Xanthelasma Palpebrum: Discover causes, symptoms, and effective treatments in this comprehensive how-to guide.
Did you know that over 1% of the adult population experiences the appearance of yellowish growths on their eyelids? These are known as xanthelasma palpebrum, small, harmless cholesterol deposits that can still cause concern due to their visibility and potential impact on self-esteem.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for xanthelasma is crucial for those affected. These growths, while benign, can grow over time and may affect vision if left untreated. They typically appear as flat or slightly raised yellowish patches on the eyelid skin.
Treatment options vary, ranging from non-invasive approaches like chemical peels to more invasive surgical excision. Recent advancements in energy-based therapies have also provided effective alternatives. However, recurrence is possible, making personalized treatment plans essential for long-term management.
This article delves into the clinical insights and evidence-based treatments, offering a comprehensive guide to managing xanthelasma palpebrum. Whether you’re seeking prevention tips or exploring removal options, this guide provides the necessary information to make informed decisions about your eyelid health.
Key Takeaways
- Xanthelasma palpebrum appears as yellowish patches on the eyelid, primarily composed of cholesterol.
- While benign, these growths can affect self-esteem and vision if they grow large.
- Treatment options include non-invasive methods, surgical removal, and energy-based therapies.
- Recurrence is possible, necessitating personalized and sometimes repeated treatments.
- Early intervention can prevent growth and reduce the risk of complications.
Introduction to Xanthelasma Palpebrum
Xanthelasma palpebrum is a common skin condition characterized by the appearance of small, yellowish patches on the eyelids. These deposits are primarily composed of cholesterol and can develop on both the upper and lower eyelids. While they are benign, they can cause significant cosmetic concern and, in some cases, may indicate underlying systemic conditions.
Understanding the Condition
The condition is often associated with lipid abnormalities, particularly elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. It tends to appear as flat or slightly raised lesions that can grow over time. Despite their benign nature, these deposits can affect self-esteem and, if large enough, may interfere with vision.
Prevalence and Impact in the United States
Epidemiological studies indicate that xanthelasma palpebrum affects approximately 1.1% of women and 0.3% of men in the United States. This condition is more prevalent among older adults, with a significant increase in incidence after the age of 40. The emotional impact of these visible skin lesions should not be underestimated, as they can lead to self-consciousness and a desire for treatment.
| Demographic | Prevalence | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Women | 1.1% | Higher LDL cholesterol, age >40 |
| Men | 0.3% | Family history, lipid disorders |
As the population ages, the prevalence of xanthelasma palpebrum is expected to rise, making it a growing concern in dermatology. Early detection and management can help mitigate both the cosmetic and potential systemic risks associated with this condition.
Pathophysiology and Risk Factors
The development of xanthelasma palpebrum is deeply rooted in lipid metabolism and cholesterol dynamics. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective management.
Role of Cholesterol and Lipid Abnormalities
High levels of LDL cholesterol are a primary contributor. When cholesterol accumulates in the blood, it can deposit in the skin, particularly around the eyes, leading to the formation of these lesions. Additionally, conditions like hyperlipidemia, characterized by excessive fats in the bloodstream, significantly increase the risk of developing xanthelasma.
Histopathological Insights
Upon examination, the lesions reveal foam cells laden with fat. These cells infiltrate the perivascular tissue, causing the characteristic yellowish patches. This histopathological feature underscores the role of lipid metabolism in the condition’s progression.
| Risk Factor | Association |
|---|---|
| Hyperlipidemia | Direct trigger for lesion formation |
| Family History | Increases likelihood due to genetic predisposition |
| Age | Higher prevalence after 40 years |
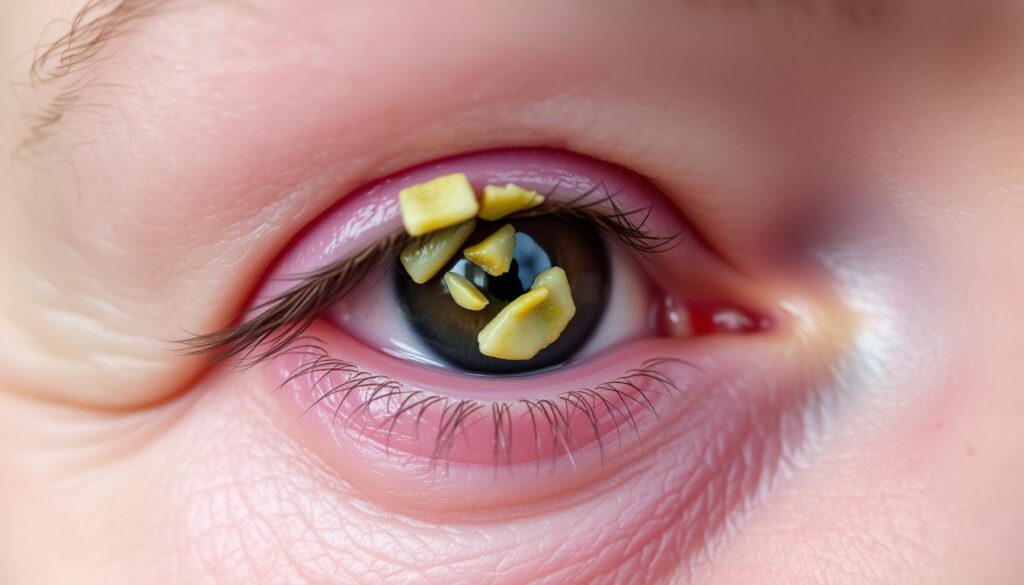
Addressing these risk factors is essential for both treatment and prevention, highlighting the need for a comprehensive management strategy.
Recognizing Signs, Symptoms, and Differential Diagnosis
Accurately identifying xanthelasma palpebrum requires a thorough examination of its unique characteristics and distinguishing it from similar skin conditions. This section explores the key features of the lesions and common misdiagnoses to ensure accurate detection.
Key Lesion Characteristics
The lesions typically appear as yellowish papules, plaques, or nodules on the eyelids. They are usually flat or slightly raised and can grow over time. Their color ranges from light yellow to deep golden, and they often cluster around the eyelid margins. The texture is generally smooth, though some may develop a slightly rough surface.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Color | Yellowish, ranging from light to deep golden |
| Texture | Smooth or slightly rough |
| Shape | Round or oval, well-defined |
| Size | Small, typically 1-5 mm in diameter |
| Location | Primarily on the upper and lower eyelids |
Common Misdiagnoses to Consider
Xanthelasma palpebrum is often confused with other dermatologic conditions such as milia, syringomas, or basal cell carcinoma. Misdiagnoses may occur due to similarities in appearance, but careful examination of lesion characteristics can help differentiate them. For instance, milia are small, white bumps, whereas xanthelasma lesions are yellowish. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Strategies and Clinical Assessment
Accurate diagnosis of xanthelasma palpebrum involves a combination of clinical evaluation and, when necessary, additional diagnostic tests. Understanding the lesion’s characteristics and assessing their impact is crucial for effective management.
Clinical Evaluation Techniques
Clinicians typically begin with a thorough visual examination. Measuring the size of the lesions helps track progression and response to treatment. Lesions are usually yellowish, flat, and located on the eyelids. Their size can range from 1 to 5 millimeters in diameter. A reference guide may be used to standardize measurements across assessments.
When to Request Additional Tests
While clinical evaluation is often sufficient, further tests may be needed. If underlying lipid disorders are suspected, blood lipid profiles are recommended. These tests provide a reference for systemic conditions. Imaging or biopsy can rule out other conditions, ensuring accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
| Diagnostic Step | Purpose | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Exam | Assess lesion size and characteristics | Standardized measurement |
| Lipid Profile | Evaluate cholesterol levels | Identify systemic issues |
| Imaging/Biopsy | Confirm diagnosis | Rule out similar conditions |
Management and Treatment Options
Effectively managing xanthelasma palpebrum involves a combination of medical, lifestyle, and surgical approaches. The choice of treatment depends on the size, number, and location of the lesions, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
Medical and Lifestyle Interventions
Medical management often begins with dietary changes and lipid-lowering medications to address underlying cholesterol issues. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly, can help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent further lesion growth. These interventions are most effective in the early stages of the condition.
Surgical, Laser, and Chemical Treatments
For larger or persistent lesions, surgical excision is a common and effective treatment. Surgical excision involves removing the lesion and is often performed under local anesthesia. Laser therapy is another popular option, using targeted energy to break down the cholesterol deposits. Chemical peeling with agents like trichloroacetic acid can also be used to remove superficial lesions.
Each treatment modality has its advantages and potential complications. Surgical excision, for instance, offers precise removal but may leave scars. Laser therapy is less invasive but can require multiple sessions. Chemical peeling is effective for small lesions but may not be as durable as surgery.
Recent studies highlight the importance of personalized treatment plans, considering both the lesion characteristics and the patient’s needs. Early intervention can prevent progression and reduce the risk of complications, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Innovative Approaches for Xanthelasma Palpebrum Treatment
Advancements in medical technology have introduced innovative methods to treat xanthelasma palpebrum, offering patients more options than ever before. These cutting-edge approaches focus on precision, minimal invasiveness, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Laser and Radiofrequency Therapies
Laser therapy has emerged as a highly effective treatment, utilizing targeted energy to break down cholesterol deposits. This method is praised for its precision, reducing the risk of scarring and promoting faster healing. Radiofrequency adds another layer of innovation by stimulating collagen production, which can tighten the skin and improve texture. Both technologies are supported by clinical studies showing significant lesion reduction with minimal downtime.
Cryotherapy and Trichloroacetic Acid Applications
Cryotherapy, which uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal cells, is another popular option. It’s known for its safety and effectiveness in delicate areas like the eyelids. Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels are also used, offering a chemical solution that gently removes superficial lesions. These methods are favored for their ability to preserve the surrounding skin, leading to better aesthetic results.
Recent clinical studies highlight the advantages of these innovative approaches over traditional surgical excision. They offer reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and improved cosmetic outcomes. Patients now have a variety of effective, modern options to choose from, each tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Personalizing Your Treatment Approach
Every patient’s journey with xanthelasma palpebrum is unique, making personalized treatment plans essential for optimal results. Factors such as lesion size, overall health, and cosmetic concerns play a significant role in shaping the best therapy option for each individual.
Collaborating with Healthcare Specialists
A multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and plastic surgeons ensures comprehensive care. These specialists work together to balance therapeutic benefits with potential risks, tailoring treatments to each patient’s specific needs.
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Excision | Precise removal, durable results | Scarring risk, invasive |
| Laser Therapy | Minimally invasive, fast healing | Multiple sessions needed |
| Chemical Peels | Effective for small lesions | Less durable, superficial |
By involving patients in decision-making and monitoring their progress, healthcare providers can adjust treatment plans as needed, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing eyelid lesions effectively requires a balanced approach that considers both clinical and personal factors. The condition, characterized by yellowish patches on the eyelid, often raises concerns about appearance and long-term eye health. Understanding the causes, such as cholesterol levels and genetic predisposition, is crucial for effective management.
When addressing these lesions, especially on the delicate lower eyelid, careful evaluation is essential. Treatment options vary from non-invasive methods like chemical peels to surgical excision, each with its own set of considerations. The risk of recurrence, lesion level, and individual preferences are key factors in determining the best treatment plan.
Collaboration between patients and specialists ensures personalized care, balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of treatment strategies are vital to prevent recurrence and maintain optimal results. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can manage their condition effectively, ensuring both cosmetic and functional well-being.
Further research and increased collaboration between patients and specialists are encouraged to enhance our understanding and treatment of this condition. With the right approach, those affected can achieve long-term management and improve their quality of life.
FAQ
Q: What is Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
A: Xanthelasma Palpebrarum is a condition characterized by the formation of yellowish plaques or lesions on the eyelids, often linked to lipid abnormalities. These deposits are composed of cholesterol and can be associated with hyperlipidemia.
Q: What causes Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
A: The exact cause is unclear, but it is often linked to high cholesterol levels and lipid metabolism issues. Aging and certain genetic factors may also increase the risk of developing these lesions.
Q: How is Xanthelasma Palpebrarum diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves a clinical evaluation by a dermatologist or ophthalmologist. They may examine the lesion’s characteristics, such as their color, size, and location, to distinguish them from other skin conditions like xanthomas.
Q: What are the treatment options for Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
A: Treatment options include surgical excision, laser therapy, and cryotherapy. Each method has its benefits and risks, and the choice depends on the patient’s specific condition and preferences.
Q: Can Xanthelasma Palpebrarum recur after treatment?
A: Yes, recurrence is possible, especially if the underlying lipid abnormalities are not addressed. Managing cholesterol levels through lifestyle changes or medication can help reduce the risk of recurrence.
Q: How can I prevent Xanthelasma Palpebrarum from developing?
A: While prevention is not guaranteed, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and managing hyperlipidemia can lower the risk of developing these lesions.
Q: Is Xanthelasma Palpebrarum a serious condition?
A: Generally, it is not serious but can be a sign of underlying lipid issues. In rare cases, it may cause discomfort or affect vision if the lesions grow large.
Q: What is the difference between Xanthelasma and Xanthoma?
A: Xanthoma refers to a broader category of skin lesions caused by lipid deposits, while Xanthelasma specifically affects the eyelids. Both are related but have distinct characteristics and locations.
Q: Can Xanthelasma Palpebrarum be treated with over-the-counter products?
A: No, over-the-counter treatments are not effective. Professional medical intervention is required for safe and effective removal of the lesions.
Q: When should I see a doctor about Xanthelasma Palpebrarum?
A: If you notice yellowish growths on your eyelids, especially if they are growing or causing discomfort, you should consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate management.
