Explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of Giant Cell Arteritis, a serious inflammatory condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Giant cell arteritis: It’s a serious condition that affects blood vessels, especially in the head. Knowing about giant cell arteritis, its symptoms, diagnosis, and management is key. This ensures quick medical help and prevents serious problems.
Giant cell arteritis needs immediate medical care. It’s important to know its symptoms, like gca symptoms, to act fast. Getting a correct diagnosis is crucial. It helps prevent long-term damage and ensures the condition is managed well.
Key Takeaways
- Giant cell arteritis is a serious inflammatory condition that affects the blood vessels in the head.
- Understanding giant cell arteritis symptoms is crucial for prompt medical attention.
- Giant cell arteritis diagnosis is complex and requires careful evaluation.
- Recognizing gca symptoms is vital for effective treatment and management.
- Giant cell arteritis can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Timely intervention is essential to prevent long-term damage.
- Effective management of giant cell arteritis requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition.
Understanding Giant Cell Arteritis: An Overview
Giant cell arteritis, also known as temporal arteritis, is a condition that causes blood vessel inflammation. This mainly affects the arteries in the head. It can lead to gca symptoms like headaches, scalp tenderness, and vision problems. Knowing about giant cell arteritis is key to understanding its effects and why quick medical help is crucial.
This condition often hits people over 50, especially women. The exact cause is still a mystery, but it’s thought to involve genetics and environment.
Definition and Basic Concepts
Giant cell arteritis is marked by giant cells in inflamed blood vessels. These cells are part of the immune system’s fight against inflammation. If not treated, it can cause blindness.
Who is Most Commonly Affected
People over 50 are most at risk, especially women. Other factors include a family history of the disease, other inflammatory diseases, and certain genes.
The Impact on Blood Vessels
The inflammation damages blood vessels, reducing blood flow. This can cause gca symptoms like headaches, scalp tenderness, and vision issues. In severe cases, it can lead to blindness or stroke.
Knowing about giant cell arteritis is vital. It helps us understand its effects and why quick medical care is important. By knowing the gca symptoms and risk factors, we can take steps to prevent it and seek help if symptoms appear.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | People over the age of 50 are more likely to develop giant cell arteritis |
| Family History | A family history of giant cell arteritis increases an individual’s risk of developing the condition |
| Genetic Predisposition | Certain genetic predispositions can increase an individual’s risk of developing giant cell arteritis |
Common Signs and Warning Signals
It’s important to know the gca symptoms of Giant Cell Arteritis early. This condition can cause headaches, scalp tenderness, and vision issues. These symptoms can affect your daily life. Knowing the giant cell arteritis causes helps you prevent it and get help fast.
Here are some common signs of Giant Cell Arteritis:
- Headaches and scalp tenderness
- Vision problems, such as double vision or blind spots
- Jaw pain or claudication
- Fever and fatigue
Knowing these gca symptoms is key. If you notice them, see a doctor right away. Early treatment can stop serious problems and help you feel better.
Risk Factors and Triggers
It’s important to know the risk factors for giant cell arteritis to prevent and manage it. Age is a big factor in getting this condition. As people get older, their risk of getting giant cell arteritis goes up.
Many things can lead to giant cell arteritis, like genes and the environment. Genetic predisposition means some people are more likely to get it because of their genes. Things like infections and toxins can also start the condition.
Age-Related Considerations
Age is a big risk factor for giant cell arteritis. Most people get it after 50. Older blood vessels are less flexible, making them more likely to get inflamed and damaged.
Genetic Predisposition
Some people might be more likely to get giant cell arteritis because of their genes. Certain genes can increase the risk. Knowing about these genes can help people take steps to lower their risk.
Environmental Factors
Things like infections and toxins can start giant cell arteritis. Knowing about these factors can help people avoid them. By understanding the risks, people can take steps to prevent and manage the condition, lowering their chance of complications.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Increased risk with age, especially over 50 |
| Genetic Predisposition | Certain genetic markers increase risk |
| Environmental Factors | Infections and exposure to toxins can trigger onset |
The Connection Between Temporal Arteritis and GCA
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell arteritis, is a condition that affects the blood vessels. It causes inflammation and damage. Temporal arteritis and giant cell arteritis are the same condition. The difference is that temporal arteritis affects the temporal arteries.
The symptoms of temporal arteritis and giant cell arteritis are similar. These include headaches, scalp tenderness, and vision problems. The diagnosis and treatment depend on the severity and location of the inflammation.
Some key facts about temporal arteritis and giant cell arteritis include:
- Temporal arteritis is a type of giant cell arteritis that affects the temporal arteries.
- Giant cell arteritis is a condition that affects the blood vessels, leading to inflammation and damage.
- The symptoms of temporal arteritis and giant cell arteritis can be similar, but the diagnosis and treatment can vary.
Understanding the connection between temporal arteritis and giant cell arteritis is crucial. Recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention is key. This way, individuals can get the right treatment and manage their condition.
| Condition | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Temporal Arteritis | Headaches, scalp tenderness, vision problems | Corticosteroids, medication to reduce inflammation |
| Giant Cell Arteritis | Headaches, scalp tenderness, vision problems, fever | Corticosteroids, medication to reduce inflammation, lifestyle modifications |
Critical Symptoms of Giant Cell Arteritis
Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. If gca symptoms are ignored, it can lead to severe problems. The giant cell arteritis diagnosis looks for key symptoms that show this condition.
Important symptoms of GCA include headaches, scalp tenderness, vision issues, and other body-wide symptoms. These signs can get worse over time. Spotting these symptoms early is key to getting the right treatment and avoiding serious issues.
Headache and Scalp Tenderness
A headache is a common sign of GCA, feeling like a dull ache on one side of the head. The scalp might also hurt when you brush your hair. These symptoms can be quite painful and may come with other signs like fever and tiredness.
Vision Problems and Complications
Vision troubles are a big worry with GCA, as they can cause permanent blindness if not treated. You might see double, have blurry vision, or lose sight in one eye. If you notice any vision problems, get medical help right away.
Other signs of giant cell arteritis diagnosis include jaw pain when you chew or talk. Spotting these symptoms early and getting medical help fast can stop serious problems and help with treatment.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Getting a correct giant cell arteritis diagnosis is key for treatment for gca. Doctors use physical checks, medical history, and tests to find the right treatment. This careful process helps doctors choose the best way to manage the condition.
Tests for giant cell arteritis include blood tests for inflammation, ultrasound or MRI for blood vessel damage, and biopsy for tissue samples. These tests confirm giant cell arteritis and rule out other causes of symptoms.
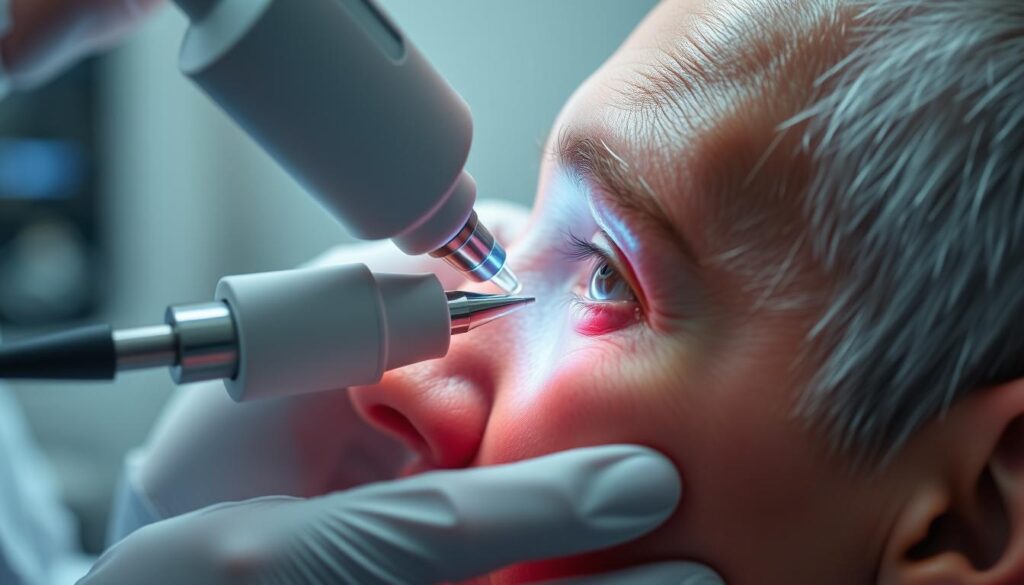
The temporal artery biopsy is a crucial test. It involves taking a small tissue sample from the affected artery. This test looks for giant cells and other signs of the condition. Blood tests like ESR and CRP also check inflammation levels.
Doctors use these tests to create a good treatment for gca plan. This plan might include medicine, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. These steps help prevent complications and manage symptoms.
Treatment Options and Medical Interventions
Managing giant cell arteritis focuses on reducing inflammation and preventing complications. The main treatment is corticosteroid therapy. It helps ease symptoms and stops vision loss.
A treatment plan for giant cell arteritis may include:
- Corticosteroid therapy to reduce inflammation
- Alternative medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications
- Regular monitoring to adjust the treatment plan as needed
Working closely with a healthcare provider is key. They help create a treatment plan for managing giant cell arteritis. With the right treatment, it’s possible to treat GCA and avoid long-term damage.
Corticosteroid Therapy
Corticosteroid therapy is the most common treatment for giant cell arteritis. It reduces inflammation and prevents complications.
Alternative Medications
Other medications may be given to manage symptoms and prevent complications. These help lower the risk of vision loss and serious complications.
Duration of Treatment
The treatment length for giant cell arteritis varies. It’s crucial to work with a healthcare provider. They help create a personalized treatment plan and make adjustments as needed.
Preventing Vision Loss and Complications
Managing giant cell arteritis is key to avoiding serious problems, especially vision loss. Gca complications can be very serious and permanent. It’s vital to catch them early and act fast. If you notice sudden vision loss, double vision, or blind spots, get help right away.
Regular visits to your doctor are crucial. They will check your blood, do imaging studies, and test your vision. This helps find problems early. By staying close to your doctor and knowing the risks, you can lower your chance of complications and live better.
Emergency Care Guidelines
If you think you’re having a complication, like sudden vision loss, get to the emergency room fast. A doctor can start treatment with corticosteroids and other medicines. This helps reduce swelling and prevent more damage. Sometimes, you might need to stay in the hospital for close care and treatment.
Early Warning Signs
- Sudden vision loss
- Double vision
- Blind spots
- Severe headache
- Jaw pain or claudication
Knowing these signs and acting quickly can help avoid complications. Managing giant cell arteritis means regular checks, quick treatment, and a focus on preventing problems. This approach helps keep you healthy and improves your life.
Living with GCA: Lifestyle Modifications
Managing giant cell arteritis (GCA) means making lifestyle changes. Healthy habits can greatly improve life for those with GCA. Simple daily changes can help manage the condition and lower the risk of problems.
Knowing about GCA is key to making good treatment and lifestyle choices. Patients should talk to their doctors to create a plan that fits their needs. This teamwork helps people take charge of their health and feel better.
Here are some tips for living with GCA:
- Regular exercise, like walking or yoga, keeps you flexible and strong
- Eating a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is important
- Getting enough sleep and using stress-reducing methods, like meditation, helps too
By making these lifestyle changes and staying informed about GCA, people can manage their condition well.

It’s important for patients to be proactive and informed in their care. This can be done through ongoing education and support. This way, people with GCA can live active and meaningful lives, even with the challenges of their condition.
| Lifestyle Modification | Benefits for GCA Management |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Improves flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of complications |
| Balanced Diet | Supports overall health and well-being, helping to manage GCA symptoms |
| Adequate Sleep and Stress Reduction | Enhances overall health and reduces the risk of GCA-related complications |
Support Systems and Resources
Living with giant cell arteritis needs a strong support system. It’s key to raise gca awareness so patients get the right care. There are many resources to help patients deal with this condition.
Joining patient support groups is a great idea. Here, people share their stories and find others facing similar issues. These groups offer a community feeling and keep patients updated on new research and treatments. There are also educational materials to help patients understand their condition better.
Patient Support Groups
- Online forums and discussion groups
- Local support groups and meetups
- Telephone support lines
Healthcare Provider Networks
Having a good relationship with healthcare providers is vital. Patients should work with a team of doctors, including rheumatologists and ophthalmologists. This ensures a personalized treatment plan. Staying in touch with the healthcare team is crucial for the best care.
By using these support systems, patients can manage their condition better. It’s important to focus on gca awareness and education. This way, patients get the support they need to live well with giant cell arteritis.
Long-term Prognosis and Monitoring
Giant cell arteritis has a good long-term outlook. Yet, it’s crucial to keep an eye on it to avoid gca complications. With the right treatment and care, most people can handle their symptoms and avoid lasting harm.
Important things to think about for managing giant cell arteritis long-term include:
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed
- Managing symptoms, such as headaches and vision problems, to prevent gca complications
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to reduce the risk of related health issues
By teaming up with a healthcare provider and sticking to a detailed treatment plan, patients with giant cell arteritis can lower their risk of gca complications. This can greatly improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a serious condition that needs quick medical help. Knowing the symptoms like headaches, scalp pain, and vision issues is key. This helps get the right treatment fast to avoid serious problems like losing your sight.
It’s important to spread the word about GCA awareness. Early treatment can make a big difference in how well someone does. Doctors, support groups, and online resources all help. They teach people about GCA and how to deal with it.
Even though GCA is tough, the right care and lifestyle changes can help a lot. People can live well with GCA by being careful and looking after their health. This way, they can play a big part in their own recovery and future health.
FAQ
Q: What is Giant Cell Arteritis?
A: Giant Cell Arteritis, also known as Temporal Arteritis, is a serious condition. It affects the blood vessels in the head and neck. If not treated, it can cause serious problems.
Q: Who is most commonly affected by Giant Cell Arteritis?
A: It mainly affects older adults, especially those over 50. Women are more likely to get it than men. It’s also more common in people of Northern European descent.
Q: What are the common symptoms of Giant Cell Arteritis?
A: Symptoms include headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain when chewing. Vision problems and fever are also common. Patients may also feel tired, lose weight, and have joint or muscle pain.
Q: How is Giant Cell Arteritis diagnosed?
A: Doctors use medical history, physical exams, blood tests, and imaging studies to diagnose it. A biopsy of the temporal artery might be needed in some cases.
Q: How is Giant Cell Arteritis treated?
A: Treatment involves corticosteroid medications to reduce inflammation. The treatment length varies. Doctors may adjust the treatment as needed to manage the condition.
Q: What are the potential complications of Giant Cell Arteritis?
A: Untreated, it can cause permanent vision loss, stroke, and even death. Early treatment is key to prevent these serious complications.
Q: How can patients manage Giant Cell Arteritis in their daily lives?
A: Patients should exercise regularly, eat healthily, and manage stress. Following the treatment plan and attending regular check-ups is crucial. Reporting any changes in symptoms or side effects is important.
Q: Where can patients find support and resources for living with Giant Cell Arteritis?
A: Patients can find support through patient groups, online forums, and healthcare networks. These resources offer educational materials, support groups, and guidance on managing the condition.
