Explore the key facts about synovial chondromatosis, a condition that involves the formation of cartilage nodules in the joints.
About 1 in 100,000 people have synovial chondromatosis, a rare joint disorder. It causes benign synovial tumors to form. This can really affect someone’s life, so it’s key to know about it.
Synovial chondromatosis makes cartilage nodules grow in joints. This leads to pain, stiffness, and trouble moving around.
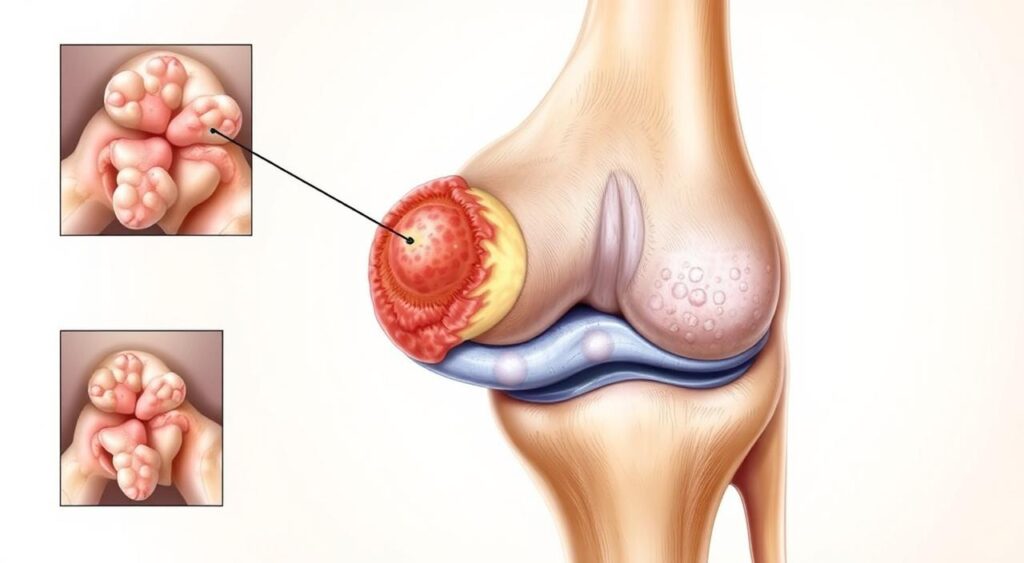
Anyone can get synovial chondromatosis, no matter their age or gender. It’s often not caught right away, which can make things worse. By learning about synovial chondromatosis, we can help people understand it better.
Key Takeaways
- Synovial chondromatosis is a rare joint disorder that affects 1 in 100,000 people.
- The condition involves the formation of benign synovial tumors in the joints.
- Synovial chondromatosis can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effective management of the condition.
- Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for individuals affected by synovial chondromatosis.
- Synovial chondromatosis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making awareness and education vital.
Understanding Synovial Chondromatosis
Synovial chondromatosis is a joint condition that causes pain and swelling. It happens when cartilage fragments and abnormal synovial tissue grow. This can make joints painful and stiff.
The condition is marked by cartilage nodules in joints, leading to pain and swelling. The synovial tissue, which lubricates joints, can get inflamed. Knowing the types of synovial chondromatosis helps people understand their condition better.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Synovial chondromatosis is about abnormal cartilage growth in joints, causing pain and swelling. It can be primary, where growth happens on its own, or secondary, caused by another condition. Understanding joint anatomy and synovial tissue’s role is key.
Types of Synovial Chondromatosis
There are two main types: primary and secondary. Primary is spontaneous cartilage growth, while secondary is caused by another condition. Knowing these types helps manage the condition and prevent complications.
Common Areas of Occurrence
Synovial chondromatosis can affect many joints, like knees, hips, and elbows. It’s more common in adults over 40. The specific joints affected vary by person and cause. Knowing where it often happens helps prevent it.
The Science Behind Joint Formation Changes
Joint formation changes are complex. They involve many factors, like joint swelling and arthroscopy. Cartilage nodules and synovial tissue can cause joint swelling. This is a common symptom of synovial chondromatosis.
This condition can lead to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure that can help. It involves removing the cartilage nodules and synovial tissue.
Understanding joint formation changes is key to effective treatment. Recognizing the role of joint swelling and arthroscopy in synovial chondromatosis is important. This helps individuals make informed decisions about their care.
- Joint swelling is a common symptom of synovial chondromatosis
- Arthroscopy can be used to diagnose and treat synovial chondromatosis
- Removing cartilage nodules and synovial tissue can help alleviate joint swelling and improve joint function
Exploring the science behind joint formation changes helps us understand synovial chondromatosis better. This knowledge aids in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Synovial chondromatosis is a joint disorder that can cause a range of symptoms. These include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms are often the first signs that something is wrong.
Primary Symptoms
The primary symptoms of synovial chondromatosis include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness and limited mobility
- Creaking or grinding sensations in the joint
These symptoms can vary in severity. They may worsen over time if left untreated.
Secondary Complications
If left untreated, synovial chondromatosis can lead to secondary complications. These include joint instability and limited mobility. In some cases, a benign synovial tumor may develop. This can cause additional symptoms and require treatment options.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you are experiencing persistent or worsening symptoms, seek medical attention. A doctor can diagnose synovial chondromatosis. They can also recommend treatment options to manage the condition and prevent further complications.
Understanding the common signs and symptoms of synovial chondromatosis is crucial. It helps individuals navigate the complexities of this condition. With the right treatment options, it is possible to manage symptoms and prevent long-term damage to the joint.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Joint pain | Persistent pain in the affected joint |
| Swelling | Inflammation and swelling in the affected joint |
| Stiffness | Limited mobility and stiffness in the affected joint |
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding the risk factors and causes of synovial chondromatosis is key. Joint pain and swelling are common symptoms. These symptoms come from cartilage fragments and synovial tissue.
Research shows that cartilage nodules and synovial tissue lead to joint pain and swelling. The exact causes are still a mystery. But several factors are believed to play a role.
- Genetic predisposition
- Joint trauma or injury
- Inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis
- Aging and wear and tear on the joints
Anyone can get synovial chondromatosis, regardless of age or sex. But some people might be more likely to get it. This could be due to their genes or lifestyle.
To lower your risk, keep a healthy weight and exercise regularly. Avoid activities that might hurt your joints. If you have symptoms, see a doctor. They can help manage synovial chondromatosis and joint pain caused by cartilage fragments.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic predisposition | Individuals with a family history of synovial chondromatosis may be more prone to developing the condition |
| Joint trauma or injury | Joint trauma or injury can cause the formation of cartilage fragments and synovial tissue, leading to synovial chondromatosis |
| Inflammatory conditions | Inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, can increase the risk of developing synovial chondromatosis |
Diagnostic Process and Testing
Diagnosing synovial chondromatosis, a joint disorder, requires a few steps. First, a doctor will do a physical exam to check for pain and swelling. Then, imaging tests like X-rays and MRI scans are used to see more details of the joint. These tests help confirm if you have the condition.
Imaging tests are key in spotting a benign synovial tumor. Arthroscopy, a surgery, can also help. In this procedure, a surgeon uses a camera and tools to remove the tumor and any damaged tissue from the joint.
Diagnostic Tests
- Physical examination to assess joint pain and swelling
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to confirm the diagnosis
- Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and joint fluid analysis, to rule out other conditions
- Arthroscopy to diagnose and treat synovial chondromatosis
Knowing how to diagnose synovial chondromatosis helps people understand their joint disorder better. If symptoms don’t go away or get worse, it’s important to see a doctor. Early treatment can prevent serious damage to the joint.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Getting a diagnosis early is crucial for treating synovial chondromatosis. It helps avoid long-term damage to the joint. With a doctor’s help, you can create a treatment plan that fits your needs. This way, you can manage your symptoms better.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical examination | To assess joint pain and swelling |
| Imaging studies | To confirm the diagnosis and identify the presence of a benign synovial tumor |
| Arthroscopy | To diagnose and treat synovial chondromatosis |
Impact on Daily Life and Mobility
Synovial chondromatosis can really affect your daily life and how you move. It causes joint pain and swelling. This makes it hard to do simple things like walking or climbing stairs.
The synovial tissue around the joint gets inflamed. This leads to more joint pain and stiffness. It’s tough to do physical activities or even simple tasks because of this.
People with synovial chondromatosis face many challenges. These include:
- Limited range of motion
- Joint instability
- Persistent joint pain
- Swelling and inflammation
It’s important to understand how synovial chondromatosis affects your life and movement. Knowing about cartilage fragments and synovial tissue inflammation helps. It lets you manage your condition better and improve your life quality.
| Common Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Joint Pain | Persistent pain in the affected joint |
| Limited Mobility | Difficulty moving the affected joint |
| Swelling and Inflammation | Inflammation and swelling in the affected joint |
Treatment Options and Approaches
Understanding the treatment options for joint disorders like synovial chondromatosis is key. The main goal is to ease symptoms, stop further problems, and boost life quality. For those with benign synovial tumors, treatment choices depend on how severe the condition is and the person’s health.
Here are some common treatments for synovial chondromatosis:
- Conservative management, which may involve physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle changes
- Surgical interventions, such as arthroscopy, for more severe cases
- Post-treatment care, crucial for a smooth recovery and to avoid complications
Exploring these treatment options helps those with synovial chondromatosis deal with the condition better. It’s vital to talk to a healthcare professional. They can help find the best treatment for a benign synovial tumor and create a plan for managing the joint disorder.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Living with synovial chondromatosis can be tough, especially when dealing with joint pain and discomfort. The condition makes cartilage fragments break off and move in the joint. This leads to inflammation and pain. It’s key to take care of synovial tissue health to ease these symptoms.
Here are some ways to manage pain and discomfort:
- Taking pain relief medications as prescribed by a doctor
- Engaging in physical therapy to improve joint mobility and strength
- Making lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition
By actively managing joint pain and discomfort, people with synovial chondromatosis can live better lives. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
With the right treatment and self-care, you can lessen the effects of cartilage fragments and synovial tissue damage. By focusing on joint health and getting medical help when needed, you can lead a more active and pain-free life.
| Management Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Pain relief medications | Reduces joint pain and inflammation |
| Physical therapy | Improves joint mobility and strength |
| Lifestyle modifications | Supports overall joint health and well-being |
Prevention and Risk Reduction
To prevent and reduce the risk of synovial chondromatosis, making lifestyle changes is key. Keeping a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive joint movements can help. This condition is often linked to a benign synovial tumor.
Here are some ways to prevent and reduce the risk of synovial chondromatosis:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress
- Avoiding repetitive joint movements that can cause wear and tear
- Engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles and improve joint mobility
Understanding treatment options and taking preventive steps can help manage synovial chondromatosis. This way, individuals can make informed health decisions.

It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare professional about the best treatment and prevention strategies. Working together, individuals can lower their risk of this condition and improve their joint health.
| Prevention Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintaining a healthy weight | Reduces joint stress and wear and tear |
| Avoiding repetitive joint movements | Prevents excessive wear and tear on the joints |
| Engaging in regular exercise | Strengthens muscles and improves joint mobility |
Long-term Outlook and Prognosis
Understanding the long-term outlook of synovial chondromatosis is key for those affected. The severity of the condition and overall health greatly influence the outcome. With the right treatment, most people can fully recover, but recovery times vary.
Joint pain is a common symptom that needs to be managed. Cartilage fragments can sometimes cause more problems, like limited mobility. But, with ongoing treatment, these issues can be managed well.
Recovery Expectations
Recovery from synovial chondromatosis depends on several factors. These include the condition’s severity and the success of treatment. Generally, with proper care, people see a big improvement in their symptoms and quality of life. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to create a treatment plan and track progress.
Potential Complications
Potential complications include limited mobility, joint instability, and ongoing pain. Cartilage fragments can also cause more damage to the joint. Regular check-ups and follow-up care help catch these issues early, allowing for quick action and management.
Latest Research and Developments
Research on synovial chondromatosis, a joint disorder with a benign synovial tumor, is ongoing. The goal is to better treatment options for those affected.
New surgical techniques and therapies are being explored. For instance, minimally invasive surgery and arthroscopy are being looked into as treatment options for synovial chondromatosis.
Researchers are also studying non-surgical methods. This includes physical therapy and pain management to help manage symptoms. These new approaches aim to improve the quality of life for those with this joint disorder.
In summary, the latest research aims to offer more effective and tailored treatment options. This is to enhance the health and well-being of those with synovial chondromatosis.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our look at synovial chondromatosis, it’s key to remember it’s manageable. Understanding its causes, spotting symptoms, and getting medical help early are crucial steps. These actions help tackle joint pain and cartilage fragments linked to this condition.
Managing synovial chondromatosis well means talking openly with doctors, trying different treatments, and being involved in care. The right mix of non-surgical and surgical steps, along with tailored care, can greatly improve life quality. Many people find relief and better health through these efforts.
With ongoing research and medical progress, there’s hope for those with synovial chondromatosis. Staying updated and pushing for health care is vital. Patients can take charge of their health and work towards the best outcomes.
FAQ
Q: What is synovial chondromatosis?
A: Synovial chondromatosis is a joint disorder. It causes cartilage nodules in the joint’s synovial tissue. This leads to pain, swelling, and limited movement.
Q: What are the different types of synovial chondromatosis?
A: There are two types: primary and secondary. Primary has no known cause. Secondary is linked to another joint issue or injury.
Q: Where does synovial chondromatosis commonly occur?
A: It often affects the knee. But it can also happen in the hip, shoulder, elbow, and ankle.
Q: What are the primary symptoms of synovial chondromatosis?
A: Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. People may also have trouble moving and feel unstable.
Q: What are the potential complications of synovial chondromatosis?
A: Complications can include osteoarthritis and joint deformity. A benign tumor in the synovium can also develop.
Q: When should someone seek medical attention for synovial chondromatosis?
A: See a doctor for persistent or worsening symptoms. Early treatment helps avoid complications.
Q: What are the risk factors and causes of synovial chondromatosis?
A: The exact cause is unknown. It’s thought to involve cartilage fragments and synovial tissue in the joint.
Q: How is synovial chondromatosis diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging studies, and lab tests. These include X-rays, MRI, and joint fluid analysis.
Q: What are the treatment options for synovial chondromatosis?
A: Treatment includes physical therapy and pain meds. Surgery, like arthroscopy, may also be needed. Post-treatment care helps recovery.
Q: How can individuals manage pain and discomfort associated with synovial chondromatosis?
A: Manage pain with meds, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Keep a healthy weight and avoid repetitive movements.
Q: What can be done to prevent or reduce the risk of synovial chondromatosis?
A: A healthy lifestyle and regular exercise may help. Avoiding repetitive joint movements is also beneficial.
Q: What is the long-term outlook and prognosis for individuals with synovial chondromatosis?
A: The outlook depends on the condition’s severity and the individual’s health. Most people recover fully, but complications like limited mobility can occur.
Q: What are the latest research and developments in the treatment of synovial chondromatosis?
A: Research aims to improve treatments. New surgical techniques and therapies are being developed to manage the condition and reduce complications.
