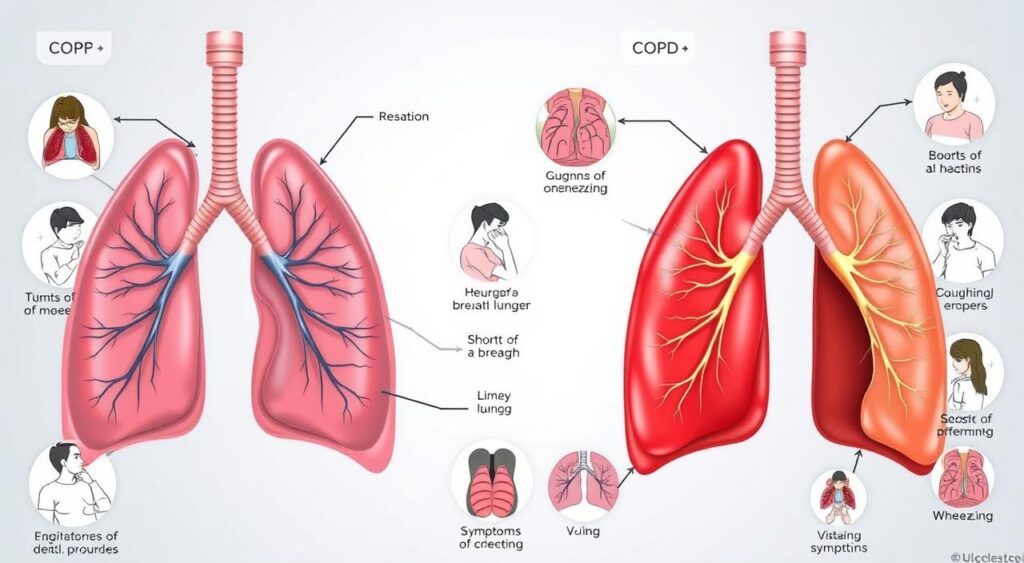
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a serious lung condition that affects millions. It makes it hard for people to breathe because their airways get blocked. Knowing the symptoms early is key to getting the right treatment.
COPD includes diseases like emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Over time, the lungs get inflamed and damaged. People with COPD often have trouble breathing, cough a lot, and produce a lot of mucus.
Key Takeaways
- COPD is a progressive lung disease that obstructs airflow and makes breathing difficult.
- COPD encompasses a range of lung conditions, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
- Early detection of COPD symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
- COPD symptoms can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life, including shortness of breath, persistent cough, and wheezing.
- Understanding the signs and symptoms of COPD is the first step in seeking appropriate medical care and managing this chronic lung condition.
What is COPD: Understanding the Basics of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a group of lung conditions that make breathing hard. It includes two main types: emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Types of COPD Conditions
Emphysema damages the air sacs in the lungs, making it hard to breathe. This is because the surface area for oxygen exchange gets smaller.
Chronic bronchitis causes inflammation and damage to the airways. It leads to a lot of mucus and a constant cough.
How COPD Affects the Respiratory System
COPD damages the airways and lungs, making them less flexible. This makes it hard for the lungs to work right. It leads to trapped air and shortness of breath.
- Destruction of alveoli (air sacs) in emphysema reduces the surface area for oxygen exchange.
- Chronic inflammation and excess mucus production in chronic bronchitis obstruct airflow.
- The overall lung damage associated with COPD impairs the respiratory system’s ability to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide effectively.
| Condition | Description | Key Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Emphysema | Destruction of alveoli (air sacs) | Airflow limitation, reduced oxygen exchange |
| Chronic Bronchitis | Persistent airway inflammation and mucus buildup | Airflow obstruction, chronic cough |
“COPD is a major cause of disability and the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is a progressive disease, meaning it typically worsens over time.”
Early Warning Signs and Common COPD Symptoms
It’s important to know the early signs and common symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a lung condition that gets worse over time. If not treated, it can greatly affect a person’s life quality.
Shortness of breath is a common symptom of COPD. As the disease gets worse, breathing becomes harder, especially when doing physical activities. A chronic cough that brings up mucus or phlegm is also common. Wheezing, a high-pitched sound when breathing, and chest tightness are symptoms many COPD patients experience.
Spotting these symptoms early is key. It lets doctors start treatment early. This can help manage the disease, reduce discomfort, and slow it down.
| Common COPD Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Shortness of breath | Difficulty in breathing, especially during physical activity |
| Chronic cough | Persistent cough, often with mucus or phlegm production |
| Wheezing | High-pitched whistling sound during breathing |
| Chest tightness | Feeling of constriction or tightness in the chest |
Telling a doctor about these symptoms early can lead to quick diagnosis and treatment. This can greatly improve the life of someone with COPD.
Risk Factors and Causes of COPD Development
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a complex condition. It is influenced by many risk factors and causes. Knowing these is key for managing and preventing this respiratory illness.
Smoking and COPD Connection
Tobacco smoke is the main risk factor for COPD. Cigarette smoking causes most COPD cases. Long-term exposure to tobacco smoke damages the lungs irreversibly.
Quitting smoking can greatly reduce COPD risk. For those already diagnosed, quitting can improve lung function and slow disease progression.
Environmental and Occupational Risk Factors
Exposure to other air pollution also increases COPD risk. This includes certain occupations with high occupational exposure to dust, chemicals, or fumes.
Genetic Predisposition to COPD
Genetics also plays a role in COPD susceptibility. Conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can increase risk. This is even without significant tobacco smoke exposure.
Understanding these risk factors helps individuals take action. Regular check-ups, lifestyle changes, and prompt treatment can improve quality of life. They can also slow COPD progression.
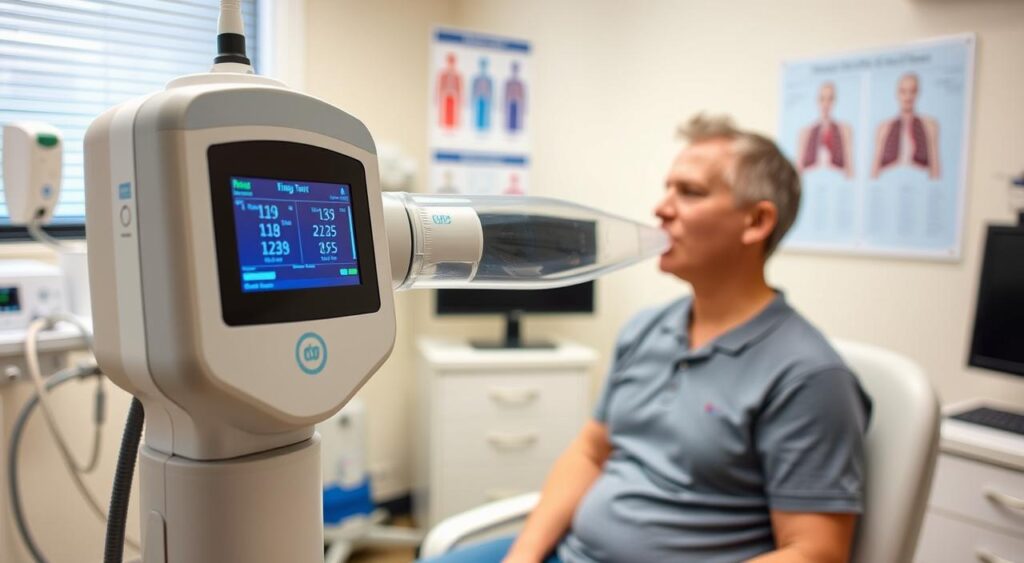
Diagnosing COPD: Tests and Medical Evaluations
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Doctors use various tests and evaluations to confirm COPD and its severity. These tools give insights into lung function and respiratory health.
Spirometry is a main test for COPD. It measures air volume and flow when you breathe in and out. This test shows how much air you can move, a key sign of COPD.
- Spirometry helps find out the type and stage of COPD, guiding treatment.
- It’s often paired with chest X-rays and CT scans to check for other lung issues and get a full picture.
Pulmonary function tests are also vital in diagnosing COPD. These tests check lung performance, like capacity, airflow, and gas exchange.
- These tests show how severe COPD is and how it changes over time.
- They help doctors create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
“Early and accurate diagnosis of COPD is essential for effective management and improved patient outcomes.”
People with suspected COPD get the right care and support through thorough testing. These tests and evaluations help doctors understand the patient’s respiratory health. This leads to more tailored and effective COPD treatment.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a complex condition. It needs a comprehensive treatment and management plan. The main goals are to ease symptoms, improve exercise ability, and lower the risk of worsening.
Medication and Inhaler Types
Inhaled bronchodilators are key in treating COPD. They help relax and open airways, making breathing easier. Corticosteroids may also be used to reduce inflammation and prevent worsening. Patients often use a mix of these medicines through inhalers to manage their COPD well.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Pulmonary rehabilitation combines exercise training, education, and counseling. It helps COPD patients improve their physical and emotional health. These programs include:
- Aerobic exercises to boost cardiovascular fitness
- Strength training to improve muscle function
- Breathing techniques to enhance respiratory efficiency
- Nutritional counseling and support
Lifestyle Modifications for COPD Patients
Along with medication and rehabilitation, lifestyle changes can help COPD patients. These include:
- Quitting smoking or avoiding secondhand smoke
- Maintaining a healthy diet and weight
- Incorporating exercise training into daily life
- Ensuring adequate oxygen therapy when needed
- Managing other health issues like heart disease or diabetes
By using these treatment options and strategies, COPD patients can manage their symptoms better. They can also improve their quality of life and lower the risk of disease worsening.
Living with COPD: Daily Management Tips
Managing COPD daily can be tough, but the right strategies can help. You can improve your life and keep your lungs healthy. Here are some tips on breathing, saving energy, and nutrition for COPD patients.
Breathing Techniques for COPD
Proper breathing is key for COPD patients. Try these breathing exercises every day:
- Diaphragmatic breathing (also known as belly breathing): Inhale deeply through your nose, letting your belly expand. Then, exhale slowly through pursed lips.
- Pursed-lip breathing: Breathe in through your nose and out through pursed lips. This can slow your breathing and reduce breathlessness.
- Chest and abdominal exercises: Do gentle stretches and movements to strengthen your breathing muscles.
Energy Conservation Strategies
COPD can make simple tasks feel like a lot of work. Here are ways to save your energy:
- Pace yourself and take breaks when you need to.
- Organize your living space to reduce unnecessary movement.
- Use devices like long-handled tools or electric appliances to make things easier.
Nutrition for COPD Management
Eating right is important for COPD patients. Eat foods that help you breathe and conserve energy. Choose lean proteins, whole grains, and fruits and vegetables. Drink plenty of water all day.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can make COPD symptoms worse. Find ways to relax, like meditation, deep breathing, or gentle exercise. Talk to friends, family, or a mental health professional if you need help.
By following these daily tips, you can manage your COPD better. This can improve your life quality and health.

COPD Complications and Emergency Situations
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a serious condition. It can lead to many complications if not managed well. It’s important for patients and their caregivers to know about these issues and emergency signs.
Recognizing COPD Exacerbations
An acute exacerbation is a sudden and serious worsening of symptoms. Patients might feel more breathless, cough more, wheeze, and see a change in mucus color or amount. These can be caused by infections, pollution, or stress.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Care
Seek immediate medical help if you notice these warning signs:
- Severe shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Rapid heart rate or irregular heartbeat
- Confusion, drowsiness, or changes in mental status
- Coughing up blood or thick, colored mucus
- Fever or signs of respiratory infection, such as pneumonia
These symptoms could mean a acute exacerbation, respiratory failure, or serious heart problems. Quick medical care is needed to avoid further problems and prevent respiratory failure or heart problems.
| Complication | Symptoms | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Exacerbation | Increased breathlessness, coughing, wheezing, change in mucus color/amount | Respiratory infections, air pollution, stress |
| Respiratory Failure | Severe shortness of breath, confusion, drowsiness | Acute exacerbation, pneumonia, heart problems |
| Cardiovascular Complications | Chest pain, rapid or irregular heart rate | Underlying heart disease, oxygen deprivation due to COPD |
By knowing the warning signs and getting medical help quickly, COPD patients can avoid serious complications. This can improve their health and quality of life.
Prevention Strategies and Lifestyle Changes
Keeping a healthy lifestyle is key to avoiding or slowing down chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Focus on quitting smoking, getting vaccinated, improving air quality, and staying active.
Quit Smoking, Breathe Easier
Smoking is the main cause of COPD. Stopping can greatly lower your risk and slow the disease’s growth. Get help from doctors, join programs, or try nicotine substitutes to quit.
Vaccination: Protecting Your Lungs
Getting regular shots, like the flu vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine, can lower the risk of lung infections. These infections can make COPD symptoms worse. Staying up-to-date with vaccines is crucial for COPD patients.
Cleaner Air, Healthier Lungs
Being around air pollutants can harm your lungs and make COPD worse. Use air purifiers, avoid secondhand smoke, and limit dust and chemical exposure. This helps keep your lungs healthy.
Get Moving, Breathe Better
Exercise regularly to improve lung function and reduce COPD symptoms. Try walking, swimming, or low-impact exercises. An active lifestyle supports your respiratory health.
| Prevention Strategy | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Smoking cessation | Reduces COPD risk and slows disease progression |
| Vaccination | Protects against respiratory infections that can exacerbate COPD |
| Improved air quality | Minimizes exposure to pollutants that can worsen COPD |
| Regular physical activity | Enhances lung function and overall well-being for COPD patients |
By using these prevention strategies and making lifestyle changes, you can lower your risk of COPD or better manage it.

“The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second best time is now.” – Chinese Proverb
Support Resources and Community Programs for COPD Patients
Living with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can be tough. But, there are many support resources and community programs to help. These include patient support groups and educational materials. They offer the information, guidance, and friendship needed to manage COPD well.
Patient Support Groups
Joining a COPD support group can change your life. These groups, run by the COPD Foundation or the American Lung Association, are safe spaces. Here, patients can share their stories, learn new ways to cope, and find support from others who get it.
Educational Resources
Knowing a lot about COPD is key. The COPD Foundation and the American Lung Association have lots of online resources. They cover everything from understanding the disease to managing treatments. This knowledge helps patients take charge of their health.
Local communities and healthcare providers also have COPD programs and groups. Patients should look for these in their area. They can find help through online forums, healthcare providers, or the COPD Foundation’s local chapters.
By using the many support resources and community programs out there, COPD patients can learn, grow, and feel supported. This helps them manage their condition better and live a better life.
Conclusion
COPD is a serious lung disease that needs careful management and ongoing support. Finding it early is key, as it lets us start treatments sooner. This can slow down the disease’s progress.
Sticking to treatment plans, joining pulmonary rehab, and changing lifestyle habits can greatly help. These steps can make life better for those with COPD.
It’s important to spread the word about COPD. Many people don’t know about it or ignore its early signs. By pushing for regular health checks, we help patients take charge of their lung health.
With the right care, people with COPD can live well despite their condition. They can manage symptoms, avoid bad episodes, and enjoy life. Let’s work together to support those with COPD and improve their lives.
FAQ
Q: What is COPD?
A: COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is a lung disease that makes breathing hard. It’s a condition that can really affect a person’s life.
Q: What are the different types of COPD conditions?
A: There are two main types of COPD: emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Emphysema damages the air sacs in the lungs. Chronic bronchitis causes inflammation and too much mucus in the airways.
Q: How does COPD affect the respiratory system?
A: COPD limits airflow and damages the lungs. This makes breathing hard, leading to symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and tightness in the chest.
Q: What are the early warning signs and common symptoms of COPD?
A: Early signs of COPD include a persistent cough, chronic sputum, and shortness of breath. Common symptoms are chest tightness, frequent infections, and trouble exercising.
Q: What are the risk factors and causes of COPD development?
A: Long-term tobacco smoke exposure is the main risk factor for COPD. But, pollution, work-related exposures, and genetics also play a role.
Q: How is COPD diagnosed?
A: Doctors diagnose COPD through medical history, physical exams, and tests like spirometry and chest X-rays. These help confirm airflow obstruction.
Q: What are the treatment options and management strategies for COPD?
A: Treatment for COPD includes medicines like bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Pulmonary rehab and lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and exercising are also key.
Q: How can COPD patients manage the condition on a daily basis?
A: COPD patients can manage their condition by using breathing techniques, saving energy, eating well, and managing stress. These steps can improve their quality of life.
Q: What are the potential complications and emergency situations associated with COPD?
A: COPD can lead to serious complications like acute exacerbations and respiratory failure. It’s crucial for patients to know when to seek urgent medical help.
Q: What prevention strategies and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of COPD?
A: Preventing COPD involves quitting smoking, improving air quality, getting vaccinated, and staying active. A healthy lifestyle can slow COPD’s progression.
Q: What support resources and community programs are available for COPD patients?
A: COPD patients can find support through groups, educational materials, and organizations like the COPD Foundation and American Lung Association. These resources help manage the condition.
