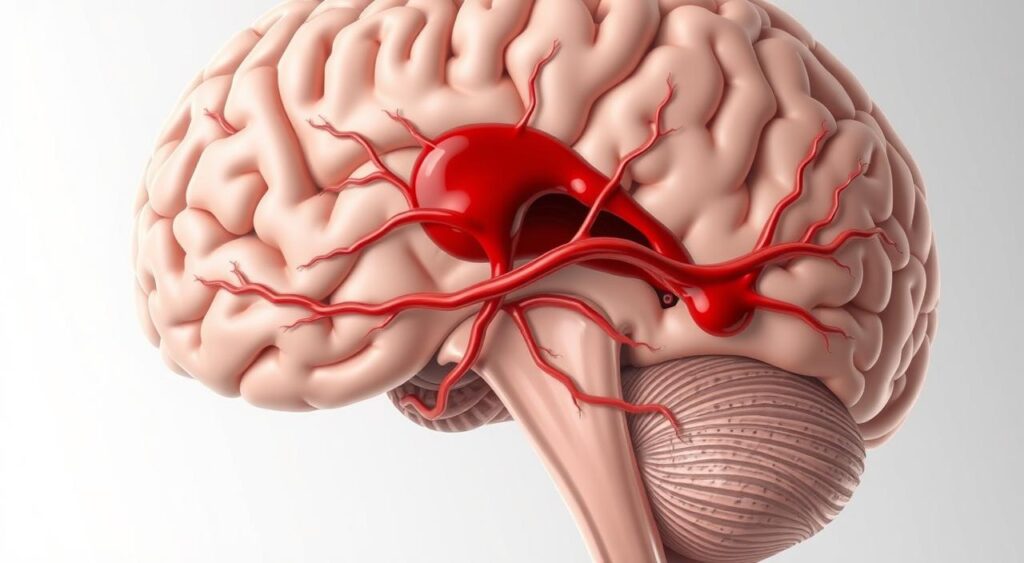
Subarachnoid haemorrhage, a rare stroke happens when blood bleeds into the brain’s space, called the subarachnoid space. This condition needs quick medical help. Knowing about subarachnoid haemorrhage is key for those affected and their families.
This guide will explore subarachnoid haemorrhage in detail. We’ll look at its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and recovery. By understanding subarachnoid haemorrhage, readers will see its effects on people and their families.
Key Takeaways
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage is a rare but serious type of stroke that requires immediate medical attention.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of subarachnoid haemorrhage is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life and cognitive function.
- Treatment options for subarachnoid haemorrhage vary depending on the severity of the condition and may include surgical procedures and medication management.
- Recovery from subarachnoid haemorrhage can be a long and challenging process, requiring patience, dedication, and support from loved ones.
- Prevention strategies and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of subarachnoid haemorrhage and promote overall brain health.
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
Understanding Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a serious condition where blood leaks into the brain’s space. This can happen when an aneurysm in the brain bursts. It can cause cerebral bleeding and serious problems. Knowing about this condition is key to getting the right medical help quickly.
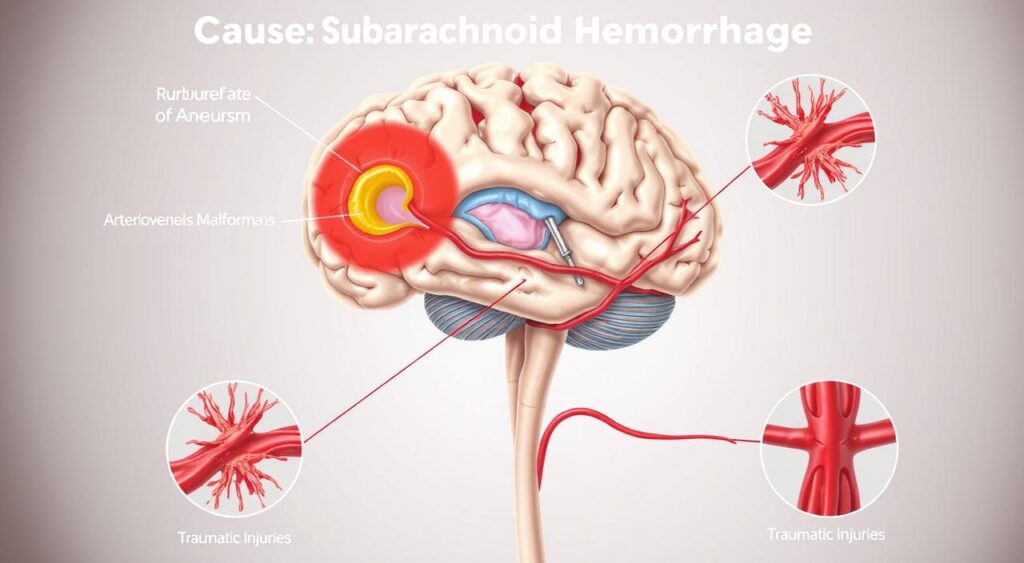
The subarachnoid hemorrhage causes fall into two main groups: aneurysmal and non-aneurysmal. Aneurysmal cases make up about 80% of all cases. Non-aneurysmal cases can be due to trauma, bleeding disorders, or tumors.
Several factors can increase the risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage. These include:
- Family history of aneurysms or subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Age, with most cases occurring in people between 40 and 60 years old
Definition and Basic Concepts
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is when blood leaks into the brain’s space. This can put pressure on the brain and lead to serious problems. It needs quick medical care. Treatment might include surgery, medicine, and supportive care.
Types of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
There are two main types of subarachnoid hemorrhage: aneurysmal and non-aneurysmal. Aneurysmal cases are the most common. Non-aneurysmal cases can be caused by trauma or bleeding disorders.
Impact on Brain Function
Subarachnoid hemorrhage can greatly affect brain function. It can lead to cerebral bleeding, increased pressure, and a decrease in consciousness. Quick medical care is vital to prevent long-term damage and improve outcomes.
| Type of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | Cause | Incidence |
|---|---|---|
| Aneurysmal | Rupture of an aneurysm in the brain | Approximately 80% of all cases |
| Non-aneurysmal | Trauma, bleeding disorders, or tumors | Approximately 20% of all cases |
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Subarachnoid hemorrhage often happens when a brain aneurysm ruptures. This is a weak spot in the blood vessel wall. The aneurysm rupture causes bleeding around the brain, leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage. A brain aneurysm can be silent for years but can burst at any time, posing a serious threat.
Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage include both things you can and can’t change. Non-modifiable risk factors include:
- Family history of brain aneurysms
- Age, with most cases occurring in people between 40 and 60 years old
- Gender, with women being more likely to experience a subarachnoid hemorrhage than men
Modifiable risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol. Managing these can lower the risk of a brain aneurysm rupture and subsequent subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Knowing the causes and risk factors of subarachnoid hemorrhage is key to prevention and early action. Recognizing warning signs and getting medical help quickly can save lives. It’s vital to be aware of risks and take steps to prevent them, especially for those with a family history of brain aneurysms or other risk factors.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. Knowing the warning signs of SAH is key to getting timely treatment. Sah symptoms can vary, but a sudden, severe headache is often a sign of a brain bleed.
The main symptoms of SAH can be hard to spot. It’s important to know the emergency signs. These include:
- Sudden, severe headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion and disorientation
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
If you or someone you know shows these symptoms, get medical help right away. Quick action can greatly improve the outcome and lower the risk of more problems from a brain bleed. Knowing sah symptoms can save lives. It’s vital to act fast if you think someone has had a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage.
Diagnostic Process and Tests
Diagnosing subarachnoid haemorrhage involves several tests to find brain bleeding. A computed tomography (CT) scan is often the first step. It quickly spots brain bleeding. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan might follow to get clearer images of the brain and its blood vessels.
A lumbar puncture might also be done. It involves taking a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid is checked for blood or other signs of the condition.
The tests used to diagnose subarachnoid haemorrhage include:
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- Lumbar puncture
These tests help doctors understand where and how much bleeding there is. They also look for any underlying causes.
Getting a quick and accurate diagnosis is key in treating subarachnoid haemorrhage. It helps doctors make the right treatment plans. This way, they can manage the condition and prevent more problems.
Treatment Options and Emergency Care
Timely and specialized care is key for Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. The main goal of treatment for sah is to stop bleeding, manage symptoms, and avoid complications. Right away, doctors must act fast to keep the patient stable.
Some important parts of treatment for sah are:
- Watching vital signs and brain health closely
- Keeping blood pressure in check and stopping more bleeding
- Managing pain and stopping seizures
Sometimes, surgery is needed to fix the damaged blood vessel. This might include coiling or clipping an aneurysm to stop bleeding. Medications are also crucial, used to prevent problems and control symptoms.
The treatment plan depends on the Subarachnoid Haemorrhage’s type and severity. A detailed plan, made just for the person, is key to the best outcome.
Recovery and Rehabilitation Journey
Recovering from a Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) is a long and tough journey. Knowing sah risk factors helps in the recovery and prevents future problems. Rehabilitation is key to getting back strength, mobility, and thinking skills.
The recovery path includes physical therapy, cognitive rehab, and managing medicines. Physical therapy helps with moving and getting strong again. Cognitive rehab tackles any thinking problems caused by SAH. The recovery timeline has several stages, like:
- Acute phase: Focus on stabilization and initial recovery
- Subacute phase: Emphasis on rehabilitation and regaining mobility and strength
- Chronic phase: Long-term management and prevention of future occurrences
Every person’s recovery is different. Understanding sah risk factors and being proactive in rehab can lessen long-term effects. This improves life quality.

Rehab helps patients become independent again and do their usual activities. With the right support, patients can overcome the recovery and rehab journey and have a good outcome.
| Stage of Recovery | Focus | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Acute phase | Stabilization and initial recovery | 1-2 weeks |
| Subacute phase | Rehabilitation and regaining mobility and strength | 2-6 weeks |
| Chronic phase | Long-term management and prevention of future occurrences | 6 months-1 year |
Prevention Strategies
To prevent a subarachnoid haemorrhage, you need to make lifestyle changes and see your doctor regularly. Keeping your blood pressure in check is key, as high blood pressure is a big risk factor. Quitting smoking and eating well can also help lower your risk of SAH.
Seeing your doctor often is crucial, especially if you have risk factors. Catching aneurysms or other problems early can help prevent SAH. Here are some important steps to take:
- Manage stress with meditation or yoga
- Avoid heavy lifting or bending to keep blood pressure down
- Stay active with walking or swimming to boost health
While you can’t prevent all subarachnoid haemorrhages, you can control many risk factors. By choosing a healthy lifestyle and keeping up with doctor visits, you can lower your risk.
Creating a prevention plan with your healthcare provider is vital. They’ll consider your unique risks and health history. Together, you can lower your risk of subarachnoid haemorrhage and stay healthy.
Long-term Outlook and Prognosis
Patients often wonder about their future after a subarachnoid hemorrhage. The severity of the bleed and how quickly treatment is given are key. Knowing the long-term effects helps patients and their families make better care choices.
Some important things to think about for the long term include:
- Survival rates, which depend on the bleed’s severity and treatment timing
- Quality of life, like how the bleed might affect physical and mental health
- Follow-up care, like regular doctor visits and ongoing treatments
Understanding the causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage is crucial. It helps patients prevent it and improve their health in the long run.
Survival Rates
Thanks to better treatments, survival rates for subarachnoid hemorrhage have gone up. But, the bleed’s severity and the patient’s health still play big roles.
Quality of Life Considerations
After a subarachnoid hemorrhage, quality of life can vary. It depends on the bleed’s severity, treatment success, and any other health issues. Cognitive rehabilitation and physical therapy can help patients regain strength and independence.
Conclusion
Subarachnoid haemorrhage is a serious condition that needs quick action. Knowing the causes, risk factors, and warning signs helps. This way, people can spot symptoms early and get medical help fast.
Thanks to new treatments and rehab options, many patients are recovering well. This gives hope and a way to get better.
It’s important for everyone to take care of their health. Learning about personal risk factors and preventing subarachnoid haemorrhage is key. Sharing this info with others can help save lives by acting early.
Acting fast and getting medical help is crucial for subarachnoid haemorrhage. By understanding and caring for our health, we can lessen the impact of this condition. This improves life for those affected.
FAQ
Q: What is Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) is a serious stroke. It happens when blood bleeds into the space around the brain. This is a life-threatening issue that needs quick medical help.
Q: What are the common causes of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: The main cause is a brain aneurysm rupture. This is a weak spot in a blood vessel. Other causes include head injuries, arteriovenous malformations, and some medical conditions.
Q: What are the primary symptoms of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: The main symptom is a sudden, severe headache. People often call it a “thunderclap headache.” Other signs include nausea, vomiting, neck stiffness, and light sensitivity.
Q: When should someone seek medical help for Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: If you have a sudden, severe headache, seek help right away. This is especially true for the emergency signs of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. Quick treatment can greatly improve your chances.
Q: How is Subarachnoid Haemorrhage diagnosed?
A: Doctors use tests like CT scans, MRI scans, and lumbar punctures to diagnose SAH. These tests show where the bleeding is in the subarachnoid space.
Q: What are the treatment options for Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: Treatment starts with medications to control blood pressure and prevent problems. Sometimes, surgery is needed to stop the bleeding. This can include clipping or coiling an aneurysm.
Q: What is the recovery process like for Subarachnoid Haemorrhage?
A: Recovery from SAH is long and may include physical and cognitive therapy. Each person’s recovery is different. The severity of the bleed and treatment speed affect the outcome.
Q: How can Subarachnoid Haemorrhage be prevented?
A: Preventing SAH is not always possible, but there are steps to lower the risk. Managing blood pressure, quitting smoking, and staying healthy are important. Regular check-ups can also help find and treat problems early.
