Every year, more people suffer from temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis. This is a serious disease that affects blood vessels in the head and neck. It can cause severe problems if not treated quickly. Symptoms include headaches, vision loss, and jaw pain.
Temporal arteritis is a complex condition that needs careful diagnosis and treatment. Quick action is key to avoid serious issues like vision loss and stroke. We will explore symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options in the following sections. This will help you understand the condition and how to manage it.
Key Takeaways
- Temporal arteritis, or giant cell arteritis, affects over 200,000 people in the US every year.
- The condition is characterized by inflammation of the temporal arteries, leading to symptoms such as headaches and vision loss.
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications such as vision loss and stroke.
- Temporal arteritis is a serious inflammatory disease that requires careful management.
- Understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of temporal arteritis is essential for effective treatment.
- Giant cell arteritis can cause significant morbidity if left untreated.
Understanding Temporal Arteritis
Temporal arteritis is a condition where the blood vessels, especially the temporal arteries, get inflamed. It’s a type of vasculitis. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own arteries, causing inflammation and damage.
The exact causes of temporal arteritis are still not fully known. It’s thought to be caused by a mix of genetic and environmental factors. People over 50 and those with a history of autoimmune diseases are at higher risk.
Definition and Mechanism
Temporal arteritis affects the temporal arteries. These arteries supply blood to the head and brain. The inflammation can cause headaches, vision problems, and jaw pain.
Role of the Immune System
The immune system is key in temporal arteritis. It mistakenly attacks the arteries, causing inflammation. This can be triggered by infections and other autoimmune diseases.
Understanding temporal arteritis is important for finding effective treatments. Recognizing the immune system’s role and risk factors helps prevent complications. By taking steps to reduce risk, individuals can manage the condition better.
| Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Temporal Arteritis | A form of vasculitis that involves inflammation of the temporal arteries |
| Autoimmune Disease | A condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues |
Common Signs and Symptoms of Temporal Arteritis
Temporal arteritis can cause a variety of symptoms, from mild to severe. A headache is one of the most common, often severe and lasting. Other symptoms include scalp tenderness, jaw pain, and vision loss.
Some people may also experience fever, fatigue, and weight loss. It’s important to notice these symptoms early. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications.
The symptoms of temporal arteritis can differ from person to person. Here are some common ones:
- Severe headache, often on one side of the head
- Scalp tenderness
- Jaw pain or claudication
- Vision loss or double vision
It’s key to recognize these symptoms early. If you’re experiencing any of them, see a healthcare professional right away. They can provide the right evaluation and care.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Headache | Severe and persistent headache, often on one side of the head |
| Vision Loss | Partial or complete loss of vision, which can be permanent if left untreated |
Risk Factors and Demographics
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, affects blood vessels in the head. It’s important to know who is at higher risk. Most cases happen in people over 50.
Studies show women are more likely to get temporal arteritis than men. Genetic predisposition might also be a factor. Some families have more cases. Environmental factors, like toxins or infections, could also play a part.
Age and Gender Considerations
Here are some key points to consider:
- Age: The risk goes up with age, especially over 50.
- Gender: Women are more likely to get it than men.
Genetic Predisposition
People with a family history might be more at risk. The exact genetic link isn’t clear yet. But research suggests genetics play a role.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to toxins or infections might also increase risk. More research is needed to understand this link.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Increases with age, particularly over 50 years old |
| Gender | Women are more likely to develop temporal arteritis than men |
| Genetic Predisposition | Individuals with a family history of temporal arteritis may be more susceptible |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to certain toxins or infections may contribute to development |
The Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing temporal arteritis can be tough because its symptoms are not always clear. Doctors need to take a detailed medical history and perform a physical exam. They look for signs like a tender or swollen temporal artery during this exam.
A temporal artery biopsy is a crucial test, but we’ll talk about it later. Blood tests might also be done to check for inflammation markers. These tests, like the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), help spot inflammation, a common sign of temporal arteritis.
- Blood tests to check for anemia or other blood disorders
- Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, to visualize the temporal artery
- A physical examination to check for signs of inflammation or other symptoms
Doctors use these tests and tools together to accurately diagnose temporal arteritis. Then, they can create a good treatment plan.
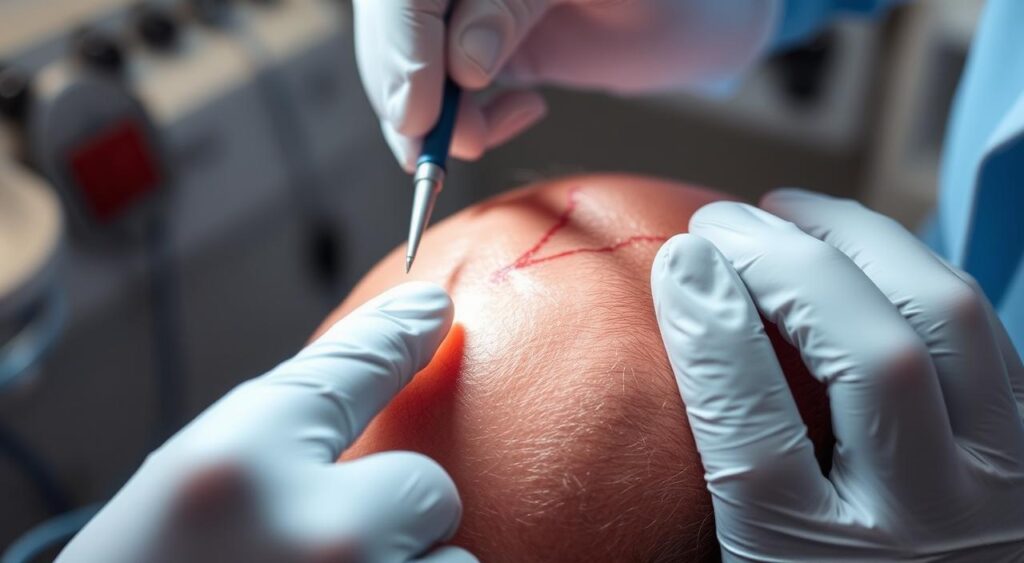
Temporal Artery Biopsy: The Gold Standard Test
A temporal artery biopsy is key for diagnosing temporal arteritis. It involves taking a small piece of the temporal artery for examination. This is done under local anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
A pathologist looks at the biopsy for signs of giant cell arteritis. This is a condition where blood vessels get inflamed. If the biopsy shows this, it helps doctors decide the best treatment. Sometimes, ultrasound or MRI is used along with the biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
What to Expect During the Biopsy Procedure
- The procedure is usually done in a doctor’s office or clinic.
- Local anesthesia numbs the area where the biopsy will be taken.
- A small incision is made in the skin to access the temporal artery.
- A section of the artery is removed and sent to a lab for examination.
Alternative Diagnostic Methods
In some cases, other tests might be used instead of a temporal artery biopsy. These include blood tests for inflammation or imaging studies to see the blood vessels. But, a temporal artery biopsy is still the best way to confirm temporal arteritis and guide treatment.
Treatment Options and Medications
Prompt treatment is key to avoid serious issues in temporal arteritis. The main treatment is prednisone treatment, which uses corticosteroids to lower inflammation. The treatment starts with high doses of prednisone, then gradually lowers the dose over time.
The aim of prednisone treatment is to ease symptoms and stop long-term damage. But, long-term use of steroids can lead to side effects like weight gain and mood swings. Doctors might use other treatments to lessen these risks, such as:
- Low-dose aspirin to prevent vision loss
- Medicines to handle side effects, like bone loss or high blood pressure
- Healthy lifestyle choices, like a good diet and exercise, to support health
It’s important to stay in close touch with a healthcare provider to find the best prednisone treatment plan. Regular check-ups help manage the condition and lower the risk of complications.
Managing Long-term Care and Prevention
Living with temporal arteritis, a form of vasculitis and autoimmune disease, needs a detailed plan. Regular check-ups with doctors are key to keep track of the disease and change treatments if needed.
People with temporal arteritis can benefit from lifestyle changes that boost overall health. Eating well, exercising often, and managing stress can help. These steps can ease symptoms and lower the risk of disease complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications
- Exercise regularly to improve overall health and well-being
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of comorbidities
Stopping complications is a big part of managing temporal arteritis. It’s important to watch for signs of flare-ups and manage other health issues. By working with doctors and making smart lifestyle choices, people can manage their condition well and live better.
Monitoring Progress
Regular check-ups and follow-ups are vital to track the disease’s progress and adjust treatments. This means watching for signs of complications like vision loss or heart disease. Adjusting lifestyle changes and treatments based on these signs is crucial.
| Complication | Monitoring Frequency |
|---|---|
| Vision Loss | Every 3-6 months |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Every 6-12 months |
Complications and Related Conditions
Temporal arteritis can cause serious problems if not treated. It can lead to vision loss because it inflames blood vessels in the eyes. This can damage the eyes and cause blindness. It also causes headache, which can be very severe.
Temporal arteritis can also raise the risk of stroke and aneurysms. It’s important to see a doctor right away if symptoms get worse. Some related conditions include:
- Polymyalgia rheumatica, a condition that causes muscle pain and stiffness
- Cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure and heart disease
- Stroke and aneurysms, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly
Getting a diagnosis and treatment early is key. It helps prevent these problems. By getting medical help and following treatment, people with temporal arteritis can lower their risk. This improves their health and quality of life.
Conclusion: Living with Temporal Arteritis
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, is a complex and chronic condition. It needs ongoing management and care. The journey to diagnosis and treatment can be tough, but there’s hope.
With the right medical care and a dedicated approach, many patients control the disease well. They can keep a good quality of life. This shows that with the right steps, living with temporal arteritis is possible.
Research is helping doctors understand temporal arteritis better. They’re finding new ways to treat it. Patients should work with their doctors to create a care plan that fits their needs.
By following their treatment plans and making lifestyle changes, people with giant cell arteritis can manage their condition. This shows that taking an active role in managing the disease is key.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Support groups and patient advocacy organizations offer valuable help. They provide education, resources, and a sense of community.
With the right medical care and self-care, living a fulfilling life with temporal arteritis is possible. It shows that with determination and support, managing this autoimmune disorder is achievable.
FAQ
Q: What is temporal arteritis?
A: Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, is a serious condition. It affects the blood vessels in the head and neck. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own arteries, leading to inflammation and potential complications.
Q: What are the common symptoms of temporal arteritis?
A: Symptoms include severe headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain. Vision problems, including vision loss, are also common. Other symptoms include fever, fatigue, and muscle aches.
Q: Who is at risk of developing temporal arteritis?
A: It mainly affects older adults, especially those over 50. Women are more likely to get it than men. Genetic and environmental factors can also increase the risk.
Q: How is temporal arteritis diagnosed?
A: Diagnosing it can be hard due to its varied symptoms. Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and blood tests. A temporal artery biopsy is the most accurate test.
Q: What is the treatment for temporal arteritis?
A: The main treatment is corticosteroids, like prednisone. Starting treatment quickly is key to avoid serious problems. The dose of prednisone is high at first and then lowered as the condition improves.
Q: What are the potential complications of temporal arteritis?
A: Untreated, it can cause permanent vision loss, stroke, and aneurysms. It can also lead to heart problems. It’s often linked to polymyalgia rheumatica, another inflammatory disorder.
Q: How can temporal arteritis be managed in the long term?
A: Long-term management includes lifestyle changes and regular check-ups. This includes a healthy diet, exercise, and monitoring symptoms. Keeping in touch with healthcare providers is key to managing the condition.
