key to managing it.
Secondary hyperlipidemias can harm your health a lot. It raises the risk of heart disease and stroke. It’s important to know the symptoms and get medical help if needed. The causes can be complex, involving health issues, lifestyle, and medicines.
It’s very important to understand secondary hyperlipidemias. By knowing the risks, you can lower your chance of getting it. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for secondary hyperlipidemias.
Key Takeaways
- Secondary hyperlipidemias are a big health problem, affecting millions in the United States.
- Knowing the causes is vital for managing and treating this condition.
- Medical conditions, lifestyle, and medicines can all lead to secondary hyperlipidemias.
- Spotting the symptoms is crucial for getting medical help and avoiding serious problems.
- Good treatments and lifestyle changes can help manage secondary hyperlipidemias and lower heart disease and stroke risks.
- Being aware and educated can help prevent secondary hyperlipidemias.
Understanding Secondary Hyperlipidemias
Secondary hyperlipidemias are disorders where blood lipid levels are too high. They can be caused by diabetes, hypothyroidism, and some medicines. Knowing the types and how to diagnose them is key to managing these conditions.
To diagnose secondary hyperlipidemias, doctors look at the patient’s history, do a physical exam, and run tests. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for a good treatment plan. There are different types, like those caused by diabetes, hypothyroidism, or medicines.
- Diabetes-related hyperlipidemia
- Hypothyroidism-related hyperlipidemia
- Medication-induced hyperlipidemia
Knowing the cause of secondary hyperlipidemias helps tailor treatments. A detailed diagnosis points to the cause and guides treatment. This way, doctors can offer the best care for patients with these conditions.
Common Types of Secondary Hyperlipidemias
Secondary hyperlipidemias can be caused by many factors. Diabetes and kidney disease are two common causes. Treating these conditions is key to managing secondary hyperlipidemias.
Some medicines, like beta-blockers and estrogen, can also raise lipid levels. To manage this, doctors might adjust the medication or add drugs to lower lipids.
- Hyperlipidemia associated with diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia associated with kidney disease
- Medication-induced hyperlipidemia
Effectivesecondary hyperlipidemias treatmentandsecondary hyperlipidemias managementneed a full plan. This includes lifestyle changes and, if needed, medication.
Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Secondary hyperlipidemias often stem from medical conditions, lifestyle choices, or medications. Knowing these causes and risk factors is key to preventing and managing secondary hyperlipidemias. Conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can raise the risk.
Lifestyle habits, such as eating too much saturated fat and cholesterol, not exercising enough, and smoking, also play a role. Some medications, like beta-blockers and antidepressants, can increase lipid levels, leading to secondary hyperlipidemias. Spotting these risk factors is vital for prevention.
Medical Conditions Leading to Secondary Hyperlipidemias
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, like a bad diet and not moving enough, can up the risk of secondary hyperlipidemias. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet and regular exercise, can lower this risk. It helps in preventing secondary hyperlipidemias.
Medication-Induced Cases
Some medications can increase the risk of secondary hyperlipidemias. If you’re on any meds, talk to your doctor about the risks. Look for alternatives to lower the risk of secondary hyperlipidemias and work on prevention.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Secondary hyperlipidemias symptoms can be hard to spot early. This makes it key to get regular check-ups and screenings. These help find high lipid levels, a sign of secondary hyperlipidemias.
Guidelines say people with a family history or who are overweight are at higher risk. This is because they might get secondary hyperlipidemias more easily.
Common signs include xanthomas, yellow patches on the skin, and pancreatitis, inflammation of the pancreas. If left untreated, it can lead to heart disease and stroke. It’s vital to follow guidelines to manage it well and avoid serious damage.
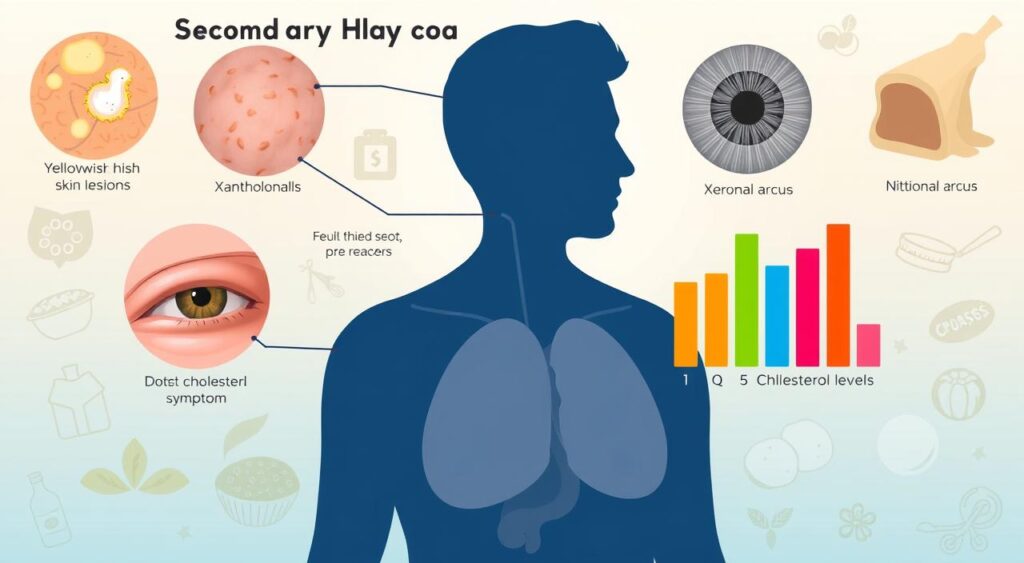
- Elevated lipid levels
- Xanthomas
- Pancreatitis
- Family history of the condition
- Being overweight or obese
By knowing the symptoms and following guidelines, you can manage the condition. This helps lower the risk of serious problems later on.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Getting a correct diagnosis is key for treating secondary hyperlipidemias. The first steps include a physical check-up, looking at your medical history, and lipid tests. These help spot risks and figure out the best treatment plan.
Reviewing your medical history is very important. It helps doctors understand why you have secondary hyperlipidemias. They look at your diet, exercise, and any medicines you take. This helps them create a treatment plan just for you.
Initial Screening Methods
The first steps usually involve a few things:
- Lipid tests to check your cholesterol and triglycerides
- Physical exams to check your health and find risks
- Looking at your medical history to see what might be causing it
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Sometimes, more detailed tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. These might include:
- Genetic tests to find out if genes play a role
- Imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans to see if arteries have plaque
Interpreting Test Results
After the tests, doctors will look at the results to decide on treatment. This might mean changing your lifestyle, taking medicine, or both. Working with your healthcare team helps you make a plan to manage your condition and lower risks.
Treatment Approaches for Secondary Hyperlipidemias
Managing secondary hyperlipidemias requires lifestyle changes and medication. The aim is to lower blood lipid levels to prevent heart disease. Secondary hyperlipidemias guidelines suggest eating better, exercising more, and managing weight.
Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle modifications: dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight management
- Medication: statins, bile acid sequestrants, and nicotinic acid
- Alternative therapies: plant sterols and stanols, and omega-3 fatty acids
A team effort is key in secondary hyperlipidemias management. Healthcare providers, dietitians, and specialists all play a role. By following secondary hyperlipidemias guidelines and making smart lifestyle choices, people can manage their condition well. This helps lower the risk of heart disease.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention Strategies
Living a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing secondary hyperlipidemias. It’s about making smart choices in what you eat, how much you exercise, and other habits. Eating foods low in saturated fats and high in fiber can help control cholesterol.
Regular exercise, like walking or jogging, can also lower the risk of secondary hyperlipidemias. Quitting smoking and drinking less alcohol are other ways to reduce risk. By changing your lifestyle, you can prevent secondary hyperlipidemias and stay healthy.
Dietary Recommendations
Eating right is vital for preventing secondary hyperlipidemias. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid processed and high-fat foods. Here are some tips to lower risk:
- Eat lean proteins like poultry and fish
- Add healthy fats like avocado and nuts to your meals
- Drink lots of water and cut down on sugary drinks
Preventive Measures
Changing your diet and exercising regularly are just the start. There are more ways to prevent secondary hyperlipidemias. These include:
- Regular health check-ups to watch cholesterol levels
- Following your doctor’s advice on medication
- Using stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga
Managing Complications and Long-term Effects
Secondary hyperlipidemias complications can greatly affect a person’s life quality. Cardiovascular disease, pancreatitis, and peripheral artery disease are possible issues. It’s key to manage secondary hyperlipidemias to avoid these problems and handle long-term effects.
To tackle secondary hyperlipidemias complications, knowing the risks is crucial. Taking early action is important. Here are some ways to manage complications:
- Regular health check-ups to monitor lipid levels and detect potential complications early
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Managing underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to secondary hyperlipidemias
By understanding the risks and taking steps early, people with secondary hyperlipidemias can lower their risk of long-term issues.

Managing secondary hyperlipidemias well needs a full plan. This includes lifestyle changes, medical care, and regular checks. With the help of a healthcare provider and making smart choices, individuals can handle secondary hyperlipidemias complications. This improves their health and well-being.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Secondary Hyperlipidemias
Managing secondary hyperlipidemias needs a full plan. Early detection, right treatment, and lifestyle changes are key. These steps help control the condition and lessen its health risks.
Working with doctors, patients can keep an eye on their lipid levels. They can tackle the root causes and find the best ways to manage their condition. This way, they can live healthier and avoid serious problems.
People with secondary hyperlipidemias can make big changes. They can handle their health issues, change their meds, or start better habits. By being informed and making healthy choices, they can improve their health and enjoy a better life.
FAQ
Q: What are secondary hyperlipidemias?
A: Secondary hyperlipidemias are when blood lipid levels go up due to other factors. These can be medical conditions, certain medicines, or lifestyle choices. They are different from primary hyperlipidemias, which are caused by genetics.
Q: How do secondary hyperlipidemias differ from primary hyperlipidemias?
A: Secondary hyperlipidemias are caused by outside factors. Primary hyperlipidemias are due to genetics. Secondary types can often be managed by fixing the cause. Primary types usually need lifelong treatment.
Q: What are the common types of secondary hyperlipidemias?
A: Common types include those linked to diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism. Obesity and certain medicines like corticosteroids also cause them.
Q: What are the primary causes and risk factors of secondary hyperlipidemias?
A: Causes and risk factors include diabetes, kidney disease, and hypothyroidism. Poor diet and lack of exercise also play a role. Some medicines can raise lipid levels too.
Q: What are the symptoms of secondary hyperlipidemias?
A: Symptoms include high blood lipid levels and xanthomas (fatty deposits under the skin). In severe cases, pancreatitis can occur. But many people with secondary hyperlipidemias don’t show symptoms.
Q: How are secondary hyperlipidemias diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves blood tests, physical exams, and medical history checks. Advanced tests like imaging studies might also be used.
Q: How are secondary hyperlipidemias treated?
A: Treatment includes lifestyle changes and medicines. The plan depends on the individual’s situation. It aims to lower lipid levels and manage the cause.
Q: What are the potential complications of secondary hyperlipidemias?
A: If not treated, secondary hyperlipidemias can lead to heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. They can also cause pancreatitis and peripheral artery disease.
Q: How can secondary hyperlipidemias be prevented?
A: Prevention involves a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. Managing any underlying conditions or medicines is also key.
